Understanding idioms is crucial for mastering English, as they add color and depth to communication. Idioms related to confusion are especially important because they help express complex feelings of bewilderment in a concise and vivid way.
This article provides a comprehensive guide to Idioms for Confused, offering definitions, examples, and practical exercises to enhance your understanding and usage. This guide is perfect for English language learners, teachers, and anyone looking to enrich their vocabulary and improve their communication skills.
By diving into the nuances of these idioms, you’ll not only expand your vocabulary but also gain a deeper appreciation for the cultural contexts in which they are used. Whether you are preparing for an English proficiency exam, aiming to improve your conversational skills, or simply curious about the richness of the English language, this article will equip you with the knowledge and tools you need to confidently navigate the world of idioms for confusion.
Contents
ToggleDefinition of Idioms for Confused
An idiom is a phrase or expression whose meaning cannot be understood from the literal meanings of its individual words. Instead, the phrase has a figurative meaning that is known through common usage.
Idioms related to confusion specifically describe states of bewilderment, uncertainty, or disorientation. These idioms often use vivid imagery or metaphors to convey the feeling of being lost, puzzled, or unsure.
Understanding idioms is essential for effective communication because they are frequently used in everyday conversation, literature, and media. Without a grasp of idiomatic expressions, one might misinterpret the intended meaning, leading to misunderstandings.
Mastering idioms for confusion allows you to express nuanced feelings of bewilderment and understand others when they do the same.
Classification of Idioms for Confused
Idioms for confusion can be classified based on the specific type of confusion they express. Some idioms describe a general state of bewilderment, while others indicate being overwhelmed by information or lacking understanding in a particular situation.
Understanding these classifications can help you choose the most appropriate idiom for a given context.
Here are some common classifications:
- General confusion: Idioms that express a broad sense of not understanding or being disoriented.
- Information overload: Idioms that describe being overwhelmed by too much information.
- Lack of understanding: Idioms that indicate a failure to comprehend something specific.
- Uncertainty: Idioms that convey a feeling of doubt or lack of clarity about a situation.
Function of Idioms for Confused
The primary function of idioms for confusion is to express a state of mental uncertainty or lack of clarity in a more colorful and expressive way than literal language allows. These idioms add emotional depth and can make communication more engaging and relatable.
They also allow speakers to convey complex feelings with fewer words, making speech more efficient.
Idioms serve various functions in communication:
- Expressing emotion: Conveys feelings of confusion, frustration, or uncertainty.
- Adding emphasis: Highlights the intensity of the confusion.
- Creating imagery: Paints a vivid picture of the state of bewilderment.
- Enhancing communication: Makes speech more engaging and relatable.
Contexts for Using Idioms for Confused
Idioms for confusion are appropriate in a variety of contexts, including informal conversations, creative writing, and even some professional settings. However, it’s important to be mindful of your audience and the level of formality required.
Overusing idioms or using them inappropriately can make your communication unclear or unprofessional.
Common contexts for using these idioms include:
- Casual conversations: Talking with friends and family about confusing situations.
- Creative writing: Describing a character’s internal state of confusion in a novel or short story.
- Presentations: Using idioms to connect with the audience by describing relatable moments of confusion.
- Problem-solving discussions: Expressing confusion or uncertainty about a potential solution.
Structural Breakdown
Idioms, by definition, do not follow standard grammatical rules when interpreted literally. Their meaning is derived from their conventional usage, not from the individual words.
Understanding the structural components of idioms involves recognizing that they function as single units of meaning.
Here’s a breakdown of the structural elements:
- Fixed structure: Idioms usually have a fixed word order, and changing the order can alter or destroy the meaning.
- Figurative meaning: The overall meaning is different from the literal meanings of the words.
- Non-compositional: The meaning of the idiom cannot be determined by combining the meanings of its parts.
For example, the idiom “to be in a fog” means to be confused, but its literal interpretation involves weather conditions. The idiom functions as a single unit conveying a specific meaning.
Common Structural Patterns
Many idioms follow common structural patterns that can help you recognize and understand them. These patterns often involve metaphors, similes, or other figures of speech.
Some common patterns include:
- Verb + preposition: Such as “mixed up” or “lost in.”
- Noun + verb: Such as “brain freeze.”
- Adjective + noun: Such as “foggy brain.”
Recognizing these patterns can make it easier to identify and interpret new idioms as you encounter them.
Variations and Flexibility
While idioms generally have a fixed structure, some idioms allow for minor variations without changing the overall meaning. These variations might involve changing the tense of a verb or adding a descriptive adjective.
For example, “to be in a fog” can also be expressed as “to have been in a fog” or “to feel like you’re in a fog.” The core meaning of confusion remains the same despite these slight variations.
Types and Categories of Idioms for Confused
Idioms for confusion can be categorized based on the specific aspect of confusion they describe. This categorization helps in selecting the most appropriate idiom for a particular situation.
General Confusion Idioms
These idioms express a broad sense of not understanding or being disoriented. They are suitable when you want to convey a general feeling of bewilderment without specifying the cause.
Examples include:
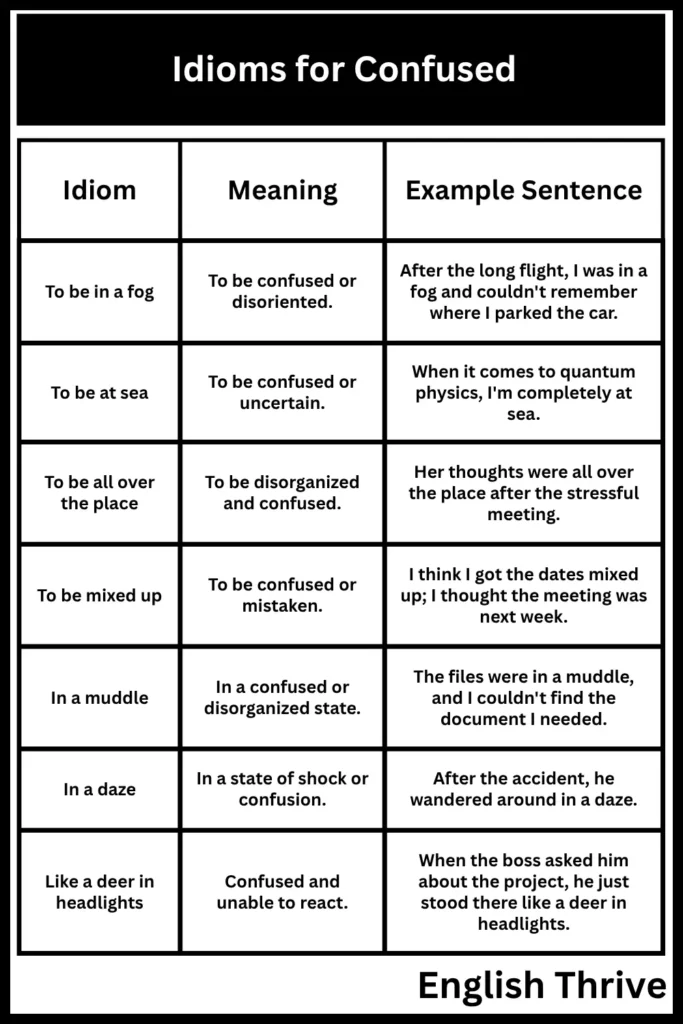
- To be in a fog: To be confused or disoriented.
- To be at sea: To be confused or uncertain.
- To be all over the place: To be disorganized and confused.
- To be mixed up: To be confused or mistaken.
Information Overload Idioms
These idioms describe the feeling of being overwhelmed by too much information. They are useful when you want to convey that you are struggling to process a large amount of data.
Examples include:
- Brain freeze: A temporary mental lapse or confusion, often caused by stress or too much information.
- Head spinning: Feeling overwhelmed and confused.
- Lost in the weeds: To be overwhelmed by details and lose sight of the main point.
- Mind-boggling: Overwhelming or difficult to comprehend.
Lack of Understanding Idioms
These idioms indicate a failure to comprehend something specific. They are appropriate when you want to express that you don’t understand a particular concept or situation.
Examples include:
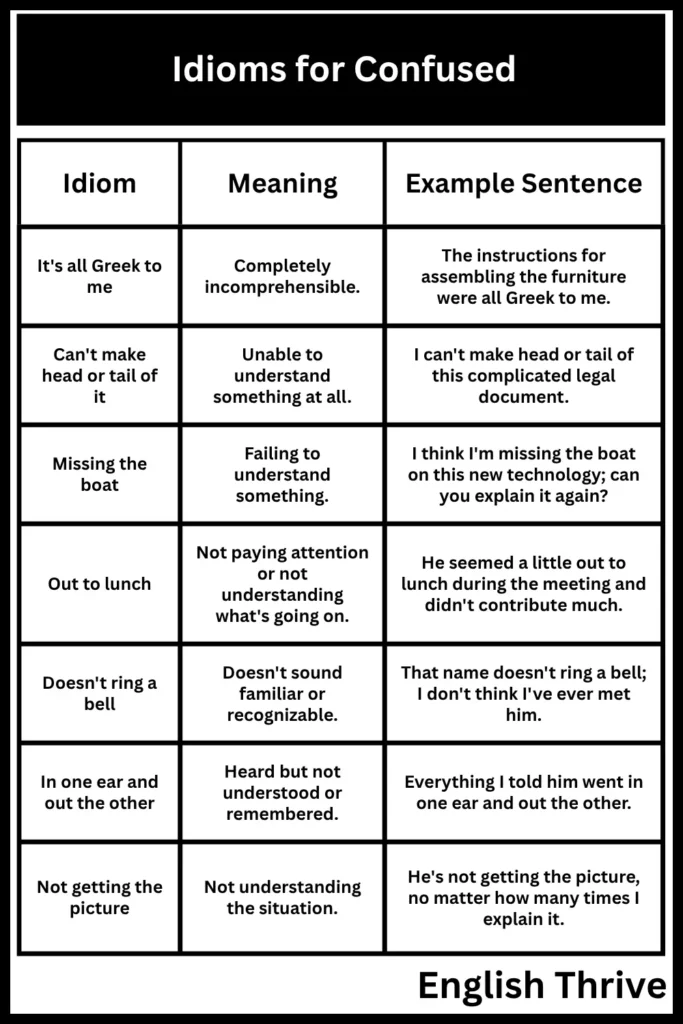
- It’s all Greek to me: Completely incomprehensible.
- Can’t make head or tail of it: Unable to understand something at all.
- Missing the boat: Failing to understand something.
- Out to lunch: Not paying attention or not understanding what’s going on.
Uncertainty Idioms
These idioms convey a feeling of doubt or lack of clarity about a situation. They are useful when you want to express that you are unsure about something or don’t know what to do.
Examples include:
- Up in the air: Uncertain or undecided.
- In two minds: Unable to decide between two options.
- On the fence: Undecided or neutral.
- Don’t have a clue: To have no idea about something.
Examples of Idioms for Confused
The following tables provide extensive examples of idioms for confusion, categorized by type. Each example is accompanied by a sentence illustrating its usage.
General Confusion Examples
This table illustrates idioms for general confusion, where the overall feeling is one of disorientation or lack of understanding.
| Idiom | Meaning | Example Sentence |
|---|---|---|
| To be in a fog | To be confused or disoriented. | After the long flight, I was in a fog and couldn’t remember where I parked the car. |
| To be at sea | To be confused or uncertain. | When it comes to quantum physics, I’m completely at sea. |
| To be all over the place | To be disorganized and confused. | Her thoughts were all over the place after the stressful meeting. |
| To be mixed up | To be confused or mistaken. | I think I got the dates mixed up; I thought the meeting was next week. |
| In a muddle | In a confused or disorganized state. | The files were in a muddle, and I couldn’t find the document I needed. |
| In a daze | In a state of shock or confusion. | After the accident, he wandered around in a daze. |
| Like a deer in headlights | Confused and unable to react. | When the boss asked him about the project, he just stood there like a deer in headlights. |
| Not know whether one is coming or going | Extremely confused and disoriented. | With all the changes happening at work, I don’t know whether I’m coming or going. |
| To be discombobulated | Confused and disconcerted. | The sudden noise discombobulated her, and she forgot what she was saying. |
| To be bamboozled | To be deceived or confused. | I felt completely bamboozled by the complicated instructions. |
| Lost one’s bearings | To become confused about one’s location or situation. | After wandering through the unfamiliar city, they lost their bearings. |
| In a spin | In a state of confusion or agitation. | The unexpected news sent her in a spin. |
| Not with it | Not alert, aware, or understanding. | I’m sorry, I’m not with it this morning; I didn’t get much sleep. |
| To be muddled | Confused and unclear in thought. | His explanation was so complex that I was left feeling completely muddled. |
| To be perplexed | Completely baffled; very puzzled. | The detective was perplexed by the lack of evidence at the crime scene. |
| To be rattled | Nervous, worried, or confused. | The sudden interruption rattled him, and he lost his train of thought. |
| To be thrown for a loop | To be shocked and confused. | The unexpected announcement threw everyone for a loop. |
| Not able to think straight | Unable to think clearly due to confusion or stress. | After the argument, I wasn’t able to think straight. |
| To be befuddled | Confused, perplexed. | The complicated instructions befuddled him, and he needed help to understand them. |
| To be disoriented | Confused about time, place, or identity. | Waking up in a strange room, he felt completely disoriented. |
| In a haze | In a state of confusion or lack of clarity. | She spent the day in a haze, unable to concentrate on anything. |
| Not know which way is up | To be completely confused or disoriented. | After the unexpected turn of events, he didn’t know which way was up. |
| To be flustered | Agitated or confused. | She became flustered when she couldn’t find her keys. |
| To be bewildered | Confused and perplexed. | He was bewildered by the strange symbols on the ancient map. |
Information Overload Examples
This table presents idioms related to information overload, where the feeling is one of being overwhelmed by too much data or details.
| Idiom | Meaning | Example Sentence |
|---|---|---|
| Brain freeze | A temporary mental lapse or confusion, often caused by stress or too much information. | During the exam, I had a complete brain freeze and couldn’t remember the formula. |
| Head spinning | Feeling overwhelmed and confused. | After the conference, my head was spinning with all the new information. |
| Lost in the weeds | To be overwhelmed by details and lose sight of the main point. | We got lost in the weeds during the discussion and forgot the original goal. |
| Mind-boggling | Overwhelming or difficult to comprehend. | The complexity of the project was mind-boggling. |
| Too much information | Overwhelmed by a large amount of data. | I tried to understand the report, but there was just too much information. |
| Drowning in data | Overwhelmed by a large amount of data. | The marketing team is drowning in data and needs help analyzing it. |
| Brain overload | The state of being overwhelmed with information. | After the lecture, I experienced brain overload and needed a break. |
| Over one’s head | Too difficult to understand. | The technical jargon in the manual was completely over my head. |
| Swamped with information | Overwhelmed by a large amount of data. | The customer service representatives are swamped with information and struggling to keep up. |
| Information overload | The state of being overwhelmed with too much information. | The internet can lead to information overload if you’re not careful. |
| Lost in a sea of data | Overwhelmed by a large amount of data. | The analysts felt lost in a sea of data, unable to find meaningful patterns. |
| Reeling from the facts | Feeling overwhelmed by presented facts. | After the presentation, the audience was still reeling from the facts. |
| Buried under details | Overwhelmed by excessive details. | The project manager was buried under details and struggling to see the big picture. |
| Mind is swimming | Feeling overwhelmed and confused due to too much information. | After the long meeting, my mind was swimming with ideas and suggestions. |
| Can’t see the forest for the trees | Being unable to see the overall situation because you are looking at too many small details. | The manager was so focused on the daily tasks that he couldn’t see the forest for the trees. |
| Lost track of things | Unable to keep up with all the information and tasks. | With so many deadlines, I’ve lost track of things. |
| Fogged over | Mentally unclear due to too much information. | My brain fogged over after trying to learn three new software programs in one day. |
| Bogged down in details | To be so involved with details that you have difficulty making progress. | The team got bogged down in details and missed the project deadline. |
| Unable to process it all | Incapable of understanding or dealing with the amount of information. | After the intense workshop, I was unable to process it all. |
| Too much to take in | An excessive amount of information to absorb. | The conference had too much to take in, and I felt overwhelmed. |
| Saturated with info | Filled to capacity with information. | After reading the report, I felt saturated with info and needed a break. |
| Overwhelmed by the sheer volume | Feeling defeated by the amount of information. | The researcher was overwhelmed by the sheer volume of data. |
| Cannot keep up | Unable to manage or understand the flow of information. | With the rapid changes, I cannot keep up with all the new developments. |
| Brain fried | Mentally exhausted from too much information. | After a day of studying, my brain was fried. |
Lack of Understanding Examples
This table provides examples of idioms indicating a lack of understanding, where the speaker is unable to comprehend something specific.
| Idiom | Meaning | Example Sentence |
|---|---|---|
| It’s all Greek to me | Completely incomprehensible. | The instructions for assembling the furniture were all Greek to me. |
| Can’t make head or tail of it | Unable to understand something at all. | I can’t make head or tail of this complicated legal document. |
| Missing the boat | Failing to understand something. | I think I’m missing the boat on this new technology; can you explain it again? |
| Out to lunch | Not paying attention or not understanding what’s going on. | He seemed a little out to lunch during the meeting and didn’t contribute much. |
| Doesn’t ring a bell | Doesn’t sound familiar or recognizable. | That name doesn’t ring a bell; I don’t think I’ve ever met him. |
| In one ear and out the other | Heard but not understood or remembered. | Everything I told him went in one ear and out the other. |
| Not getting the picture | Not understanding the situation. | He’s not getting the picture, no matter how many times I explain it. |
| Beyond me | Too difficult for me to understand. | Nuclear physics is completely beyond me. |
| Not following | Not understanding the explanation. | I’m not following; can you explain that again? |
| In the dark | Uninformed or unaware. | They kept me in the dark about the changes to the project. |
| Not grasping the concept | Failing to understand the idea. | The student was not grasping the concept, even after several explanations. |
| At a loss | Not knowing what to do or say. | I was at a loss to explain why the experiment failed. |
| Not seeing the light | Not understanding or realizing something. | He’s still not seeing the light about the importance of teamwork. |
| Left scratching one’s head | Confused and puzzled. | The ambiguous message left everyone scratching their heads. |
| Not clicking | Not understanding or connecting with something. | The new software just isn’t clicking with me. |
| Not getting through | Failing to make someone understand. | I can’t seem to get through to him about the importance of deadlines. |
| Not registering | Not being understood or noticed. | My advice just wasn’t registering with her. |
| Not sinking in | Not being fully understood or absorbed. | The information just wasn’t sinking in, no matter how hard I tried. |
| Not twigging | (British English) Not understanding. | He’s not twigging what I’m trying to say. |
| Not getting it | Not understanding something. | I’m still not getting it; can you give me another example? |
| Lost for words | Unable to speak because of surprise or confusion. | The news left her lost for words. |
| Not getting the message | Failing to understand the intended communication. | He’s not getting the message that he needs to improve his performance. |
| Not grasping | Failing to understand something. | She’s not grasping the basic principles of the subject. |
| Not comprehending | Failing to understand fully. | He was not comprehending the complexity of the situation. |
Uncertainty Examples
This table lists idioms that express uncertainty, where the speaker is unsure about a situation or decision.
| Idiom | Meaning | Example Sentence |
|---|---|---|
| Up in the air | Uncertain or undecided. | Our plans for the summer are still up in the air. |
| In two minds | Unable to decide between two options. | I’m in two minds about whether to accept the new job offer. |
| On the fence | Undecided or neutral. | I’m still on the fence about which candidate to vote for. |
| Don’t have a clue | To have no idea about something. | I don’t have a clue how to fix this computer. |
| Beats me | I don’t know. | “Where did he go?” “Beats me!” |
| Your guess is as good as mine | I don’t know either. | “What’s going to happen next?” “Your guess is as good as mine.” |
| Haven’t got a clue | To have no idea about something. | I haven’t got a clue what he’s talking about. |
| In limbo | In an uncertain or undecided state. | The project is in limbo until we get funding. |
| A question mark | Something that is uncertain or unknown. | His future at the company is a question mark. |
| Uncertain future | A future that is not clear or predictable. | The company faces an uncertain future due to the economic downturn. |
| In a quandary | In a state of perplexity or uncertainty. | She was in a quandary about which path to take. |
| Undecided | Not having made a decision. | The committee is still undecided on the matter. |
| Not sure | Lacking certainty. | I’m not sure if I can make it to the party. |
| Without a doubt | Definitely uncertain. | It is without a doubt that the future is uncertain. |
| Not set in stone | Not definite or unchangeable. | The plans are not set in stone; we can still make changes. |
| Hazy | Unclear or vague. | The details of the agreement are still hazy. |
| Vague idea | A general or unclear notion. | I have a vague idea of what needs to be done, but I need more information. |
| Unclear | Not clear or easy to understand. | The instructions were unclear, and I couldn’t follow them. |
| Cloudy | Unclear or confusing. | The situation is still cloudy, and we need more information. |
| Unresolved | Not resolved or decided. | The issue remains unresolved. |
| Toss-up | An outcome that is uncertain and can go either way. | The election is a toss-up between the two candidates. |
| Unpredictable | Not able to be predicted. | The weather is unpredictable this time of year. |
| Unforeseeable | Not able to be foreseen or anticipated. | The accident was due to unforeseeable circumstances. |
| Up for grabs | Available to be won or obtained. | The contract is still up for grabs. |
| In the balance | In a state where the outcome is uncertain. | The team’s chances of winning are in the balance. |
Usage Rules for Idioms for Confused
Using idioms correctly requires understanding their specific meanings and contexts. While idioms add color to your language, misusing them can lead to confusion.
Contextual Appropriateness
Consider the context of your communication when using idioms. Some idioms are more appropriate for informal settings, while others can be used in more formal situations.
For example, “It’s all Greek to me” is suitable for casual conversation, but might not be appropriate in a business presentation.
Audience Awareness
Be aware of your audience’s familiarity with idioms. If you are speaking to non-native English speakers, it’s best to use idioms sparingly or explain their meanings.
Overusing idioms can make your communication harder to understand.
Grammatical Consistency
Ensure that the idiom fits grammatically within the sentence. While idioms themselves don’t follow standard grammatical rules, the surrounding sentence should be grammatically correct.
For example, “I am in a fog” is grammatically correct, while “I is in a fog” is not.
Avoid Overuse
Using too many idioms in a single conversation or piece of writing can make your language sound unnatural or contrived. Use idioms sparingly and only when they add value to your communication.
Literal vs. Figurative Meaning
Always remember that idioms have a figurative meaning that is different from the literal meaning of the words. Avoid interpreting idioms literally, as this can lead to misunderstandings.
For example, “head spinning” doesn’t literally mean that your head is rotating; it means that you are feeling overwhelmed.
Common Mistakes When Using Idioms for Confused
Even advanced learners of English can make mistakes when using idioms. Here are some common errors and how to avoid them.
| Incorrect | Correct | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| I am in a fogs. | I am in a fog. | Idioms usually have a fixed structure and cannot be pluralized. |
| He is at the sea. | He is at sea. | The correct idiom is “at sea,” not “at the sea.” |
| My head is spin. | My head is spinning. | The correct idiom is “head spinning,” which requires the present participle form of the verb. |
| It’s all Greek for me. | It’s all Greek to me. | The correct idiom is “to me,” not “for me.” |
| I don’t have a idea. | I don’t have a clue. | The correct idiom is “clue,” not “idea.” |
| I am on the fences. | I am on the fence. | The correct idiom is “on the fence,” not “on the fences.” |
| He has no clues. | He doesn’t have a clue. | The idiom requires the singular form “a clue”. |
| The future is up in airs. | The future is up in the air. | The idiom is “up in the air,” not “up in airs.” |
Practice Exercises
Test your understanding of idioms for confusion with these exercises. Choose the correct idiom to complete each sentence.
Exercise 1: Fill in the Blanks
Choose the correct idiom from the list to complete each sentence.
Idiom List: in a fog, at sea, all over the place, mixed up, brain freeze, head spinning, it’s all Greek to me, don’t have a clue, on the fence, lost in the weeds
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| 1. After the intense meeting, my thoughts were __________. | all over the place |
| 2. When I tried to solve the complex equation, I had a complete __________. | brain freeze |
| 3. The instructions for the new software are __________. | it’s all Greek to me |
| 4. I __________ how to fix this problem; can you help me? | don’t have a clue |
| 5. After the accident, he was __________ and couldn’t remember what happened. | in a fog |
| 6. I’m completely __________ with all these new regulations; I need some guidance. | at sea |
| 7. I got the dates __________ and missed the deadline. | mixed up |
| 8. The project got __________ with too many details, and we lost sight of the main goal. | lost in the weeds |
| 9. My __________ after trying to understand the physics lecture. | head spinning |
| 10. I’m still __________ about whether to accept the job offer or not. | on the fence |
Exercise 2: Matching
Match the idiom with its correct meaning.
| Idiom | Meaning |
|---|---|
| 1. In two minds | a. Overwhelmed by details and losing sight of the main point |
| 2. Missing the boat | b. Unable to decide between two options |
| 3. Lost in the weeds | c. Completely incomprehensible |
| 4. It’s all Greek to me | d. To have no idea about something |
| 5. Haven’t got a clue | e. Failing to understand something |
Answers:
- 1-b
- 2-e
- 3-a
- 4-c
- 5-d
Exercise 3: Correct the Sentence
Identify and correct the misused idiom in each sentence.
| Incorrect Sentence | Correct Sentence |
|---|---|
| 1. I’m in a fogs after the long meeting. | I’m in a fog after the long meeting. |
| 2. He is at the sea when it comes to technology. | He is at sea when it comes to technology. |
| 3. My head is spin after reading that report. | My head is spinning after reading that report. |
| 4. It’s all Greek for me; I don’t understand anything. | It’s all Greek to me; I don’t understand anything. |
| 5. I don’t have a idea how to solve this problem. | I don’t have a clue how to solve this problem. |
Advanced Topics
For those looking to deepen their understanding of idioms for confusion, here are some advanced topics to explore.
Historical Origins of Idioms
Many idioms have interesting historical origins that shed light on their meanings. Researching the etymology of idioms can provide a deeper appreciation for their usage.
Cultural Variations in Idioms
Idioms can vary across different cultures and regions. Understanding these variations is important for effective cross-cultural communication.
Some idioms may not exist in other languages, or they may have different meanings.
Idioms in Literature and Media
Analyzing how idioms are used in literature and media can provide insights into their nuances and impact. Authors and speakers often use idioms to add depth, humor, or emotional resonance to their work.
Creating Your Own Idioms
While most idioms are established expressions, it’s possible to create your own idioms. This requires a strong understanding of language and culture, as well as creativity and a sense of humor.
New idioms can emerge and gain popularity over time.
FAQs on Idioms for Confused
Here are some frequently asked questions about idioms for confusion.
What is the difference between an idiom and a metaphor?
An idiom is a phrase whose meaning is not deducible from the literal meanings of the words, while a metaphor is a figure of speech that directly compares two unrelated things. Idioms are often metaphorical, but not all metaphors are idioms.
How can I improve my understanding of idioms?
Read widely, listen to native speakers, and pay attention to the context in which idioms are used. Practice using idioms in your own speech and writing, and ask for feedback from native speakers.
Are idioms important for learning English?
Yes, idioms are essential for mastering English. They are frequently used in everyday conversation, literature, and media, and understanding them is crucial for effective communication.
Can I use idioms in formal writing?
It depends on the idiom and the context. Some idioms are appropriate for formal writing, while others are more suitable for informal settings.
Consider your audience and the level of formality required.
How can I avoid misusing idioms?
Learn the specific meanings and contexts of idioms, and practice using them correctly. Ask native speakers for feedback, and avoid using idioms if you are unsure of their meaning.
What is the best way to memorize idioms?
Use flashcards, create example sentences, and practice using idioms in conversation. Associate idioms with vivid images or personal experiences to make them more memorable.
Conclusion
Mastering idioms for confusion is a valuable skill for anyone learning or using the English language. These expressions add color, depth, and nuance to your communication, allowing you to express complex feelings of bewilderment and uncertainty with greater precision.
By understanding the definitions, structures, and usage rules of these idioms, you can enhance your vocabulary, improve your conversational skills, and gain a deeper appreciation for the richness of the English language.
Continue to practice and explore new idioms to further expand your knowledge and confidence. Remember to consider the context, audience, and grammatical consistency when using idioms, and avoid common mistakes.
With dedication and practice, you can confidently navigate the world of idioms for confusion and communicate more effectively in English.