Idioms are an essential part of the English language, adding color and depth to everyday conversations and writing. Among the vast array of idioms, those specifically related to people provide unique insights into character, behavior, and relationships.
Understanding these idioms not only enhances your comprehension of English but also allows you to express yourself more creatively and accurately. This article aims to provide a comprehensive guide to idioms about people, covering their definitions, structures, usage rules, and common mistakes, along with numerous examples and practice exercises to help you master this fascinating aspect of English grammar.
This guide is beneficial for English language learners of all levels, from beginners seeking to expand their vocabulary to advanced speakers aiming for fluency and nuance.
Contents
ToggleDefinition of Idioms About People
An idiom is a phrase or expression whose meaning cannot be understood from the ordinary meanings of the words it contains. In other words, idioms are figurative expressions where the overall meaning is different from the literal meaning of the individual words.
Idioms about people specifically refer to phrases that describe aspects of a person, such as their personality, behavior, relationships, skills, or stage of life. They provide a concise and often colorful way to convey complex ideas about individuals.
Idioms function as a form of figurative language, enriching communication by adding layers of meaning and emotional nuance. They are deeply embedded in culture and often reflect shared experiences and perspectives.
Understanding idioms is crucial for comprehending native English speakers and for avoiding misinterpretations that can arise from taking these expressions literally. The context in which an idiom is used is vital for accurate interpretation.
Idioms about people can be classified based on the aspect of a person they describe. This classification helps in understanding and categorizing these idioms for easier learning and application.
They enhance communication, adding depth and color to descriptions of individuals and their interactions.
Structural Breakdown
Idioms, by their nature, often defy typical grammatical rules. Their structure can vary widely, ranging from simple phrases to complex clauses.
The meaning of an idiom is not derived from the grammatical arrangement of its components but rather from its established usage and cultural context.
The structure of idioms about people can involve various parts of speech, including nouns, verbs, adjectives, and prepositions. For example, an idiom like “a couch potato” uses a noun phrase to describe a lazy person.
Another example is “to have a heart of gold,” where a verb (“to have”) is combined with a noun phrase (“a heart of gold”) to describe a kind and generous person. The combination of these elements creates a meaning that is distinct from the individual words.
Some idioms maintain a fixed structure, meaning the words cannot be changed without altering or destroying the idiom’s meaning. Other idioms allow for some flexibility, such as changing the verb tense or using a possessive pronoun.
For instance, “to pull someone’s leg” can be modified to “I was just pulling your leg” without losing its idiomatic meaning. However, it’s essential to recognize the limitations of such modifications to avoid misusing the idiom.
Types and Categories of Idioms About People
Idioms about people can be grouped into several categories based on the specific aspect of a person they describe. These categories include personality traits, behavior and actions, relationships, skills and abilities, and age and life stages.
Understanding these categories can help learners better organize and remember different idioms.
Idioms Describing Personality Traits
These idioms describe a person’s character, disposition, or temperament. They often convey positive or negative qualities in a vivid and memorable way.
For example, “a heart of gold” describes someone who is exceptionally kind and generous, while “a cold fish” describes someone who is unemotional and distant.
Idioms Describing Behavior and Actions
This category includes idioms that describe how a person acts or behaves in certain situations. These idioms can refer to habitual behaviors, specific actions, or general patterns of conduct.
For example, “to wear your heart on your sleeve” describes someone who openly expresses their emotions, while “to stab someone in the back” describes someone who betrays another person’s trust.
Idioms Describing Relationships
These idioms describe the nature of connections between people, such as friendships, romantic relationships, or family ties. They can convey the strength, quality, or dynamics of these relationships.
For example, “to be joined at the hip” describes two people who are very close and inseparable, while “to be on the rocks” describes a relationship that is experiencing difficulties.
Idioms Describing Skills and Abilities
This category includes idioms that describe a person’s talents, capabilities, or areas of expertise. These idioms can refer to specific skills, general competence, or lack thereof.
For example, “to have a green thumb” describes someone who is skilled at gardening, while “to be all thumbs” describes someone who is clumsy or inept.
Idioms Describing Age and Life Stages
These idioms describe a person’s age or stage of life, often with connotations about their experiences, maturity, or vitality. For example, “to be wet behind the ears” describes someone who is young and inexperienced, while “over the hill” describes someone who is past their prime.
Examples of Idioms About People
The following sections provide extensive examples of idioms about people, organized by category. Each example includes the idiom, its meaning, and a sample sentence to illustrate its usage.
Personality Trait Idioms Examples
This table provides examples of idioms that describe personality traits.
| Idiom | Meaning | Example Sentence |
|---|---|---|
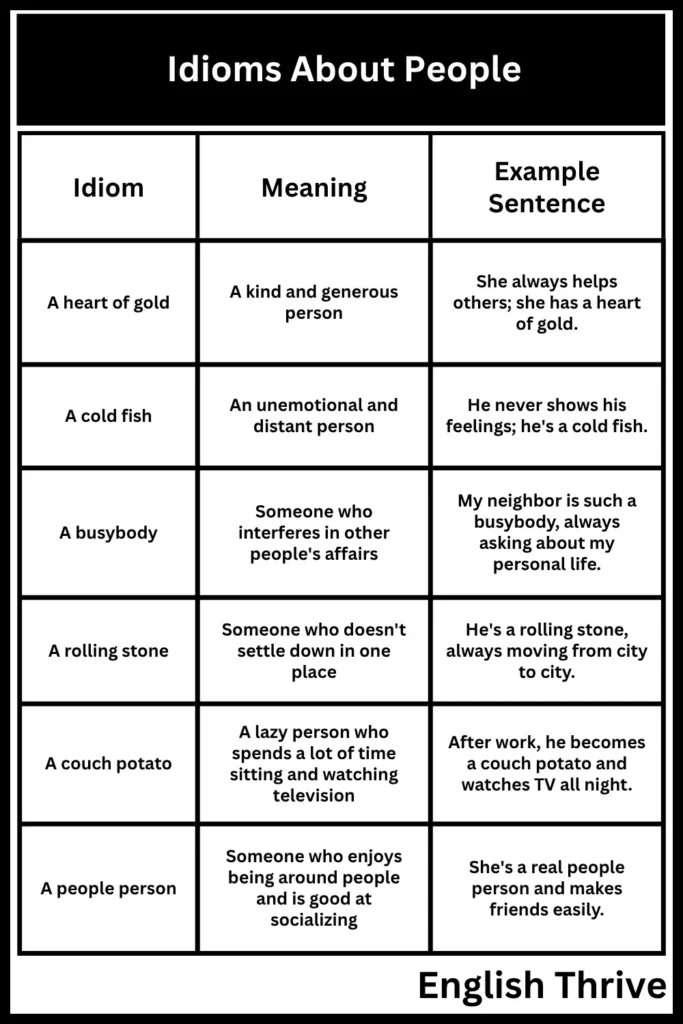
| A heart of gold | A kind and generous person | She always helps others; she has a heart of gold. |
| A cold fish | An unemotional and distant person | He never shows his feelings; he’s a cold fish. |
| A busybody | Someone who interferes in other people’s affairs | My neighbor is such a busybody, always asking about my personal life. |
| A rolling stone | Someone who doesn’t settle down in one place | He’s a rolling stone, always moving from city to city. |
| A couch potato | A lazy person who spends a lot of time sitting and watching television | After work, he becomes a couch potato and watches TV all night. |
| A people person | Someone who enjoys being around people and is good at socializing | She’s a real people person and makes friends easily. |
| A tough cookie | A strong and resilient person | She’s been through a lot, but she’s a tough cookie. |
| A wet blanket | Someone who spoils the fun | Don’t invite him; he’s a wet blanket and always complains. |
| A dark horse | Someone who surprises people with unexpected talent or success | He was a dark horse in the competition and ended up winning. |
| A lone wolf | Someone who prefers to be alone | She’s a bit of a lone wolf and prefers to work independently. |
| A chatterbox | Someone who talks a lot | She’s such a chatterbox, always talking about something. |
| A penny-pincher | Someone who is very careful with money and avoids spending it | He’s a real penny-pincher and always looks for the best deals. |
| A daydreamer | Someone who spends time imagining pleasant things | She’s such a daydreamer and often loses track of time. |
| An early bird | Someone who gets up early in the morning | He’s an early bird and always starts his day before sunrise. |
| A night owl | Someone who stays up late at night | She’s a night owl and does her best work in the evening. |
| A worrywart | Someone who worries excessively | She’s a worrywart and always anticipates the worst. |
| A go-getter | Someone who is ambitious and energetic | He’s a real go-getter and always strives for success. |
| A yes-man | Someone who always agrees with their superior | He’s a yes-man and never challenges the boss’s decisions. |
| A know-it-all | Someone who acts as if they know everything | He’s such a know-it-all and always corrects everyone. |
| A shrinking violet | A shy or timid person | She’s a shrinking violet and doesn’t like to be the center of attention. |
| A social butterfly | Someone who is very social and enjoys flitting from group to group at parties | She’s a social butterfly and knows everyone at the party. |
| A drama queen | Someone who exaggerates their reactions or problems | She’s such a drama queen and always makes a big deal out of small things. |
| A control freak | Someone who tries to control everything and everyone around them | He’s a control freak and always wants things done his way. |
| A complainer | Someone who constantly complains | He’s a complainer and always finds something to whine about. |
| A daredevil | Someone who enjoys taking risks | He’s a daredevil and loves extreme sports. |
Behavior and Action Idioms Examples
This table provides examples of idioms that describe behavior and actions.
| Idiom | Meaning | Example Sentence |
|---|---|---|
| To wear your heart on your sleeve | To openly express your emotions | She wears her heart on her sleeve, so everyone knows how she feels. |
| To stab someone in the back | To betray someone’s trust | He stabbed me in the back by telling my boss about my mistake. |
| To pull someone’s leg | To tease or joke with someone | I was just pulling your leg; I didn’t really win the lottery. |
| To have a short fuse | To get angry easily | He has a short fuse, so be careful what you say to him. |
| To be a pain in the neck | To be annoying or troublesome | My little brother is such a pain in the neck. |
| To be a backseat driver | Someone who constantly gives unwanted advice or instructions | My mother is a backseat driver, always telling me how to drive. |
| To be a copycat | Someone who imitates others | She’s such a copycat, always copying my style. |
| To be a know-it-all | Someone who acts as if they know everything | He’s such a know-it-all, always correcting everyone. |
| To be a pushover | Someone who is easily persuaded or taken advantage of | He’s a pushover and always agrees to do things he doesn’t want to do. |
| To be a show-off | Someone who tries to impress others with their abilities or possessions | He’s such a show-off, always bragging about his achievements. |
| To be a troublemaker | Someone who causes problems or difficulties | He’s a troublemaker and always gets into fights. |
| To be an attention seeker | Someone who tries to get attention | She’s an attention seeker and always does things to get noticed. |
| To be full of hot air | To talk a lot without saying anything meaningful | He’s full of hot air and never delivers on his promises. |
| To be on cloud nine | To be extremely happy | She’s been on cloud nine since she got engaged. |
| To be down in the dumps | To be sad or depressed | He’s been down in the dumps since he lost his job. |
| To be green with envy | To be very jealous | She was green with envy when she saw my new car. |
| To be in the doghouse | To be in trouble or out of favor | He’s in the doghouse with his wife after forgetting their anniversary. |
| To be sitting pretty | To be in a comfortable or advantageous situation | After getting the promotion, she’s sitting pretty. |
| To be walking on eggshells | To be very careful not to offend someone | I have to walk on eggshells around my boss because he’s so sensitive. |
| To fly off the handle | To suddenly become very angry | He flew off the handle when I told him I crashed his car. |
| To get a kick out of something | To find something amusing or enjoyable | I get a kick out of watching funny cat videos. |
| To get your act together | To start behaving responsibly | It’s time for you to get your act together and start taking your studies seriously. |
| To let your hair down | To relax and enjoy yourself | After a long week of work, it’s nice to let your hair down and have some fun. |
| To make waves | To cause trouble or disruption | He’s always making waves at work by challenging the management. |
| To march to the beat of your own drum | To do things your own way, regardless of what others think | She’s always marched to the beat of her own drum and never followed the crowd. |
Relationship Idioms Examples
This table provides examples of idioms that describe relationships.
| Idiom | Meaning | Example Sentence |
|---|---|---|
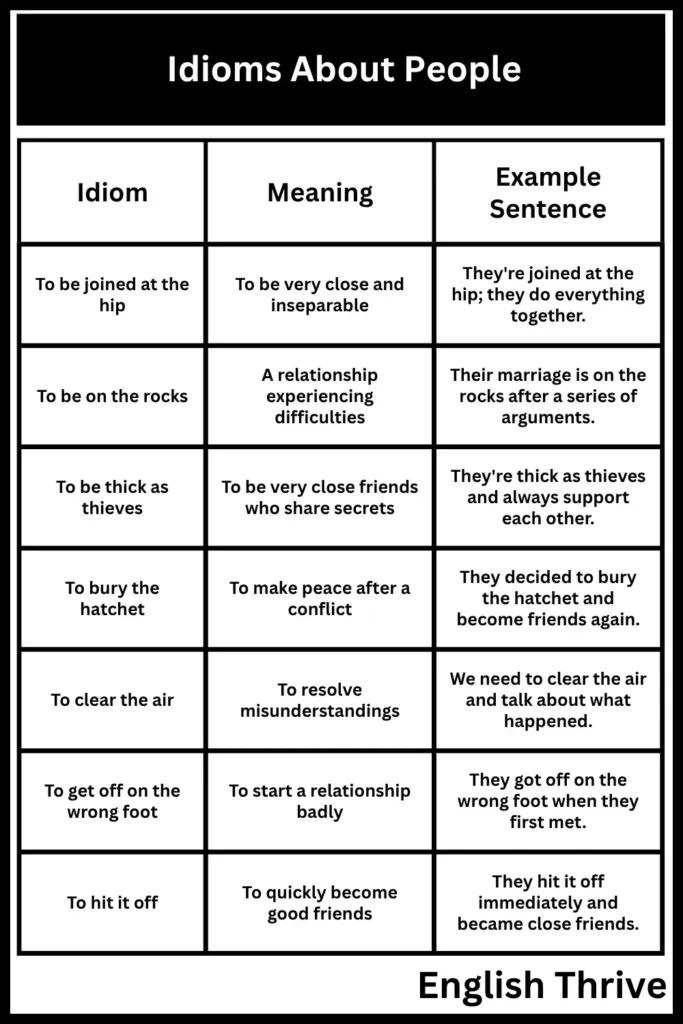
| To be joined at the hip | To be very close and inseparable | They’re joined at the hip; they do everything together. |
| To be on the rocks | A relationship experiencing difficulties | Their marriage is on the rocks after a series of arguments. |
| To be thick as thieves | To be very close friends who share secrets | They’re thick as thieves and always support each other. |
| To bury the hatchet | To make peace after a conflict | They decided to bury the hatchet and become friends again. |
| To clear the air | To resolve misunderstandings | We need to clear the air and talk about what happened. |
| To get off on the wrong foot | To start a relationship badly | They got off on the wrong foot when they first met. |
| To hit it off | To quickly become good friends | They hit it off immediately and became close friends. |
| To be like two peas in a pod | To be very similar | They are like two peas in a pod and have many things in common. |
| To be at each other’s throats | To argue a lot | They are always at each other’s throats and can’t seem to agree on anything. |
| To have a soft spot for someone | To feel affection for someone | She has a soft spot for her younger brother. |
| To have someone’s back | To support someone | I always have your back, no matter what. |
| To see eye to eye | To agree | They rarely see eye to eye on political issues. |
| To turn your back on someone | To abandon someone | He turned his back on his friends when he became famous. |
| To wear the pants in the family | To be the dominant person in the relationship | She wears the pants in their family. |
| To be tied to someone’s apron strings | To be overly dependent on someone | He’s still tied to his mother’s apron strings. |
| To keep someone at arm’s length | To avoid being too close to someone | She keeps everyone at arm’s length because she’s afraid of getting hurt. |
| To get under someone’s skin | To annoy someone | He really gets under my skin sometimes. |
| To be in someone’s good books | To be in favor with someone | I’m trying to get in my boss’s good books. |
| To twist someone around your little finger | To easily manipulate someone | She can twist him around her little finger. |
| To be a shoulder to cry on | Someone who provides emotional support | She’s always been a shoulder to cry on for me. |
| To be on the same wavelength | To understand each other easily | They are on the same wavelength and work well together. |
| To be two-faced | To be insincere and deceitful | I don’t trust him; he’s two-faced. |
| To build bridges | To improve relationships | We need to build bridges between our two departments. |
| To burn bridges | To damage relationships irreparably | He burned bridges when he left the company. |
| To go Dutch | To split the bill equally | Let’s go Dutch on dinner tonight. |
Skills and Abilities Idioms Examples
This table provides examples of idioms that describe skills and abilities.
| Idiom | Meaning | Example Sentence |
|---|---|---|
| To have a green thumb | To be skilled at gardening | She has a green thumb; her garden is beautiful. |
| To be all thumbs | To be clumsy or inept | I’m all thumbs when it comes to fixing things. |
| To have an ear for music | To be good at recognizing and reproducing musical sounds | He has an ear for music and can play any instrument. |
| To have a way with words | To be skilled at speaking or writing | She has a way with words and can write compelling stories. |
| To have a head for numbers | To be good at mathematics | He has a head for numbers and excels in accounting. |
| To be quick on the uptake | To understand things quickly | She’s quick on the uptake and learns new things easily. |
| To be slow on the uptake | To understand things slowly | He’s slow on the uptake and needs things explained multiple times. |
| To be a jack-of-all-trades | Someone who can do many different jobs | He’s a jack-of-all-trades and can fix anything around the house. |
| To be a master of none | Someone who is good at many things but excellent at nothing | He’s a jack-of-all-trades, but a master of none. |
| To be a whiz | To be very good at something | She’s a whiz at computer programming. |
| To be rusty | To have lost skill due to lack of practice | My piano skills are rusty because I haven’t played in years. |
| To be out of practice | To have lost skill due to lack of practice | I’m out of practice with my Spanish after not using it for so long. |
| To be on the ball | To be alert and competent | She’s always on the ball and gets things done efficiently. |
| To be a natural | To have a natural talent for something | He’s a natural at playing the guitar. |
| To be gifted | To have exceptional talent | She’s a gifted artist. |
| To be sharp as a tack | To be very intelligent | He’s sharp as a tack and always knows the answer. |
| To be streets ahead | To be much more advanced than others | Their technology is streets ahead of the competition. |
| To have a knack for something | To have a natural skill for something | She has a knack for languages. |
| To be a quick study | To learn quickly | He’s a quick study and picked up the new software easily. |
| To be a slow learner | To learn slowly | He’s a slow learner and needs extra help. |
| To have a silver tongue | To be persuasive and eloquent | He has a silver tongue and can convince anyone of anything. |
| To know something like the back of your hand | To be very familiar with something | I know this city like the back of my hand. |
| To learn the ropes | To learn how to do something | It takes time to learn the ropes in a new job. |
| To pick something up quickly | To learn something easily | She picks up new languages quickly. |
| To get the hang of something | To learn how to do something | It took me a while to get the hang of riding a bike. |
Age and Life Stage Idioms Examples
This table provides examples of idioms that describe age and life stages.
| Idiom | Meaning | Example Sentence |
|---|---|---|
| To be wet behind the ears | To be young and inexperienced | He’s wet behind the ears and doesn’t know much about the world. |
| Over the hill | Past one’s prime | Some people think he’s over the hill, but he’s still going strong. |
| Young at heart | To have a youthful spirit despite being old | She’s 80 years old, but she’s still young at heart. |
| In the prime of life | At the best stage of one’s life | He’s in the prime of his life and enjoying every moment. |
| In your salad days | In your youth | In my salad days, I used to travel the world. |
| Middle-aged spread | Weight gain in middle age | He’s starting to get a middle-aged spread. |
| Golden years | Retirement years | They are enjoying their golden years traveling and relaxing. |
| Second childhood | Behaving like a child in old age | He’s in his second childhood and loves playing with toys. |
| Old as the hills | Very old | That joke is as old as the hills. |
| Not a day over | Looking younger than one’s age | She doesn’t look a day over thirty. |
| Coming of age | Reaching adulthood | The movie is about a young boy coming of age. |
| The baby of the family | The youngest child in the family | She’s the baby of the family and gets special treatment. |
| An old soul | Someone who seems wise beyond their years | She’s an old soul and gives good advice. |
| Life begins at forty | Life gets better after forty | He believes life begins at forty. |
| Born yesterday | Naive or easily deceived | I wasn’t born yesterday; I know what you’re up to. |
| Cutting your teeth | Gaining initial experience | I’m cutting my teeth in the industry. |
| Over the hill and far away | Past one’s prime and irrelevant | He’s over the hill and far away, so his opinions don’t matter anymore. |
| In the autumn of one’s years | In old age | He’s in the autumn of his years and enjoying a peaceful life. |
| A spring chicken | A young person | She’s not exactly a spring chicken anymore. |
| In the twilight years | In the final years of life | They are enjoying their twilight years together. |
| To get a new lease on life | To experience renewed energy or purpose | After retiring, he got a new lease on life. |
| To be past it | To be too old to do something | He’s past it and can’t keep up with the younger players. |
| To be green | To be young and inexperienced | He’s still green and needs more training. |
| To have one foot in the grave | To be near death | He has one foot in the grave and isn’t expected to live much longer. |
| To turn over a new leaf | To start behaving in a better way | He decided to turn over a new leaf and quit drinking. |
Usage Rules for Idioms About People
Using idioms correctly requires understanding their specific meanings and contexts. Here are some key rules to follow:
- Context is Key: Always consider the context in which you are using an idiom. The meaning of an idiom can change depending on the situation.
- Word Order: Many idioms have a fixed word order that cannot be changed without altering their meaning.
- Verb Tense: Some idioms allow for changes in verb tense, while others do not. Be mindful of the correct tense usage.
- Pronoun Usage: When using idioms that involve pronouns, ensure that the pronouns agree with the subject of the sentence.
- Cultural Sensitivity: Be aware that some idioms may be culturally specific and may not be understood or appreciated by everyone.
It’s important to note that while some idioms allow for slight variations, such as changing the verb tense, others are rigid and must be used exactly as they are. For example, you can say “He pulled my leg” or “I was pulling your leg,” but you cannot change the core components of the idiom without losing its meaning.
Understanding these nuances comes with practice and exposure to the language.
Common Mistakes When Using Idioms About People
One of the most common mistakes is taking idioms literally. Because idioms are figurative expressions, understanding the intended meaning is crucial.
Another common error is misusing the words within an idiom or altering the word order, which can change the meaning or make the expression nonsensical. Here are some examples of common mistakes and their corrections:
| Incorrect | Correct | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| She has a golden heart. | She has a heart of gold. | The correct phrase is “heart of gold,” not “golden heart.” |
| He stabbed me in the face. | He stabbed me in the back. | The correct idiom is “stab someone in the back,” meaning to betray someone. |
| I was moving your leg. | I was pulling your leg. | The idiom is “pull someone’s leg,” meaning to tease or joke with someone. |
| He has a short light. | He has a short fuse. | The correct idiom is “short fuse,” referring to someone who gets angry easily. |
| They are connected at the hip. | They are joined at the hip. | The correct idiom is “joined at the hip,” meaning very close and inseparable. |
| Their marriage is on the stones. | Their marriage is on the rocks. | The correct idiom is “on the rocks,” meaning experiencing difficulties. |
| She has a green finger. | She has a green thumb. | The correct idiom is “green thumb,” meaning skilled at gardening. |
| He is all hands. | He is all thumbs. | The correct idiom is “all thumbs,” meaning clumsy or inept. |
Another frequent mistake is using idioms in inappropriate contexts. For example, using a very informal idiom in a formal presentation can be jarring.
Always consider your audience and the formality of the situation when choosing idioms.
Practice Exercises
These exercises will help you practice using idioms about people correctly. Each exercise focuses on a different aspect of idiom usage, from identifying idioms to using them in context.
Exercise 1: Identifying Idioms
Identify the idiom in each sentence
and explain its meaning.
- He’s such a couch potato; he never leaves the house.
- She always wears her heart on her sleeve, which makes her vulnerable.
- They’re thick as thieves and share all their secrets.
- He’s quick on the uptake and learns new things easily.
- She’s still wet behind the ears and needs more experience.
Exercise 2: Using Idioms in Context
Fill in the blank with the appropriate idiom from the list below.
Idiom List:
- a heart of gold
- stabbed me in the back
- pulling your leg
- short fuse
- on cloud nine
- I was just ________ when I said I won the lottery; it was a joke.
- She has ________; she’s always helping those in need.
- He ________ by telling my boss about my mistake.
- She’s been ________ since she got engaged.
- He has a ________, so be careful what you say to him.
Exercise 3: Matching Idioms to Definitions
Match each idiom with its correct definition.
- To be a pain in the neck
- To be on the ball
- To fly off the handle
- To get a kick out of something
- To get your act together
Definitions:
- To find something amusing or enjoyable
- To start behaving responsibly
- To suddenly become very angry
- To be annoying or troublesome
- To be alert and competent
FAQs About Idioms About People
What is the difference between an idiom and a proverb?
An idiom is a phrase whose meaning is different from the literal meaning of its words, while a proverb is a short, well-known saying that expresses a general truth or piece of advice.
How can I improve my understanding of idioms?
Read widely, listen to native speakers, and practice using idioms in context. Keep a notebook of new idioms and review them regularly.
Are idioms the same in all English-speaking countries?
No, idioms can vary between different English-speaking countries. Some idioms are specific to certain regions or cultures.
Is it okay to use idioms in formal writing?
It depends on the context and audience. In general, it’s best to avoid very informal idioms in formal writing.
Choose idioms that are appropriate for the tone and style of your writing.
How can I avoid misusing idioms?
Pay attention to the context, understand the specific meaning of the idiom, and practice using it correctly. If you’re unsure, it’s better to avoid using the idiom altogether.
Conclusion
Mastering idioms about people is a valuable skill for anyone learning English. By understanding their definitions, structures, and usage rules, you can enhance your comprehension, improve your communication, and add color and depth to your language.
Remember to practice regularly, pay attention to context, and be mindful of common mistakes. With dedication and effort, you can become proficient in using idioms about people and express yourself with greater fluency and accuracy.
Keep exploring, keep practicing, and enjoy the richness and diversity of the English language!