Understanding idioms is essential for mastering English, as they add color and nuance to speech and writing. Idioms for Running are especially vivid, using physical activity metaphorically to describe various life situations.
This article explores a wide range of idioms associated with running, providing definitions, examples, usage rules, and practice exercises to help learners of all levels enhance their understanding and application of these expressions.
This comprehensive guide benefits English language learners, writers, and anyone interested in expanding their vocabulary and improving their communication skills. By delving into the meanings and contexts of these idioms, readers will gain a deeper appreciation for the richness and expressiveness of the English language.
Contents
ToggleDefinition of Running Idioms
Running idioms are phrases or expressions that use the concept of running metaphorically to convey a different meaning than the literal one. These idioms often relate to progress, effort, competition, or avoidance.
They are a form of figurative language where the words, when taken together, have a unique meaning that is different from the dictionary definitions of the individual words.
Classification: Running idioms fall under the broader category of idioms, which are fixed expressions with non-literal meanings. They can be further classified based on the specific aspect of running they relate to, such as speed, endurance, or obstacles.
Function: The primary function of running idioms is to add color and expressiveness to language. They allow speakers and writers to convey complex ideas in a concise and memorable way. They also reflect cultural values and perspectives related to perseverance and competition.
Contexts: Running idioms are used in a wide range of contexts, including business, sports, politics, and personal relationships. They can be found in everyday conversations, news articles, literature, and other forms of communication.
Structural Breakdown
Running idioms, like other idioms, typically consist of a combination of words that create a fixed expression. The structure can vary, but they often include verbs related to running (e.g., *run*, *sprint*, *dash*) and nouns that add context (e.g., *race*, *marathon*, *hurdle*).
The meaning is derived from the entire phrase, not from the individual words.
The basic structure often involves a verb of motion and a prepositional phrase or complement that alters the verb’s meaning. For example, in the idiom “run into trouble,” the verb “run” is combined with the prepositional phrase “into trouble” to mean “encounter difficulties.”
Understanding the grammatical structure of an idiom can help in recognizing it, but it is crucial to remember that the meaning is not compositional. That is, you cannot determine the meaning of an idiom simply by analyzing the grammatical roles and meanings of its parts.
Types and Categories of Running Idioms
Running idioms can be categorized based on the specific aspect of running they relate to:
Idioms Related to Speed and Urgency
These idioms describe situations requiring quick action or progress.
Idioms Related to Endurance and Perseverance
These idioms focus on long-term effort and the ability to overcome challenges.
Idioms Related to Avoiding Problems
These idioms describe escaping or sidestepping difficulties.
Idioms Related to Competition
These idioms use running metaphors to describe competitive situations.
Examples of Running Idioms
This section provides a comprehensive list of running idioms, categorized for easy understanding. Each idiom is accompanied by a definition and example sentence to illustrate its usage.
Idioms Related to Speed and Urgency
The following table provides examples of idioms related to speed and urgency. These idioms often imply a need for quick action or immediate progress.
Understanding these idioms can help you describe time-sensitive situations more effectively.
| Idiom | Definition | Example Sentence |
|---|---|---|
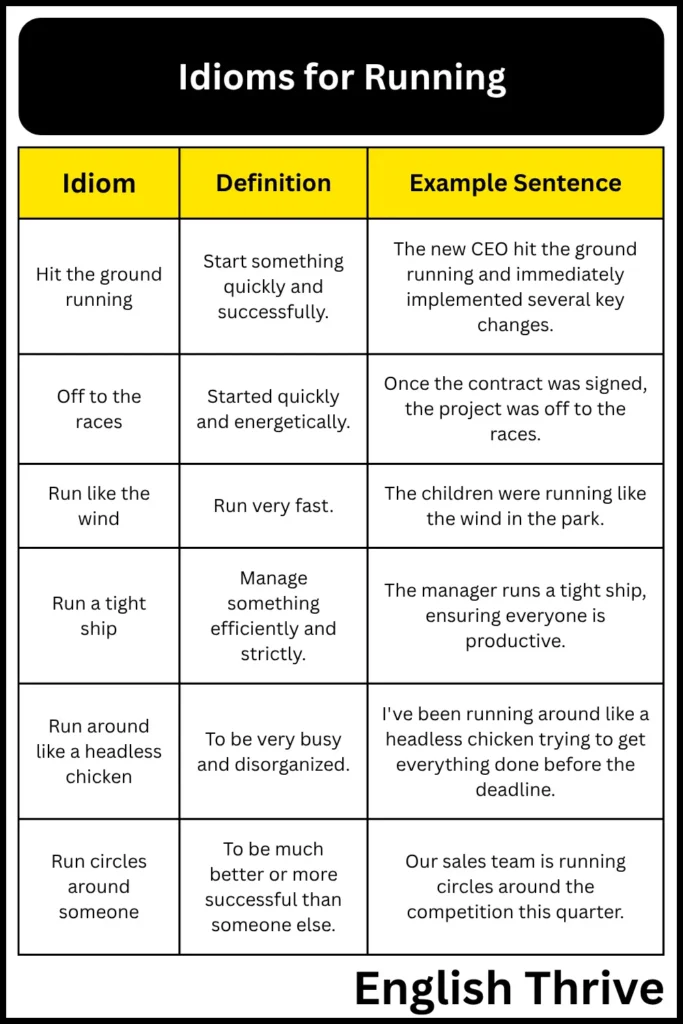
| Hit the ground running | Start something quickly and successfully. | The new CEO hit the ground running and immediately implemented several key changes. |
| Off to the races | Started quickly and energetically. | Once the contract was signed, the project was off to the races. |
| Run like the wind | Run very fast. | The children were running like the wind in the park. |
| Run a tight ship | Manage something efficiently and strictly. | The manager runs a tight ship, ensuring everyone is productive. |
| Run around like a headless chicken | To be very busy and disorganized. | I’ve been running around like a headless chicken trying to get everything done before the deadline. |
| Run circles around someone | To be much better or more successful than someone else. | Our sales team is running circles around the competition this quarter. |
| Run for it | To escape or flee quickly. | When the alarm went off, everyone had to run for it. |
| Get a running start | To begin something with momentum. | We need to get a running start on this project to meet the deadline. |
| At a running pace | Moving or progressing quickly. | The project is moving at a running pace, and we expect it to be completed soon. |
| Give someone a run for their money | To provide strong competition. | The underdog team really gave the favorites a run for their money. |
| Run wild | To behave without control or restraint. | The children were allowed to run wild in the backyard. |
| Run rampant | To spread uncontrollably. | Rumors began to run rampant after the announcement. |
| Run its course | To come to a natural end. | The illness just needs to run its course. |
| Make a run for it | To attempt to escape. | Seeing the police, the suspect made a run for it. |
| Run interference | To block or obstruct someone’s path. | The lawyer had to run interference for his client. |
| Run amok | To behave uncontrollably and disruptively. | The protesters ran amok in the streets. |
| Run roughshod over | To treat someone without respect or consideration. | The company ran roughshod over the employees’ rights. |
| Run with the ball | To take charge of a situation. | The project manager was given the opportunity to run with the ball. |
| Run a temperature | To have a fever. | The child was running a temperature and had to stay home from school. |
| Run dry | To be completely used up. | The well ran dry during the drought. |
| Run late | To be behind schedule. | I’m running late for my appointment. |
| Run short | To have less than needed. | We’re running short on supplies. |
| Run scared | To act cautiously due to fear. | The team is running scared after their recent losses. |
 Idioms for Running
Idioms for Running
Idioms Related to Endurance and Perseverance
The following table provides examples of idioms related to endurance and perseverance. These idioms often describe situations requiring long-term effort and resilience.
Using these idioms can add depth to your descriptions of challenging endeavors.
| Idiom | Definition | Example Sentence |
|---|---|---|
| Run the extra mile | Go above and beyond what is expected. | She always runs the extra mile for her clients. |
| Long run | In the distant future. | In the long run, this investment will pay off. |
| Run the gauntlet | Endure a series of difficult or unpleasant experiences. | He had to run the gauntlet of media interviews after the scandal. |
| Run its course | To come to a natural end. | The illness just needs to run its course. |
| For the long haul | For a long period of time. | We are committed to this project for the long haul. |
| Run out of steam | To lose energy or enthusiasm. | The team ran out of steam towards the end of the project. |
| Run on fumes | To continue operating with very little energy or resources. | After working all night, I was running on fumes. |
| Run the risk | To take a chance that something bad might happen. | If you drive without a license, you run the risk of getting arrested. |
| Run interference | To help someone by removing obstacles. | His assistant had to run interference to keep him on schedule. |
| Run deep | To have a strong or profound effect. | The scars from the accident run deep. |
| Run counter to | To go against or oppose something. | His beliefs run counter to the company’s values. |
| Run into the ground | To ruin something by overusing or mismanaging it. | The company ran the product into the ground with excessive advertising. |
| Run ragged | To be exhausted from being overworked. | The nurses were run ragged during the pandemic. |
| Run the show | To be in charge and make decisions. | She’s been running the show since the manager left. |
| Run a business | To manage and operate a commercial enterprise. | He runs a successful small business. |
| Run alongside | To support or assist someone. | We will run alongside you during this difficult time. |
| Run interference for | To protect or shield someone from difficulties. | The secretary had to run interference for her boss all day. |
| Run the risk of | To expose oneself to the possibility of danger or harm. | If you skip the safety briefing, you run the risk of injury. |
| Run one’s course | To proceed to a natural or logical conclusion. | Let the situation run its course before intervening. |
| Run on empty | To continue functioning despite being depleted of resources or energy. | After the marathon, I was running on empty. |
| Run out of time | To exhaust the available time. | We ran out of time to finish the project. |
| Run up against a wall | To encounter an insurmountable obstacle. | We ran up against a wall trying to get funding for the project. |
Idioms Related to Avoiding Problems
The following table provides examples of idioms related to avoiding problems. These idioms often describe escaping or sidestepping difficulties.
They are useful for explaining strategies and outcomes related to problem-solving.
| Idiom | Definition | Example Sentence |
|---|---|---|
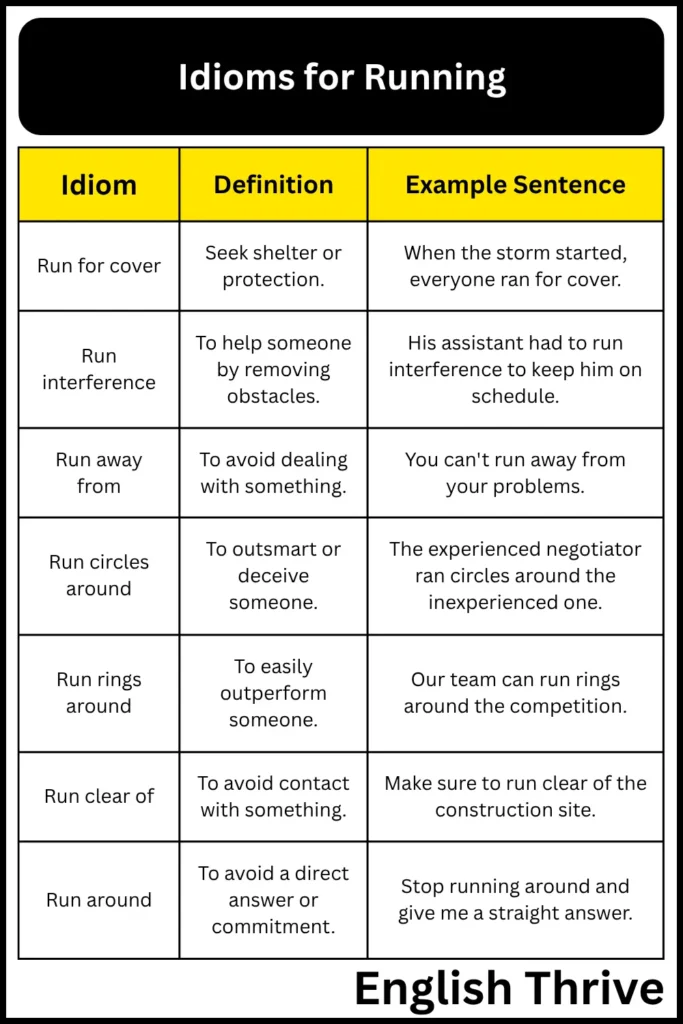
| Run for cover | Seek shelter or protection. | When the storm started, everyone ran for cover. |
| Run interference | To help someone by removing obstacles. | His assistant had to run interference to keep him on schedule. |
| Run away from | To avoid dealing with something. | You can’t run away from your problems. |
| Run circles around | To outsmart or deceive someone. | The experienced negotiator ran circles around the inexperienced one. |
| Run rings around | To easily outperform someone. | Our team can run rings around the competition. |
| Run clear of | To avoid contact with something. | Make sure to run clear of the construction site. |
| Run around | To avoid a direct answer or commitment. | Stop running around and give me a straight answer. |
| Run interference for | To block or obstruct someone or something. | The lawyer had to run interference for his client in the case. |
| Run from responsibility | To evade or avoid taking responsibility. | He always tries to run from responsibility when things go wrong. |
| Run a check | To investigate or verify something. | Let’s run a check on his background before hiring him. |
| Run scared | To act cautiously and fearfully due to a perceived threat. | The company is running scared after the new regulations were announced. |
| Run for the hills | To flee or escape from a dangerous or unpleasant situation. | When I heard the boss was angry, I wanted to run for the hills. |
| Run from the truth | To avoid facing or acknowledging reality. | You can’t run from the truth forever. |
| Run away with the idea | To become overly enthusiastic or carried away with an idea. | He ran away with the idea and started planning the whole project without consulting anyone. |
 Idioms for Running
Idioms for Running
Idioms Related to Competition
The following table provides examples of idioms related to competition. These idioms use running metaphors to describe competitive situations.
They are useful for discussing business, sports, and other competitive environments.
| Idiom | Definition | Example Sentence |
|---|---|---|
| Give someone a run for their money | Provide strong competition. | The underdog team gave the champions a run for their money. |
| Neck and neck | Very close in a competition. | The two candidates were neck and neck in the polls. |
| In the running | Having a chance of winning. | She is still in the running for the promotion. |
| Front runner | The leading candidate or competitor. | He is the front runner in the election. |
| Run away with | To win easily. | The team ran away with the championship. |
| Too close to call | The outcome is too uncertain to predict. | The election is too close to call. |
| Run circles around | To easily outperform or outdo someone in a competition. | Our sales team is running circles around the competition this quarter. |
| Run neck and neck | To be in a very close race or competition. | The two candidates are running neck and neck in the polls. |
| Run the table | To win every game or contest in a competition. | The team hopes to run the table and win the championship. |
| Run out ahead | To gain a lead or advantage in a competition. | The company is trying to run out ahead of its competitors. |
Usage Rules for Running Idioms
Using idioms correctly requires understanding their specific meanings and contexts. Here are some general rules to follow:
- Context Matters: Always consider the context in which you are using an idiom. Make sure the meaning aligns with the overall message you are trying to convey.
- Audience Awareness: Be mindful of your audience. Some idioms may not be familiar to non-native speakers or people from different cultural backgrounds.
- Formal vs. Informal: Most idioms are informal and should be used in casual conversations or less formal writing. Avoid using them in formal academic or professional settings unless you are certain they are appropriate.
- Word Order: Idioms are fixed expressions, so the word order cannot be changed without altering the meaning or making the phrase nonsensical.
- Substitution: You generally cannot substitute words within an idiom. For example, you can’t change “run the extra mile” to “walk the extra mile” without changing the meaning.
Common Mistakes with Running Idioms
One of the most common mistakes is misinterpreting the literal meaning of the words in the idiom. For example, someone might think “hit the ground running” literally means to physically run upon landing, rather than starting something quickly and successfully.
Another common mistake is using the wrong form of the verb within the idiom. For example, saying “ran circles around” instead of “run circles around” when the context requires the present tense.
Here are some examples of common mistakes and their corrections:
| Incorrect | Correct | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| He hitted the ground running. | He hit the ground running. | The past tense of “hit” is “hit,” not “hitted.” |
| She is running the more mile. | She is running the extra mile. | The correct idiom is “run the extra mile.” |
| They are in the race for the promotion. | They are in the running for the promotion. | The correct idiom is “in the running.” |
| He gave him a walk for his money. | He gave him a run for his money. | The correct idiom is “give someone a run for their money”. |
| The project is off to the races. | The project is off to races. | The word “the” is required before “races” in this idiom. |
Practice Exercises: Idioms for Running
Test your understanding of running idioms with these practice exercises. Fill in the blanks with the correct idiom from the list provided.
Each exercise includes 10 questions to reinforce your learning.
Idiom List: *hit the ground running*, *run the extra mile*, *in the long run*, *give someone a run for their money*, *run out of steam*, *run for cover*, *run interference*, *run wild*, *run a tight ship*, *off to the races*
Exercise 1:
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| 1. The new manager wanted to ________ and make immediate improvements. | hit the ground running |
| 2. She always ________ for her clients, providing exceptional service. | runs the extra mile |
| 3. ________, this investment will prove to be very profitable. | In the long run |
| 4. The underdog team managed to ________ against the champions. | give someone a run for their money |
| 5. The project ________ towards the end due to lack of resources. | ran out of steam |
| 6. When the storm started, everyone had to ________. | run for cover |
| 7. The assistant had to ________ for the CEO to keep him on schedule. | run interference |
| 8. The children were allowed to ________ in the backyard. | run wild |
| 9. The supervisor ________ to ensure everyone is productive and efficient. | runs a tight ship |
| 10. With the contract signed, the project was ________. | off to the races |
Exercise 2:
Idiom List: *run the gauntlet*, *run its course*, *run on fumes*, *run the risk*, *run deep*, *run counter to*, *run into the ground*, *run ragged*, *run the show*, *run a business*
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| 1. After the scandal, the politician had to ________ of media scrutiny. | run the gauntlet |
| 2. The illness just needs to ________ before he feels better. | run its course |
| 3. After working all night, I was ________. | running on fumes |
| 4. If you drive without a license, you ________ of getting arrested. | run the risk |
| 5. The scars from the accident ________. | run deep |
| 6. His beliefs ________ to the company’s values. | run counter to |
| 7. The company ________ with excessive advertising. | ran the product into the ground |
| 8. The nurses were ________ during the pandemic. | run ragged |
| 9. She’s been ________ since the manager left. | running the show |
| 10. He ________ successfully. | runs a business |
Advanced Topics
For advanced learners, exploring the etymology and historical context of running idioms can provide a deeper understanding of their meanings and usage. Many idioms have roots in historical events, cultural practices, or literary works.
Additionally, analyzing how running idioms are used in different genres of writing, such as literature, journalism, and business communication, can reveal nuances in their application and interpretation.
Furthermore, comparing running idioms across different languages can highlight cultural differences in how physical activity is used metaphorically. This comparative analysis can enhance cross-cultural communication skills.
FAQs About Idioms for Running
Is running out of time an idiom?
Yes, “running out of time” is an idiom! It means that there is very little time left to complete something or meet a deadline. For example, “We’re running out of time, hurry up!”
Do a runner idiom examples?
“Do a runner” means to leave suddenly or escape, especially to avoid responsibility. Example: “He did a runner after the argument, leaving everyone confused.”
What is a good quote for running?
A great quote for running is: “The miracle isn’t that I finished. The miracle is that I had the courage to start.” — John Bingham. It celebrates the courage to begin any challenge, especially in running.
What is the idiom for running fast?
The idiom for running fast is “run like the wind.” It describes someone running at incredible speed. For example, “She ran like the wind to catch the bus.”
What is an idiom for run?
“Run the show” is a popular idiom meaning to be in charge or to control a situation. Example: “She runs the show at work, making all the important decisions.”
Conclusion: Idioms for Running
Mastering idioms for running can significantly enhance your ability to communicate effectively and expressively in English. By understanding the meanings, usage rules, and common mistakes associated with these idioms, you can add color and nuance to your conversations and writing.
Remember to consider the context and your audience when using idioms, and continue to expand your knowledge through practice and exposure to the language.
Continued practice and exposure to the English language are key to mastering idioms. Don’t be afraid to use these idioms in your daily conversations and writing to reinforce your understanding and improve your fluency.
With consistent effort, you’ll be able to use running idioms with confidence and precision, adding richness and depth to your communication skills. Keep running towards fluency!