Tenses are one of the most important parts of English grammar. They help us understand when an action happens – in the present, past or future. The sentences we speak or write use a tense that shows time and meaning.
Whether you’re learning English for an exam, communicating or improving your writing, understanding verb tenses will make your sentences clearer and more accurate.
In this complete guide, we’ll provide examples of present past and future tense and explore the three main tenses in English – present, past and future – with simple explanations.
Contents
ToggleWhat Is a Verb Tense in English Grammar?
A verb tense shows the time of an action or event. English has three basic tenses — Present, Past, and Future — and each tense has four forms, making 12 total tenses.
| Tense Type | Structure | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Present | Subject + Verb (base form) | I walk to school. |
| Past | Subject + Verb (past form) | I walked to school. |
| Future | Subject + will/shall + Verb | I will walk to school. |
Each tense helps you describe what happened, what is happening, or what will happen.
Let’s get start to learning examples of present, past and future tenses:
1. Present Tense Examples
The Present Tense describes actions happening now, things that happen regularly, or facts that are always true.
There are four forms of the Present Tense:
1️⃣ Simple Present
2️⃣ Present Continuous
3️⃣ Present Perfect
4️⃣ Present Perfect Continuous
Let’s look at each one with clear sentence examples:
A. Simple Present Tense
Structure: Subject + base verb (+ s/es for third person singular)
Use: To express habits, routines, general truths, or fixed arrangements.
Examples:
- I read books every evening.
- She plays the piano beautifully.
- They go to school by bus.
- The sun rises in the east.
- We eat breakfast at 8 a.m.
- He teaches English at a local school.
- My parents live in London.
- Dogs bark loudly at night.
- It rains a lot in winter.
- You look tired today.
B. Present Continuous Tense
Structure: am/is/are + verb + ing
Use: To describe actions happening right now or around this moment.
Examples:
- I am writing an article.
- She is cooking dinner for her family.
- We are watching a movie together.
- They are building a new bridge.
- He is reading his favorite novel.
- The children are playing football in the park.
- It is raining heavily outside.
- My brother is learning to drive.
- I am studying for my exam.
- The birds are singing beautifully.
C. Present Perfect Tense
Structure: has/have + past participle
Use: To describe actions that started in the past but continue or have relevance in the present.
Examples:
- I have finished my homework.
- She has visited Paris twice.
- We have known each other for years.
- They have already left for the airport.
- He has worked here since 2010.
- The teacher has explained the lesson well.
- I have eaten lunch already.
- She has seen that movie before.
- We have just arrived home.
- He has lost his wallet again.
D. Present Perfect Continuous Tense
Structure: has/have + been + verb + ing
Use: To describe actions that began in the past and are still continuing.
Examples:
- I have been studying English for three years.
- She has been working at this company since June.
- They have been waiting for the bus for half an hour.
- We have been watching TV since morning.
- He has been running every day to stay fit.
2. Past Tense Examples
The Past Tense describes actions or events that already happened.
It can express completed actions, ongoing situations in the past, or actions that happened before another past action.
There are four forms of the Past Tense:
1️⃣ Simple Past
2️⃣ Past Continuous
3️⃣ Past Perfect
4️⃣ Past Perfect Continuous
Let’s explore each with easy examples:
A. Simple Past Tense
Structure: Subject + Verb (past form)
Use: To describe completed actions or habits in the past.
Examples:
- I visited my grandparents last weekend.
- She cooked pasta for dinner yesterday.
- They watched a movie on Friday night.
- He walked to school this morning.
- We studied together after class.
- The teacher gave us homework.
- I forgot my keys at home.
- She cleaned her room last night.
- He worked in a bank for five years.
- They played football after lunch.
B. Past Continuous Tense
Structure: was/were + verb + ing
Use: To describe an action that was happening at a specific time in the past or when another event interrupted it.
Examples:
- I was reading when you called.
- They were watching TV at 8 p.m.
- She was cooking while I was cleaning.
- We were playing cricket yesterday evening.
- He was driving to work when it started raining.
- The students were studying for their exams.
- The dog was barking loudly all night.
- I was writing a letter when the lights went out.
- They were dancing at the party.
- She was sleeping when I arrived home.
C. Past Perfect Tense
Structure: had + past participle
Use: To describe an action that happened before another past action or time.
Examples:
- I had finished my homework before dinner.
- She had already left when we arrived.
- They had built the bridge before the storm hit.
- We had eaten breakfast before going to school.
- He had called me twice before I answered.
- The train had departed before we reached the station.
- I had never seen such a beautiful place before.
- She had completed the project on time.
- We had cleaned the house before the guests came.
- He had forgotten his wallet at home.
D. Past Perfect Continuous Tense
Structure: had + been + verb + ing
Use: To show that an action continued for some time before another past event.
Examples:
- I had been studying for two hours before the exam started.
- She had been working there for a decade before she retired.
- They had been waiting for the bus for 20 minutes.
- We had been traveling all day when we finally reached home.
- He had been practicing guitar for months before his first concert.
3. Future Tense Examples
The Future Tense describes actions or events that will happen later. It is used to express predictions, intentions, plans, and expectations.
There are four forms of the Future Tense:
1️⃣ Simple Future
2️⃣ Future Continuous
3️⃣ Future Perfect
4️⃣ Future Perfect Continuous
Let’s go through each one with simple, real-world examples
A. Simple Future Tense
Structure: will/shall + base verb
Use: To express future actions, decisions, or predictions.
Examples:
- I will visit my cousin tomorrow.
- She will start college next month.
- They will travel to Japan next year.
- He will buy a new car soon.
- We will go to the beach this weekend.
- It will rain this evening.
- The teacher will check our homework tomorrow.
- I will call you after lunch.
- She will help you with your assignment.
- They will meet us at the restaurant at 7 p.m.
B. Future Continuous Tense
Structure: will be + verb + ing
Use: To describe an action that will be in progress at a specific time in the future.
Examples:
- I will be studying at 8 p.m. tonight.
- She will be traveling to London next week.
- They will be waiting for us at the airport.
- He will be working on his project tomorrow afternoon.
- We will be staying at a hotel by the sea.
- The kids will be playing outside after lunch.
- I will be cooking dinner when you arrive.
- She will be attending a meeting all day.
- They will be celebrating their anniversary next Sunday.
- We will be watching the sunset together.
C. Future Perfect Tense
Structure: will have + past participle
Use: To show an action that will be completed before a certain future time.
Examples:
- I will have finished my work by 5 p.m.
- She will have completed her studies by next year.
- They will have reached home before it gets dark.
- We will have eaten dinner by the time you arrive.
- He will have repaired the car by tomorrow.
- The team will have won the match by evening.
- I will have saved enough money to buy a new laptop.
- She will have read all the chapters before the exam.
- They will have built the new bridge by next month.
- We will have left before the rain starts.
D. Future Perfect Continuous Tense
Structure: will have been + verb + ing
Use: To describe an action that will continue up to a point in the future.
Examples:
- I will have been working here for five years next June.
- She will have been studying for two hours when you call her.
- They will have been traveling for ten hours by midnight.
- He will have been living in New York for a decade by 2030.
- We will have been waiting for over an hour when the bus arrives.
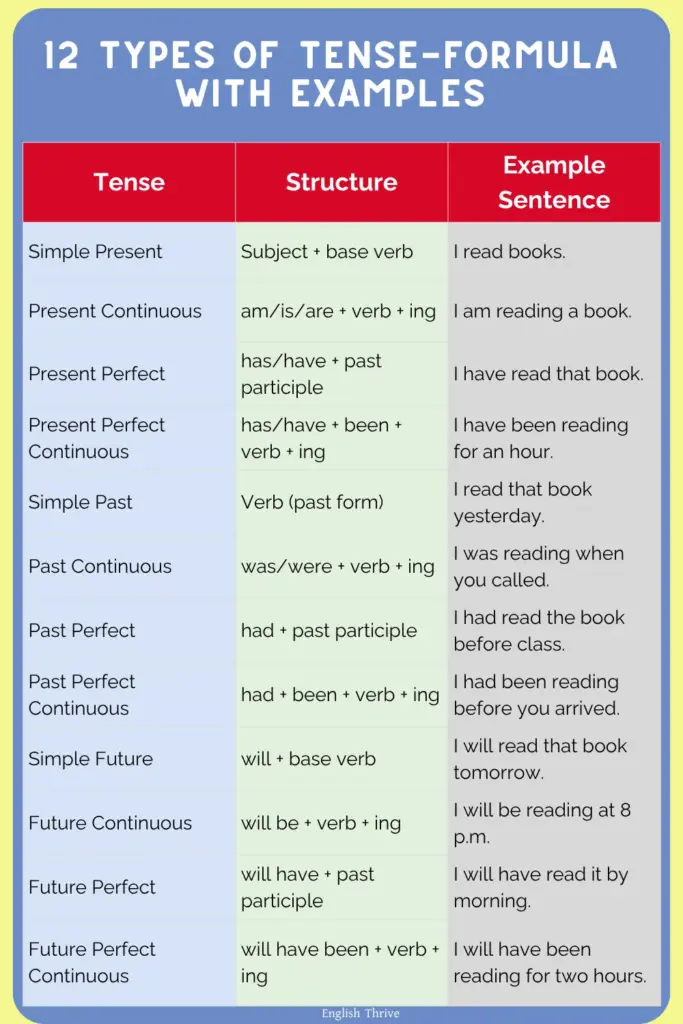
12 Types of Tense with Examples and Formula
| Tense | Structure | Example Sentence |
|---|---|---|
| Simple Present | Subject + base verb | I read books. |
| Present Continuous | am/is/are + verb + ing | I am reading a book. |
| Present Perfect | has/have + past participle | I have read that book. |
| Present Perfect Continuous | has/have + been + verb + ing | I have been reading for an hour. |
| Simple Past | Verb (past form) | I read that book yesterday. |
| Past Continuous | was/were + verb + ing | I was reading when you called. |
| Past Perfect | had + past participle | I had read the book before class. |
| Past Perfect Continuous | had + been + verb + ing | I had been reading before you arrived. |
| Simple Future | will + base verb | I will read that book tomorrow. |
| Future Continuous | will be + verb + ing | I will be reading at 8 p.m. |
| Future Perfect | will have + past participle | I will have read it by morning. |
| Future Perfect Continuous | will have been + verb + ing | I will have been reading for two hours. |
Simple Grammar Tips for Mastering Tenses
1. Focus on Time Words
Use time indicators like yesterday, today, tomorrow, for, since, by the time, before, etc., to identify which tense fits best.
2. Practice Daily
Write short diary entries or sentences using all three tenses. For example:
- Today I work on my project.
- Yesterday I worked hard on it.
- Tomorrow I will complete it.
3. Avoid Common Mistakes
- Don’t mix tenses in the same sentence unless necessary.
- Remember subject-verb agreement in the present tense.
- Use “will” for promises or decisions, and “going to” for planned actions.
4. Learn Through Context
Watch English shows, read news articles, or listen to podcasts to see how native speakers naturally use tenses.
Download Free PDF: 100 Examples of Present, Past, and Future Tense
FAQs about Examples of Present Past and Future Tense
1. What are the 12 tenses in English grammar?
There are 12: 4 Present, 4 Past, and 4 Future forms — Simple, Continuous, Perfect, and Perfect Continuous.
2. What are 3 examples of each tense?
Example:
- Present: I read, I am reading, I have read.
- Past: I read, I was reading, I had read.
- Future: I will read, I will be reading, I will have read.
3. What is the easiest way to learn tenses?
Start by learning time signals, sentence patterns, and practicing with short paragraphs daily.
4. Can one sentence use two tenses?
Yes, especially when describing actions that happened at different times. Example: I was cooking when he arrived.
5. Why are tenses important in English?
They clarify when something happens and make communication accurate and professional.
Conclusion
Understanding English tenses helps you express yourself clearly, no matter what you’re saying – past experiences, present moments, or future plans.
By practicing these 100 examples every day, you’ll quickly improve your writing and speaking skills.
“Tenses aren’t just grammar rules – they’re the timeline of your story.”
Keep practicing, be consistent, and soon you’ll be using each tense naturally and confidently.