Understanding verb forms is essential for learning English grammar properly. In English, verbs are used in various forms to express actions or states across different tenses, persons, and voices. These verb forms help us convey when an action happens, who is performing it, and whether the action is completed, ongoing, or habitual.
In this guide, we’ll explore the five key Verb Forms v1 v2 v3 v4 v5, explaining their usage, providing examples, and offering a list of 100 verbs for practice.
Contents
ToggleWhat Are Verb Forms V1, V2, V3, V4, and V5?
Verb forms in English can appear in different ways depending on the tense, aspect, and voice of the sentence. Here’s a breakdown of the five main verb forms:
V1 (Base Form)
The base form is the simplest form of a verb, often used in the present simple tense or when the verb appears with auxiliary verbs like “to.”
- Example:
- eat
- go
- run
V2 (Past Simple)
The past simple form is used to describe actions completed in the past, often with a specific time reference.
- Example:
- ate (from eat)
- went (from go)
- ran (from run)
V3 (Past Participle)
The past participle is used to form perfect tenses (present perfect, past perfect, etc.) and passive voice. It often follows auxiliary verbs like “have,” “has,” or “had.”
- Example:
- eaten (from eat)
- gone (from go)
- run (from run)
V4 (Present Participle/Gerund)
The present participle is formed by adding “-ing” to the base form of a verb. It’s used in continuous tenses and as a gerund (a verb acting as a noun).
- Example:
- eating (from eat)
- going (from go)
- running (from run)
V5 (Third-Person Singular Present)
The V5 form is used when the subject is third-person singular (he, she, it) in the present simple tense. It often adds “s” or “es” to the base form.
- Example:
- eats (from eat)
- goes (from go)
- runs (from run)

How to Use V1, V2, V3, V4, and V5 Verb Forms in Sentences
Each verb form serves a unique role in English grammar. Let’s look at how to use these forms in sentences:
V1 Usage: Base Form
- Present Simple: The base form is used in the present simple tense for general statements or habitual actions.
- Example: “She reads books every day.”
- Commands: The base form is used when giving commands or instructions.
- Example: “Please eat your lunch.”
V2 Usage: Past Simple
- Past Tense: The past simple form describes actions that occurred at a specific point in the past.
- Example: “I went to the store yesterday.”
V3 Usage: Past Participle
- Perfect Tenses: The past participle is used with auxiliary verbs like “have,” “has,” or “had” to form perfect tenses.
- Example: “She has finished her homework.”
- Passive Voice: The past participle is also used to form the passive voice.
- Example: “The letter was written by John.”
V4 Usage: Present Participle/Gerund
- Continuous Tenses: The present participle (V4) is used to show ongoing actions.
- Example: “I am reading a book.”
- Gerunds: It can also function as a noun in the form of a gerund.
- Example: “Reading is my favorite hobby.”
V5 Usage: Third-Person Singular Present
- Present Simple (Third Person): V5 is used for third-person singular subjects in the present simple tense.
- Example: “She goes to school every morning.”
Verb Forms v1 v2 v3 v4 v5 100 Words
Here’s a list of 100 verbs in their V1, V2, V3, V4, and V5 forms to help you understand how these verbs are used in different contexts.
Below are 50 examples of regular verbs and 50 examples of irregular verbs in their V1, V2, V3, V4, and V5 forms.
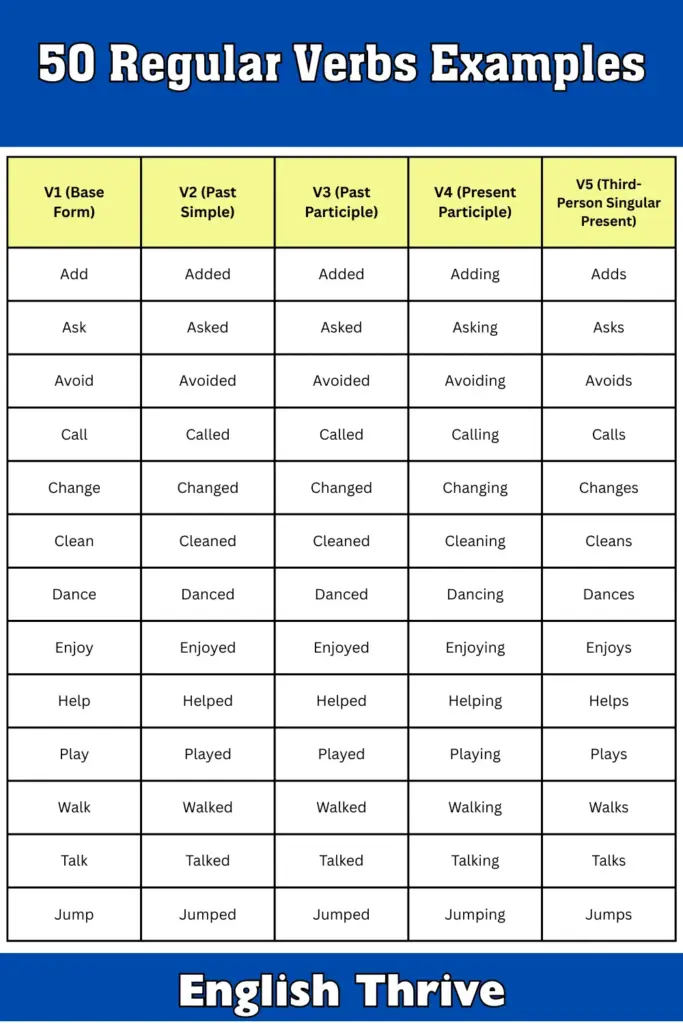
Regular Verbs: 50 Examples
| V1 (Base Form) | V2 (Past Simple) | V3 (Past Participle) | V4 (Present Participle) | V5 (Third-Person Singular Present) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Add | Added | Added | Adding | Adds |
| Ask | Asked | Asked | Asking | Asks |
| Avoid | Avoided | Avoided | Avoiding | Avoids |
| Call | Called | Called | Calling | Calls |
| Change | Changed | Changed | Changing | Changes |
| Clean | Cleaned | Cleaned | Cleaning | Cleans |
| Dance | Danced | Danced | Dancing | Dances |
| Enjoy | Enjoyed | Enjoyed | Enjoying | Enjoys |
| Help | Helped | Helped | Helping | Helps |
| Play | Played | Played | Playing | Plays |
| Walk | Walked | Walked | Walking | Walks |
| Talk | Talked | Talked | Talking | Talks |
| Jump | Jumped | Jumped | Jumping | Jumps |
| Listen | Listened | Listened | Listening | Listens |
| Love | Loved | Loved | Loving | Loves |
| Watch | Watched | Watched | Watching | Watches |
| Move | Moved | Moved | Moving | Moves |
| Wait | Waited | Waited | Waiting | Waits |
| Laugh | Laughed | Laughed | Laughing | Laughs |
| Work | Worked | Worked | Working | Works |
| Travel | Travelled | Travelled | Travelling | Travels |
| Start | Started | Started | Starting | Starts |
| Cook | Cooked | Cooked | Cooking | Cooks |
| Watch | Watched | Watched | Watching | Watches |
| Build | Built | Built | Building | Builds |
| Try | Tried | Tried | Trying | Tries |
| Move | Moved | Moved | Moving | Moves |
| Open | Opened | Opened | Opening | Opens |
| Talk | Talked | Talked | Talking | Talks |
| Visit | Visited | Visited | Visiting | Visits |
| Kick | Kicked | Kicked | Kicking | Kicks |
| Call | Called | Called | Calling | Calls |
| Accept | Accepted | Accepted | Accepting | Accepts |
| Call | Called | Called | Calling | Calls |
| Wait | Waited | Waited | Waiting | Waits |
| Paint | Painted | Painted | Painting | Paints |
| Push | Pushed | Pushed | Pushing | Pushes |
| Talk | Talked | Talked | Talking | Talks |
| Help | Helped | Helped | Helping | Helps |
| Play | Played | Played | Playing | Plays |
| Shop | Shopped | Shopped | Shopping | Shops |
| Visit | Visited | Visited | Visiting | Visits |
| Write | Wrote | Written | Writing | Writes |
| Watch | Watched | Watched | Watching | Watches |
| Clean | Cleaned | Cleaned | Cleaning | Cleans |
| Open | Opened | Opened | Opening | Opens |
| Move | Moved | Moved | Moving | Moves |
| Plan | Planned | Planned | Planning | Plans |
| Play | Played | Played | Playing | Plays |
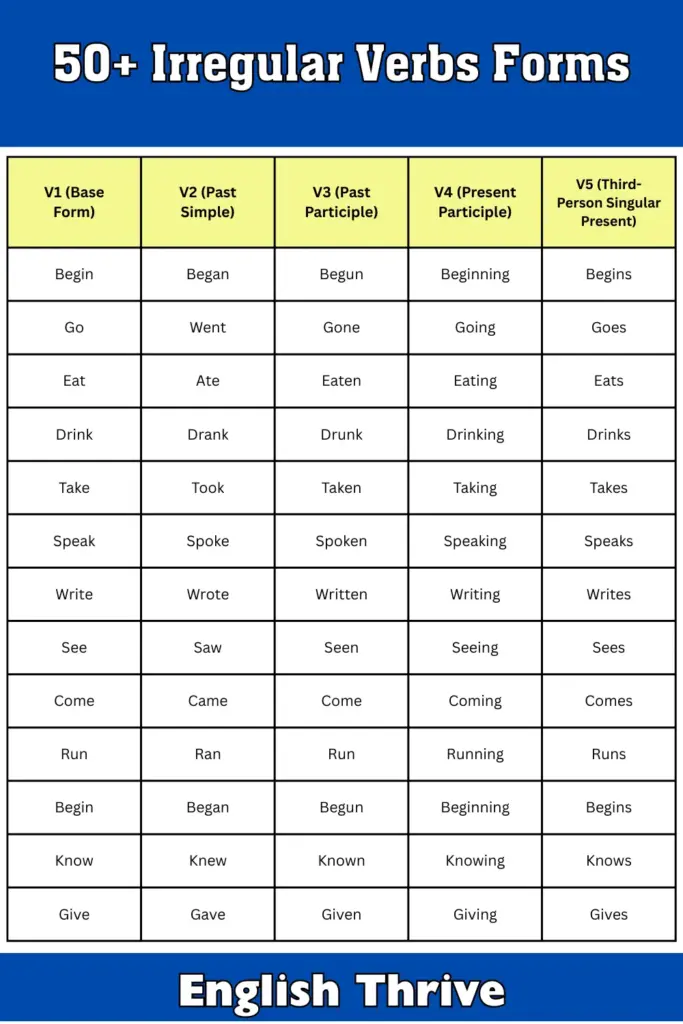
Irregular Verbs: 50 Examples
| V1 (Base Form) | V2 (Past Simple) | V3 (Past Participle) | V4 (Present Participle) | V5 (Third-Person Singular Present) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Begin | Began | Begun | Beginning | Begins |
| Go | Went | Gone | Going | Goes |
| Eat | Ate | Eaten | Eating | Eats |
| Drink | Drank | Drunk | Drinking | Drinks |
| Take | Took | Taken | Taking | Takes |
| Speak | Spoke | Spoken | Speaking | Speaks |
| Write | Wrote | Written | Writing | Writes |
| See | Saw | Seen | Seeing | Sees |
| Come | Came | Come | Coming | Comes |
| Run | Ran | Run | Running | Runs |
| Begin | Began | Begun | Beginning | Begins |
| Know | Knew | Known | Knowing | Knows |
| Give | Gave | Given | Giving | Gives |
| Find | Found | Found | Finding | Finds |
| Take | Took | Taken | Taking | Takes |
| Sing | Sang | Sung | Singing | Sings |
| Build | Built | Built | Building | Builds |
| Choose | Chose | Chosen | Choosing | Chooses |
| Catch | Caught | Caught | Catching | Catches |
| Run | Ran | Run | Running | Runs |
| Fall | Fell | Fallen | Falling | Falls |
| Fly | Flew | Flown | Flying | Flies |
| Take | Took | Taken | Taking | Takes |
| Become | Became | Become | Becoming | Becomes |
| Leave | Left | Left | Leaving | Leaves |
| Begin | Began | Begun | Beginning | Begins |
| Fight | Fought | Fought | Fighting | Fights |
| Think | Thought | Thought | Thinking | Thinks |
| Do | Did | Done | Doing | Does |
| Stand | Stood | Stood | Standing | Stands |
| Sit | Sat | Sat | Sitting | Sits |
| Drink | Drank | Drunk | Drinking | Drinks |
| Speak | Spoke | Spoken | Speaking | Speaks |
| Sweep | Swept | Swept | Sweeping | Sweeps |
| Find | Found | Found | Finding | Finds |
| Wear | Wore | Worn | Wearing | Wears |
| Drive | Drove | Driven | Driving | Drives |
| Bring | Brought | Brought | Bringing | Brings |
| Tell | Told | Told | Telling | Tells |
| Shine | Shone | Shone | Shining | Shines |
| Teach | Taught | Taught | Teaching | Teaches |
| Sleep | Slept | Slept | Sleeping | Sleeps |
| Throw | Threw | Thrown | Throwing | Throws |
| Seek | Sought | Sought | Seeking | Seeks |
| Wake | Woke | Woken | Waking | Wakes |
| Run | Ran | Run | Running | Runs |
| Bite | Bit | Bitten | Biting | Bites |
| Cut | Cut | Cut | Cutting | Cuts |
| Hit | Hit | Hit | Hitting | Hits |
| Teach | Taught | Taught | Teaching | Teaches |
| Win | Won | Won | Winning | Wins |
| Draw | Drew | Drawn | Drawing | Draws |
| Feel | Felt | Felt | Feeling | Feels |
Download the list of 100 verbs with their V1, V2, V3, V4, and V5 forms
FAQs about Verb Forms v1 v2 v3 v4 v5
1. What are the five main verb forms (V1, V2, V3, V4, V5)?
These five forms help express actions in different tenses and aspects:
- V1 (Base Form): Used for present simple and infinitives.
- V2 (Past Simple): Used for past actions.
- V3 (Past Participle): Used with auxiliary verbs for perfect tenses and passive voice.
- V4 (Present Participle/Gerund): Used for continuous tenses and gerunds.
- V5 (Third-Person Singular Present): Used for third-person singular subjects in the present simple tense.
2. What is the difference between regular and irregular verbs in V2 and V3?
Regular verbs follow a predictable pattern by adding “-ed” for V2 and V3, while irregular verbs can change in unpredictable ways.
3. How do I use V4 and V5 correctly in sentences?
- V4 is used for continuous actions (“She is singing“).
- V5 is used for third-person singular subjects in the present tense (“He plays soccer”).
Conclusion
Understanding the five verb forms—V1, V2, V3, V4, and V5—is essential for using English correctly. Understanding when to use each form will help you improve both written and spoken communication. By practicing regularly with the examples provided, you’ll become more confident in using these verb forms fluently.

