Science is a vast and intricate field, filled with specialized terminology that can often feel like a language of its own. Among these terms, science words that start with Z may appear less common, yet they play an essential role across multiple scientific disciplines.
Understanding these terms is essential not only for students and researchers but also for anyone interested in comprehending scientific literature and discussions. This article aims to demystify these “Z” words, providing clear definitions, examples, and practical usage guidelines.
Whether you’re a budding scientist, a seasoned academic, or simply a curious learner, this guide will equip you with the knowledge to confidently navigate the scientific lexicon.
This article breaks down complex concepts into manageable parts, offering illustrative examples and practice exercises to solidify your understanding. By exploring the etymology, structural components, and contextual applications of these words, you’ll gain a deeper appreciation for their significance in the scientific world.
This knowledge is particularly useful for students studying biology, chemistry, physics, and environmental science, as well as professionals working in related fields. Dive in to expand your scientific vocabulary and enhance your comprehension of the world around you.
Contents
ToggleDefinition of Science Words Starting with Z
Science words starting with “Z” encompass a diverse range of terms used across various scientific disciplines. These words often describe specific phenomena, tools, concepts, or processes that are fundamental to scientific understanding.
While not as numerous as words starting with other letters, “Z” words are vital in their respective fields. They often represent specialized concepts that require precise definition and application.
The function of these words is to provide a standardized and unambiguous way to communicate scientific ideas. They allow scientists to share their findings, conduct research, and build upon existing knowledge.
Understanding these terms is crucial for interpreting scientific literature, participating in scientific discussions, and conducting experiments effectively. The contexts in which these words are used vary widely, ranging from laboratory experiments to theoretical models to field observations.
Structural Breakdown of Z-Words in Science
Many scientific words starting with “Z” have roots in Greek or Latin, reflecting the historical development of scientific terminology. Understanding these etymological roots can often provide valuable insights into the meaning and usage of the words.
For example, many words may contain prefixes or suffixes that modify their core meaning. Recognizing these structural elements can aid in deciphering the meaning of unfamiliar terms.
The phonetic structure of these words can also influence their usage and pronunciation. Some “Z” words are relatively straightforward to pronounce, while others may present challenges for non-native speakers.
Paying attention to the stress patterns and vowel sounds can improve pronunciation accuracy. Furthermore, some “Z” words may have multiple syllables, requiring careful articulation to ensure clarity.
Types and Categories of Science Z-Words
Science words starting with “Z” can be categorized based on the scientific discipline in which they are primarily used. Here are some of the major categories:
Physics
In physics, “Z” words often relate to concepts in particle physics, electromagnetism, and optics. These terms are essential for describing fundamental properties of matter and energy.
Biology
Biology uses “Z” words to describe enzymes, proteins, and other biological molecules. These terms are crucial for understanding cellular processes and genetic mechanisms.
Chemistry
In chemistry, “Z” words may refer to specific chemical compounds, reactions, or techniques. These terms are vital for understanding the composition and behavior of matter.
Geology
Geology uses “Z” words to describe minerals, geological formations, and processes. These terms are important for understanding the Earth’s structure and history.
Examples of Science Words Starting with Z
Here, we will explore examples of science words that start with the letter “Z,” categorized by their respective scientific disciplines. Each example will be accompanied by a definition and illustrative sentences to provide context and enhance understanding.
| Word | Definition | Example Sentence |
|---|---|---|
| Zeal | Great energy or enthusiasm in pursuit of a cause or objective. | The young scientist approached her research with unwavering zeal, working tirelessly to uncover new insights. |
| Zenith | The point in the sky or celestial sphere directly above an observer. | The astronomer used a telescope to observe the stars at their zenith. |
| Zero | A numerical value representing nothing; the absence of quantity. | Absolute zero is the lowest possible temperature, where all molecular motion stops. |
| Zeta Potential | The electrical potential difference between the dispersion medium and the stationary layer of fluid attached to the dispersed particle. | The zeta potential of the colloidal solution was measured to determine its stability. |
| Zigzag | A line or course that proceeds in a series of alternating sharp turns. | The earthquake’s fault line followed a zigzag pattern across the landscape. |
| Ziggurat | A rectangular stepped tower, sometimes surmounted by a temple. | Archaeologists discovered remnants of an ancient ziggurat in Mesopotamia. |
| Zinc | A metallic chemical element; essential for various biological processes. | The experiment required a small amount of zinc to catalyze the reaction. |
| Zircon | A mineral occurring as prismatic crystals, typically brown but sometimes colorless or brightly colored. | Geologists analyzed the zircon crystals to determine the age of the rock formation. |
| Zoa | Plural of zoon; an animal, especially a single-celled one. | The scientist studied the movement patterns of various zoa under the microscope. |
| Zonal | Arranged in or relating to zones. | The Earth’s climate is influenced by zonal wind patterns. |
| Zone | An area or region distinguished from others by some characteristic feature. | The rainforest is located in the tropical zone of the Earth. |
| Zoo | An establishment that maintains a collection of wild animals, typically in a park or gardens, for study, conservation, or display to the public. | The biologist conducted research on animal behavior at the local zoo. |
| Zoology | The scientific study of the behavior, physiology, classification, and distribution of animals. | Her passion for zoology led her to pursue a career in wildlife conservation. |
| Zoomorphism | The attribution of animal forms or qualities to gods, humans, or objects. | The ancient cultures often practiced zoomorphism, depicting their deities with animal characteristics. |
| Zooplankton | Plankton consisting of small animals and the immature stages of larger animals. | The marine ecosystem relies heavily on zooplankton as a food source for larger organisms. |
| Zwitterion | A molecule or ion having separate positively and negatively charged groups. | Amino acids exist as zwitterions at physiological pH, which influences their chemical behavior. |
| Zygote | A diploid cell resulting from the fusion of two haploid gametes; a fertilized ovum. | The zygote undergoes rapid cell division to form an embryo. |
| Zymogen | An inactive precursor of an enzyme. | Pepsinogen is a zymogen that is converted to the active enzyme pepsin in the stomach. |
| Zeolite | A crystalline aluminosilicate with a framework structure containing cavities occupied by water molecules and cations, which can be exchanged with other cations. | Zeolites are used as molecular sieves and catalysts in various industrial processes. |
| Zero-valent Iron | Iron in its elemental form (Fe0), used in environmental remediation to treat contaminated water and soil. | Zero-valent iron is effective in removing pollutants from groundwater through reduction reactions. |
| Zonula Adherens | A cell junction, also known as the adherent junction, that provides strong adhesion between cells. | The zonula adherens plays a crucial role in maintaining tissue integrity in epithelial cells. |
| Zone of Inhibition | A clear area around an antimicrobial agent on an agar plate, indicating the agent’s effectiveness against bacterial growth. | The antibiotic’s zone of inhibition indicated its high effectiveness against the tested bacteria. |
| Zonal Wind | A wind blowing along a line of latitude, either from the east or west. | The zonal wind patterns significantly impact weather systems in the mid-latitudes. |
| Zoonosis | A disease that can be transmitted to humans from animals. | Rabies is a well-known zoonosis that can be fatal if left untreated. |
| Zygotene | The second stage of prophase I in meiosis, during which homologous chromosomes pair up in synapsis. | During the zygotene stage, the homologous chromosomes align precisely to facilitate genetic recombination. |
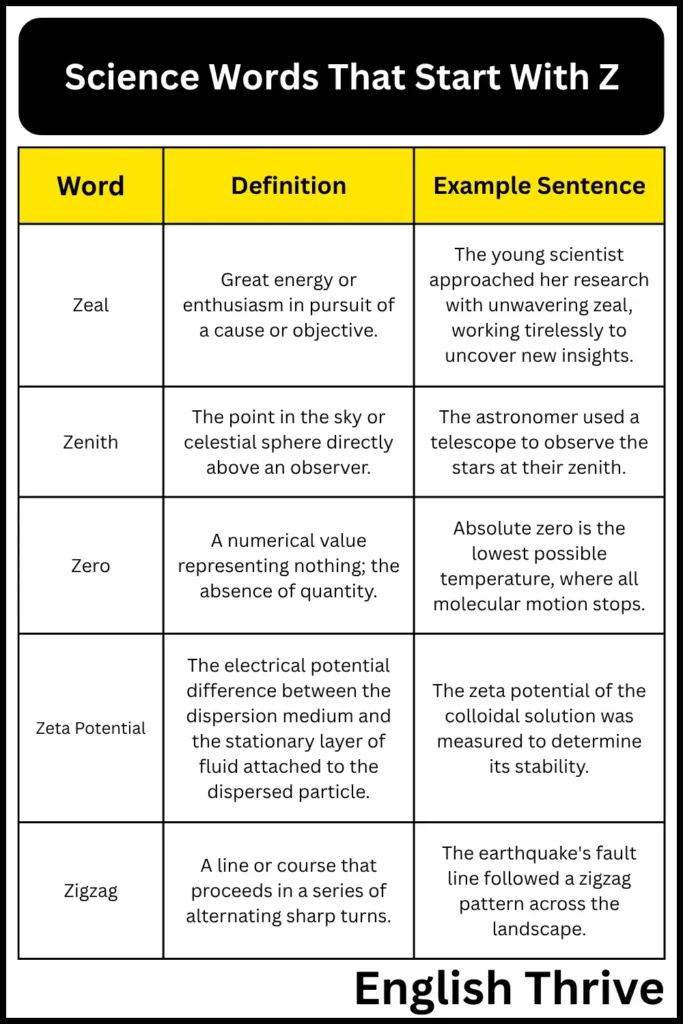
The table above provides a diverse set of science words starting with the letter “Z,” covering various scientific disciplines. These examples offer a glimpse into the specialized vocabulary used in different fields and demonstrate the importance of understanding these terms for effective scientific communication.
| Word | Discipline | Usage Example |
|---|---|---|
| Zeal | General Science | Her zeal for scientific discovery was evident in her relentless pursuit of answers. |
| Zenith | Astronomy | The telescope was positioned to observe the comet at its zenith. |
| Zero | Mathematics/Physics | The experiment started with the initial temperature set to zero degrees Celsius. |
| Zeta Potential | Colloid Chemistry | Controlling the zeta potential is crucial for stabilizing the colloidal suspension. |
| Zigzag | Geology | The river followed a zigzag course through the mountainous terrain. |
| Ziggurat | Archaeology | The unearthed ziggurat provided valuable insights into the ancient civilization. |
| Zinc | Chemistry/Biology | Zinc is an essential trace element required for enzyme function. |
| Zircon | Geology | The age of the rock was determined by analyzing the uranium content in zircon crystals. |
| Zoa | Biology | The pond water was teeming with various types of zoa. |
| Zonal | Meteorology | The zonal flow of air influences weather patterns across the continent. |
| Zone | Geography | The area was designated as a protected conservation zone. |
| Zoo | Zoology | The local zoo is actively involved in wildlife conservation efforts. |
| Zoology | Biology | She studied zoology to understand animal behavior and ecology. |
| Zoomorphism | Anthropology | The cave paintings exhibited zoomorphism, depicting human figures with animal features. |
| Zooplankton | Marine Biology | Zooplankton form the base of the food web in many marine ecosystems. |
| Zwitterion | Biochemistry | Amino acids can act as both acids and bases due to their zwitterion structure. |
| Zygote | Genetics | The zygote contains the complete genetic information from both parents. |
| Zymogen | Biochemistry | Trypsin is produced as a zymogen called trypsinogen in the pancreas. |
| Zeolite | Material Science | Zeolites are used in detergents as water softeners. |
| Zero-valent Iron | Environmental Science | Zero-valent iron is used to remediate groundwater contaminated with heavy metals. |
| Zonula Adherens | Cell Biology | The zonula adherens helps to maintain the structural integrity of epithelial tissues. |
| Zone of Inhibition | Microbiology | A large zone of inhibition around the antibiotic disk indicated high sensitivity of the bacteria. |
| Zonal Wind | Climatology | Changes in the strength of the zonal wind can affect regional climates. |
| Zoonosis | Epidemiology | Lyme disease is a zoonosis transmitted by ticks from animals to humans. |
| Zygotene | Genetics | During zygotene, homologous chromosomes pair up to form synaptonemal complexes. |
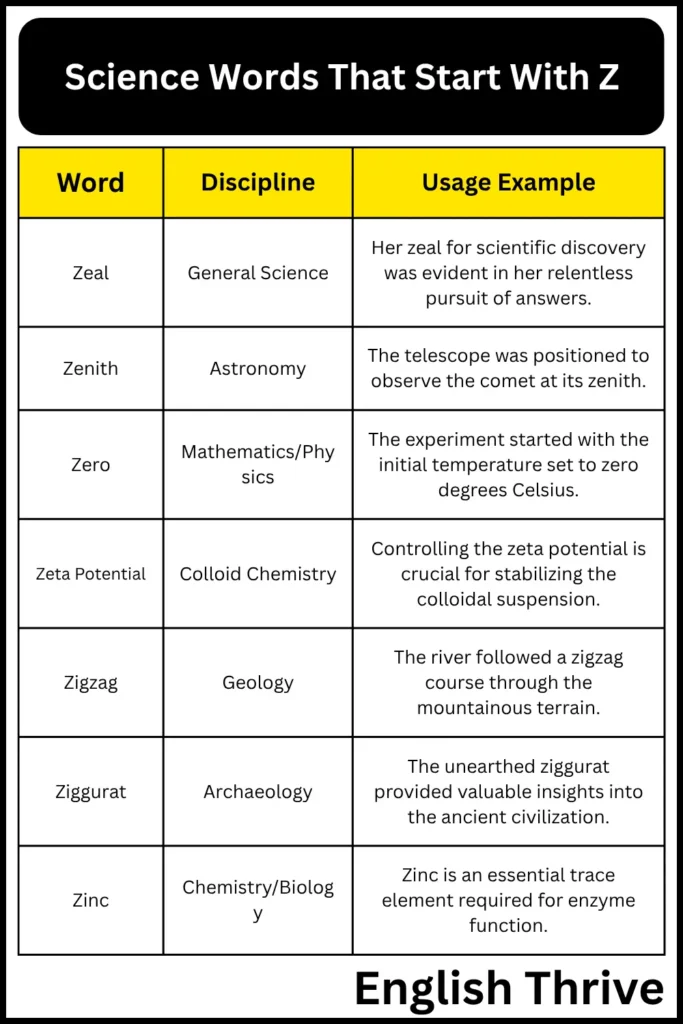
This table organizes the “Z” words by discipline, providing a clear indication of where each term is most commonly used. This categorization helps to contextualize the words and facilitates their application in specific scientific fields.
| Word | Synonyms/Related Terms | Antonyms/Opposite Concepts |
|---|---|---|
| Zeal | Enthusiasm, passion, fervor | Apathy, indifference, disinterest |
| Zenith | Apex, peak, summit | Nadir, base, bottom |
| Zero | Null, nil, nothing | Positive, non-zero, something |
| Zeta Potential | Surface charge, electrokinetic potential | Isoelectric point, neutral charge |
| Zigzag | Meandering, serpentine, winding | Straight, direct, linear |
| Zinc | Zn (chemical symbol) | (Various, depending on context, e.g., other metals) |
| Zone | Region, area, sector | (Non-specific, depending on context) |
| Zoology | Animal biology, animal science | Botany, plant biology |
| Zygote | Fertilized egg, conceptus | Gamete, sperm, egg |
Understanding synonyms and antonyms can help clarify the meaning of “Z” words and enable more precise communication. This table provides a list of related and opposite terms for some of the key vocabulary items discussed.
Usage Rules for Science Z-Words
Using science words correctly requires attention to detail and an understanding of the specific context in which they are applied. Here are some general rules to follow:
- Use precise definitions: Ensure that you understand the exact meaning of the word before using it in your writing or speaking.
- Consider the audience: Adjust your vocabulary based on the knowledge level of your audience. Avoid using overly technical terms when communicating with non-experts.
- Maintain consistency: Use the same term consistently throughout your writing to avoid confusion.
- Check spelling and grammar: Pay attention to the spelling and grammatical rules of the English language.
- Consult reliable sources: When in doubt, consult dictionaries, textbooks, or other reliable sources to verify the meaning and usage of a word.
In addition to these general rules, there may be specific conventions for using certain “Z” words in particular scientific disciplines. For example, in chemistry, it is important to use the correct chemical nomenclature when referring to specific compounds.
In biology, it is essential to use the proper taxonomic classifications when discussing different species.
Common Mistakes When Using Z-Words
Even experienced scientists can sometimes make mistakes when using specialized vocabulary. Here are some common errors to watch out for:
| Incorrect Usage | Correct Usage | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| “The scientist had a lot of zealot for the research.” | “The scientist had a lot of zeal for the research.” | “Zealot” refers to a fanatic, while “zeal” means enthusiasm. |
| “The sun was at its nadir.” | “The sun was at its zenith.” | “Nadir” is the lowest point; “zenith” is the highest. |
| “He added zinc oxide to the solution.” | “He added zinc to the solution.” | Ensure the correct substance is specified and appropriate to the context. |
The table above highlights some common mistakes in using “Z” words, along with the correct usage and explanations. Avoiding these errors will improve the clarity and accuracy of your scientific communication.
Practice Exercises: Science Words That Start With Z
Test your understanding of science words starting with “Z” by completing the following exercises.
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What term describes the point directly overhead in the sky? | Zenith |
| Which metallic element is essential for many biological processes? | Zinc |
| What is the scientific study of animals called? | Zoology |
| What is a disease that can be transmitted from animals to humans? | Zoonosis |
| What is the term for the fertilized egg cell? | Zygote |
| Question | Your Answer |
|---|---|
| Complete the sentence: The scientist showed great _____ for her research. | |
| What type of plankton consists of small animals? | |
| What is the inactive precursor of an enzyme called? | |
| What is the term for a molecule with both positive and negative charges? | |
| What is the term for wind blowing along a line of latitude? |
Answers:
- Zeal
- Zooplankton
- Zymogen
- Zwitterion
- Zonal Wind
Advanced Topics
For advanced learners, it’s beneficial to delve into more complex aspects of scientific terminology. This includes understanding the nuances of etymology, the historical context of word development, and the subtle differences in meaning between seemingly synonymous terms.
Furthermore, exploring the use of “Z” words in specialized sub-disciplines can provide a deeper understanding of their application.
Advanced research often involves critically evaluating scientific literature and identifying potential ambiguities or inconsistencies in the use of terminology. Therefore, a thorough understanding of the nuances of scientific language is essential for conducting rigorous and impactful research.
FAQs on Science Words That Start With Z
Why are there relatively few science words starting with “Z”?
The distribution of words across the alphabet is not uniform. Some letters, like “S” and “C,” are more common in English vocabulary, including scientific terms, due to historical linguistic influences and the frequency of certain prefixes and suffixes. The letter “Z” simply occurs less frequently in the roots of words that have been adopted into scientific language.
How can I improve my scientific vocabulary?
Consistent reading of scientific literature, active note-taking of new terms, and regular use of these terms in your own writing and discussions are effective strategies. Utilizing flashcards or vocabulary-building apps can also be helpful. Additionally, understanding the etymology of words can provide valuable context and aid in memorization.
Are there differences in the usage of “Z” words across different scientific disciplines?
Yes, the meaning and usage of “Z” words can vary depending on the specific scientific discipline. For example, “zeta potential” has a very specific meaning in colloid chemistry, while “zone” can refer to different types of regions in geography, biology, or physics. Always consider the context in which the word is used.
What is the best way to learn the pronunciation of scientific terms?
Consulting dictionaries that provide phonetic transcriptions is a good starting point. Listening to recordings of native speakers using the terms can also be helpful. Pay attention to stress patterns and vowel sounds. Practice pronouncing the words aloud, and don’t hesitate to ask for feedback from colleagues or instructors.
How important is it to use scientific terms correctly?
Using scientific terms correctly is crucial for clear and accurate communication. Misusing terminology can lead to misunderstandings, misinterpretations, and even errors in research. Precision in language is essential for maintaining the integrity of scientific discourse.
Conclusion: Science Words That Start With Z
Mastering science words starting with “Z” is a valuable step in expanding your scientific literacy. While these words may not be as common as those starting with other letters, they are nonetheless essential for understanding specific concepts and phenomena across various scientific disciplines.
By understanding the definitions, usage rules, and common mistakes associated with these terms, you can communicate more effectively and confidently in scientific contexts.
Remember that continuous learning and practice are key to building a strong scientific vocabulary. Embrace the challenge of learning new words, and don’t hesitate to consult reliable sources when in doubt.
With dedication and perseverance, you can unlock the power of scientific language and gain a deeper understanding of the world around you. Keep exploring, keep questioning, and keep expanding your knowledge – the world of science awaits!

