The animal kingdom is full of incredible diversity, and today we’re exploring some of its most fascinating members—animals that start with L. From the powerful lion to the playful lemur, these creatures show just how rich and varied life on Earth can be.
In this guide, you’ll discover the names, scientific classifications, habitats, and diets of 50 unique species that begin with the letter L. Whether you’re a student, wildlife enthusiast, or ESL learner, this article will help you appreciate nature’s variety while expanding your vocabulary and knowledge.
Contents
ToggleWhy Learn About Animals That Start With L?
Studying animals by their alphabetical names isn’t just fun—it’s educational! It helps learners recognize patterns in language, remember scientific names, and understand how different species adapt to their environments. Each animal on this list plays an important role in its ecosystem—from top predators to tiny insects that keep nature in balance.
List of 50 Animals That Start With L
| Common Name | Scientific Name |
|---|---|
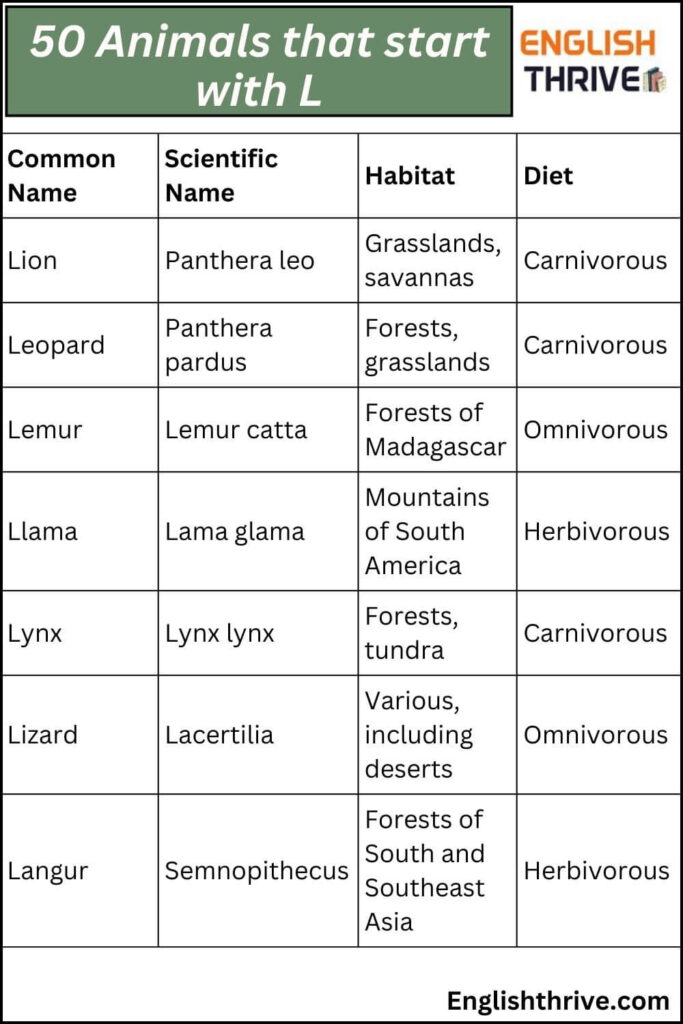
| Lion | Panthera leo |
| Leopard | Panthera pardus |
| Lemur | Lemur catta |
| Llama | Lama glama |
| Lynx | Lynx lynx |
| Lizard | Lacertilia |
| Langur | Semnopithecus |
| Loris | Loris tardigradus |
| Lobster | Homarus americanus |
| Lovebird | Agapornis |
| Loon | Gavia immer |
| Leaf-tailed Gecko | Uroplatus |
| Ladybug | Coccinella septempunctata |
| Lamprey | Petromyzontidae |
| Leech | Hirudinea |
| Lancelet | Branchiostoma |
| Lappet-faced Vulture | Torgos tracheliotos |
| Lark | Alauda arvensis |
| Leafcutter Ant | Atta |
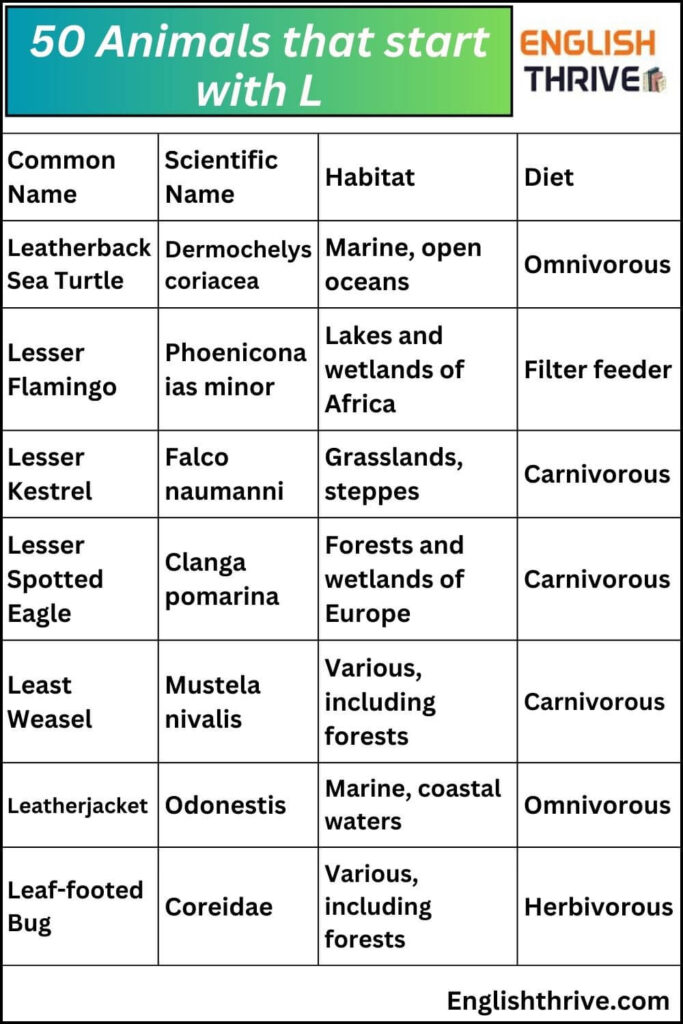
| Leatherback Sea Turtle | Dermochelys coriacea |
| Lesser Flamingo | Phoeniconaias minor |
| Leaf-nosed Bat | Phyllostomidae |
| Leaf Insect | Phylliidae |
| Least Weasel | Mustela nivalis |
| Leatherjacket | Odonestis |
| Leaf Warbler | Phylloscopus |
| Leaf Beetle | Chrysomelidae |
| Leaf-footed Bug | Coreidae |
| Leaf-eared Mouse | Phyllotis |
| Leaf-cutting Bee | Megachile |
| Leafhopper | Cicadellidae |
| Leaf-nosed Snake | Phyllorhynchus |
| Leaf-tailed Salamander | Anaptomecum |
| Leaf-footed Lizard | Sphaerodactylus |
| Langur Monkey | Presbytis entellus |
| Leaf Dragon | Hypsilurus |
| Leaf-nosed Bat | Hipposideros |
| Leaf-tailed Dragon | Gonocephalus |
| Leaf-tailed Gecko (Australia) | Saltuarius |
| Leaf-footed Mouse | Peromyscus |
| Leaf-eared Seal | Phocarctos hookeri |
| Leaf-nosed Lizard | Phrynosoma |
| Leaf-nosed Viper | Bothriechis |
| Leaf-tailed Gecko (Madagascar) | Uroplatus fimbriatus |
| Leaf-eating Caterpillar | Various species |
| Leaf-nosed Bat | Hipposideros |
| Leaf-tailed Dragon (Pacific) | Hypsilurus |
| Leaf-tailed Frog | Ascaphus |
| Leaf-tailed Dragon (Australia) | Hypsilurus |
| Leaf-tailed Gecko (Pacific) | Uroplatus fimbriatus |
| Leaf-footed Bug | Coreidae |
Interesting Facts About Animals That Start With L
Lions—The Kings of the Grasslands
Lions are social big cats that live in family groups called prides. Males protect their territory while females hunt cooperatively. Sadly, due to habitat loss and human conflict, lions are now classified as vulnerable by the IUCN.
Leopards—Masters of Camouflage
Leopards can survive almost anywhere—forests, deserts, or even near cities. Their spotted coat helps them hide while hunting, and their strength allows them to drag heavy prey into trees for safety.
Lemurs—Madagascar’s Gentle Primates
Found only in Madagascar, lemurs are known for their long tails and expressive eyes. They play a key role in spreading seeds, helping forests grow. Many lemur species are endangered due to deforestation.
Llamas—The Friendly Helpers
Domesticated for thousands of years in South America, llamas provide wool, carry loads, and protect livestock. They are gentle, intelligent, and well-adapted to high mountain climates.
Lynx—Silent Hunters of the Snow
The lynx is a solitary cat with tufted ears and thick fur that blends into snowy forests. It preys mainly on hares and small mammals and plays an essential part in maintaining ecosystem balance.
FAQs on Animals Starting With L
1. What are some famous animals that start with L?
Some popular examples include lion, leopard, lemur, llama, lynx, lobster, and ladybug. Each represents a different habitat—from the savanna to the sea.
2. Why are lions called the “king of the jungle”?
Even though lions live mostly in grasslands, the title “king of the jungle” refers to their dominance and leadership in the animal kingdom.
3. How do leopards adapt to their surroundings?
Leopards use their spotted coats for camouflage, climb trees to store food safely, and adapt to various climates from forests to deserts.
4. What makes lemurs unique?
Lemurs are found only in Madagascar. They have strong social bonds, communicate with sounds, and help forests regenerate by spreading seeds.
5. How do llamas help humans?
Llamas provide wool, serve as pack animals, and even guard sheep from predators. Their calm nature makes them important in Andean communities.
Conclusion
Exploring animals that start with L shows how every species contributes to nature’s balance. From the mighty lion to the tiny ladybug, each plays a vital role in keeping ecosystems healthy. Learning about them not only deepens our understanding of wildlife but also reminds us of the need to protect their habitats.
Let’s continue discovering more amazing creatures and celebrating the beauty of life on Earth—one letter at a time.