When you think of Animals Starting with D, several fascinating creatures may come to mind—dolphins, dogs, deer, and more. These creatures are not only diverse in their habitat and behavior but also play crucial roles in the ecosystems they inhabit. Whether you’re a student studying biology or just someone fascinated by the animal kingdom, understanding these animals and their unique traits can be both fun and educational. In this article, we’ll take a closer look at a variety of Animals Starting with D, exploring their characteristics, habitats, and importance.
In the following sections, we will break down a list of these animals, provide detailed insights into their biology, and answer some common questions to deepen your understanding. Let’s dive into the fascinating world of Animals Starting with D!
Contents
Toggle50 Animals Starting with D
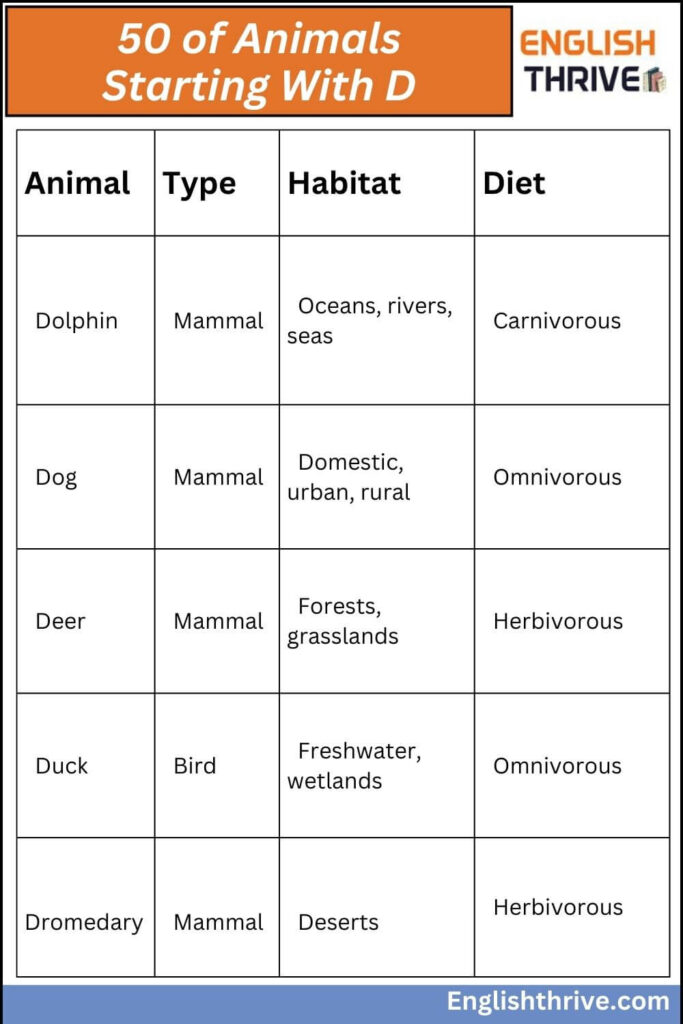
| Animal | Type | Habitat | Diet | Interesting Fact |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dolphin | Mammal | Oceans, rivers, seas | Carnivorous | Known for their intelligence and use of echolocation. |
| Dog | Mammal | Domestic, urban, rural | Omnivorous | The domesticated dog has been a human companion for thousands of years. |
| Deer | Mammal | Forests, grasslands | Herbivorous | Deer shed and regrow their antlers every year. |
| Duck | Bird | Freshwater, wetlands | Omnivorous | Known for their swimming ability, ducks use webbed feet for speed. |
| Dromedary | Mammal | Deserts | Herbivorous | Can survive for several days without water due to fat storage in its hump. |
| Dragonfly | Insect | Wetlands, ponds, lakes | Carnivorous | Known for their incredible agility in flight, including hovering. |
| Dingo | Mammal | Australia (wild) | Carnivorous | A wild dog species known for its independence and hunting skills. |
| Dodo | Extinct Bird | Island of Mauritius | Herbivorous | Became extinct in the late 1600s due to human overhunting. |
| Durrell’s Vontsira | Mammal | Madagascar’s forests | Carnivorous | A rare carnivorous mammal from Madagascar, recently rediscovered. |
| Dassie | Mammal | South Africa (rocky areas) | Herbivorous | Also known as the rock hyrax; genetically closer to elephants than rodents. |
| Duckbill Platypus | Mammal | Australia (waterways) | Carnivorous | One of the few mammals that lay eggs. |
| Dart Frog | Amphibian | Central/South America | Carnivorous | Known for their vibrant colors and toxic skin. |
| Dhole | Mammal | Asia, forested areas | Carnivorous | Social carnivores that live and hunt in packs. |
| Desert Tortoise | Reptile | North American deserts | Herbivorous | Can live for over 50 years and survive extreme heat in the desert. |
| Dogfish Shark | Fish | Oceans | Carnivorous | A small shark species known for its resilience in cold waters. |
| Dartmoor Pony | Mammal | United Kingdom (Dartmoor) | Herbivorous | A hardy, native British pony breed, known for endurance. |
| Dusky Dolphin | Mammal | South Pacific Ocean | Carnivorous | Known for their playful behavior and acrobatic skills. |
| Double-crested Cormorant | Bird | Coastal waters | Carnivorous | Known for diving and fishing, this bird has two crests on its head. |
| Dung Beetle | Insect | Everywhere, especially forests | Herbivorous (feeds on dung) | Dung beetles play a vital role in recycling nutrients in ecosystems. |
| Diprotodon | Extinct Mammal | Australia | Herbivorous | Largest marsupial to have ever lived, similar to giant wombats. |
| Dolly Varden Trout | Fish | Rivers in North America | Carnivorous | A species of salmon found in the colder regions of North America. |
| Devil’s Coach Horse | Insect | Forests, woodlands | Carnivorous | A predatory beetle known for its intimidating appearance. |
| Diamondback Rattlesnake | Reptile | North America (deserts) | Carnivorous (rodents) | Recognizable by its rattle, it uses venom to immobilize prey. |
| Dungfish | Fish | Wetlands, rivers | Carnivorous | Often found in muddy waters, they feed on organic matter. |
| Darkling Beetle | Insect | Deserts, forests | Herbivorous | A resilient beetle that can withstand dry conditions. |
| Dwarf Crocodile | Reptile | West Africa, swamps | Carnivorous | One of the smallest species of crocodiles, found in tropical regions. |
| Damselfish | Fish | Coral reefs, oceans | Herbivorous | Small but aggressive fish that defend territories on coral reefs. |
| Dugong | Mammal | Shallow coastal waters | Herbivorous | A marine mammal closely related to the manatee, with a dolphin-like tail. |
| Dwarf Seahorse | Fish | Warm coastal waters | Herbivorous | One of the smallest seahorse species, known for its unique behavior. |
| Duck-billed Dinosaur | Dinosaur | North America | Herbivorous | An ancient species of dinosaur with a distinctive duck-like bill. |
| Desert Finch | Bird | Deserts | Omnivorous | A small bird that thrives in arid, desert regions. |
| Dartmouth Skipper | Insect | North America | Herbivorous | A butterfly species known for its small size and fast flight. |
| Dromaeosaurus | Dinosaur | North America | Carnivorous | Known for its bird-like features, it is related to modern-day raptors. |
| Drake Mallard | Bird | Freshwater, wetlands | Omnivorous | The male mallard duck is known for its bright green head and vibrant plumage. |
| Dunlin | Bird | Wetlands, coastal regions | Omnivorous | A small shorebird, recognized by its long bill and migratory nature. |
| Desert Iguana | Reptile | Southwestern U.S. deserts | Herbivorous | A desert-dwelling lizard that can withstand extreme heat. |
| Dust Mite | Arachnid | Warm, humid environments | Carnivorous | Tiny creatures that thrive in household dust, feeding on organic matter. |
| Desert Cottontail | Mammal | Southwestern U.S. deserts | Herbivorous | A small, nocturnal rabbit found in dry desert habitats. |
| Douglas-fir Beetle | Insect | Forests | Herbivorous | Known for infesting and damaging Douglas-fir trees. |
| Dwarf Gourami | Fish | Freshwater, Asia | Omnivorous | A colorful freshwater fish popular in aquariums. |
| Dunnock | Bird | Europe, Asia | Insectivorous | A small, nondescript bird, often seen in hedgerows and gardens. |
| Deinonychus | Dinosaur | North America | Carnivorous | A fierce predator and one of the first discovered raptors. |
| Dwarf Pygmy Goat | Mammal | Domestic farms | Herbivorous | A miniature breed of goat known for its friendly nature. |
| Diplodocus | Dinosaur | North America | Herbivorous | A long-necked, long-tailed dinosaur that lived during the Jurassic period. |
| Dryocopus | Bird | Forested areas | Omnivorous | A genus of woodpeckers, including the endangered ivory-billed woodpecker. |
| Dwarf Wall Gecko | Reptile | Europe, Africa | Insectivorous | A small, nocturnal lizard often found in rocky areas. |
| Desert Leopard Gecko | Reptile | Southwestern U.S. deserts | Insectivorous | Known for its adaptability and ability to thrive in arid regions. |
| Diprotodon | Extinct Mammal | Australia | Herbivorous | The largest known marsupial, similar in size to a giant wombat. |
| Dovekie | Bird | Arctic regions | Carnivorous | A small seabird that is well adapted to the frigid northern seas. |
| Dasyure | Mammal | Australia | Carnivorous | A predatory marsupial from the family of quolls. |
| Dendrobatid Frog | Amphibian | Central/South America | Carnivorous | Famous for their bright colors and toxic skin. |
| Demersal Fish | Fish | Ocean floor, deep waters | Omnivorous | A type of fish that lives on or near the seabed. |
| Deep-sea Anglerfish | Fish | Deep ocean | Carnivorous | Known for its bioluminescent lure used to attract prey. |
| Damnified Fish | Fish | Tropical oceans | Carnivorous | A deep-sea predator, known for its terrifying appearance. |
Frequently Asked Questions About Animals Starting with D
1. What are some examples of mammals that start with D?
Several mammals begin with the letter D, each exhibiting unique traits. Some well-known examples include:
Dolphins: These marine mammals are known for their high intelligence and social behavior. They are found in oceans and rivers worldwide and use echolocation to hunt.
Dogs: Arguably the most famous mammal that starts with D, dogs have been domesticated for thousands of years. Known for their loyalty, dogs vary in breeds, size, and behavior, making them perfect companions in almost every environment.
Deer: These herbivores are found in forests and grasslands around the world. Male deer typically grow antlers, which they shed each year. Species like the white-tailed deer and moose are common examples.
Dromedary: Also known as the Arabian camel, these large mammals thrive in hot desert environments. They can survive without water for several days, thanks to their ability to store fat in their humps.
These animals represent a broad range of habitats, from forests and grasslands to deserts and oceans, and they each play an important role in their ecosystems.
2. Are there any birds that start with D?
Yes, there are birds that start with D! Some of the most interesting include:
Ducks: These waterfowl are found in freshwater bodies like ponds, lakes, and rivers. They have webbed feet for swimming and a varied diet that includes plants, insects, and small fish. Some species, like the mallard duck, are commonly found in gardens and parks.
Dodo: Though now extinct, the Dodo was a flightless bird that lived on the island of Mauritius. The Dodo became extinct in the late 1600s, largely due to human activity such as hunting and the introduction of invasive species.
These birds highlight the diversity within the avian world, from the adaptable and ubiquitous duck to the tragic extinction of the Dodo.
3. What is a Dromedary, and how is it different from a regular camel?
The Dromedary is a type of camel that is native to the Middle East and parts of North Africa. Unlike the Bactrian camel, which has two humps, the dromedary has only one. This hump is not used for storing water, as commonly believed, but for storing fat. In arid environments, the dromedary can survive for extended periods without water, relying on the fat reserves in its hump for energy.
Dromedaries are often used as pack animals and are well-suited for desert life due to their ability to withstand extreme temperatures and go without water for days. Their long legs, narrow hooves, and thick coats help them navigate the desert terrain effectively.
4. Why are dolphins considered to be highly intelligent animals?
Dolphins are considered one of the most intelligent animals on Earth. This intelligence is demonstrated in several ways:
- Echolocation: Dolphins use sound waves to locate objects and prey, a skill that requires advanced cognitive abilities.
- Social Structure: Dolphins live in complex social groups known as pods. They engage in cooperative hunting, play, and communication, all of which require problem-solving skills.
- Tool Use: Some species of dolphins have been observed using tools, such as sponges, to protect their snouts while foraging on the ocean floor.
Studies have shown that dolphins can recognize themselves in mirrors, a trait that is often associated with higher intelligence. Their ability to learn, adapt, and communicate makes them a fascinating example of animal cognition.
5. What is the significance of the Dodo’s extinction?
The extinction of the Dodo in the late 1600s is often seen as a cautionary tale about the impact of human activity on wildlife. Native to the island of Mauritius, the Dodo evolved in isolation, having no natural predators. However, when humans arrived on the island, they brought with them invasive species, such as rats, pigs, and monkeys, which disrupted the delicate ecosystem.
The Dodo’s extinction highlights the dangers of introducing non-native species into fragile environments. It also serves as an early example of how human colonization has led to the destruction of unique and irreplaceable species. Despite its extinction, the Dodo remains a symbol of both the wonder and the fragility of biodiversity.
Conclusion
Animals that start with D encompass a wide range of species, each with its own unique characteristics and importance in the natural world. From the playful dolphin to the extinct dodo, these creatures capture our imagination and highlight the beauty and complexity of life on Earth. Understanding these animals helps us appreciate the diversity of life and the role each species plays in maintaining balance within ecosystems.
Whether you are fascinated by the adaptability of the dromedary or intrigued by the mystery surrounding extinct species like the dodo, there’s always something new to learn. As we continue to explore the animal kingdom, it’s crucial to remain mindful of how human activity impacts these creatures and to work toward preserving their habitats.
By better understanding animals that start with D, we gain a deeper appreciation for the wonders of nature. Always keep your curiosity alive—it’s the key to unlocking the endless mysteries of the animal world.