In English grammar, the concepts of active and passive voice are essential tools to help express ideas clearly and effectively. Whether you’re writing an academic paper, a business email, or simply communicating with friends, understanding the difference between these two voices is crucial for precise communication.
Contents
ToggleWhat is Active Voice?
In active voice, the subject of the sentence performs the action. This voice is direct, dynamic, and often more straightforward. For example, in the sentence “The teacher explains the lesson,” the subject (the teacher) is actively performing the action of explaining.
What is passive voice?
On the other hand, passive voice emphasizes the action being done to the subject. In passive voice, the object of the action becomes the subject of the sentence. For instance, “The lesson is explained by the teacher” shifts the focus to the lesson being explained rather than the teacher performing the action.
Understanding when to use active or passive voice can help you adjust the tone of your writing. Active voice tends to be more engaging and easier to understand, whereas passive voice is useful when the focus is on the action or when the doer of the action is unknown or irrelevant.
Why Active and Passive Voice Matter
Active voice is often preferred in writing because it is generally clearer, shorter, and more direct. Passive voice, however, can be useful when the action or the result is more important than the person performing it or when the agent is unknown. This is especially important in scientific writing, journalism, and other formal contexts.
In this article, we will explore 100 examples of active and passive voice to help you master the correct usage of these two voices in English. By understanding the rules and seeing numerous examples, you’ll become more adept at switching between the two when necessary.
Differences Between Active and Passive Voice
Understanding the fundamental differences between active and passive voice can help you recognize when each one should be used. Below, we break down these differences for clarity.
Active Voice
- Definition: In active voice, the subject performs the action directly. The sentence follows a straightforward structure: subject + verb + object.
- Example: “She makes dinner.”
- Explanation: The subject (she) is doing the action (making) to the object (dinner).
Passive Voice
- Definition: In passive voice, the action is done to the subject. The focus shifts to the action itself or the recipient of the action. The sentence structure follows: subject + verb (in past participle) + by + agent.
- Example: “Dinner is made by her.”
- Explanation: Here, the subject (Dinner) is receiving the action (made) from the agent (her).
When to Use Active vs. Passive Voice
While active voice is often the preferred choice for clear and direct communication, passive voice can be useful in certain contexts. Here are a few scenarios where each voice may be more appropriate:
- Active voice is best when:
- You want to highlight the subject (the person performing the action).
- The sentence is focused on clarity and brevity.
- The subject is important and must be emphasized.
- Passive voice is best when:
- The focus is on the action or the object, not the subject.
- The subject performing the action is unknown, unimportant, or deliberately omitted.
- You want to create a formal or objective tone.
Example Comparison: Active vs. Passive
| Active Voice | Passive Voice |
|---|---|
| She reads the book. | The book is read by her. |
| He fixes the car. | The car is fixed by him. |
| They write the report. | The report is written by them. |
| We play the game. | The game is played by us. |
In the active voice examples, the subjects (She, He, They, We) perform the actions directly. In the passive voice examples, the action is done to the object (book, car, report, game), and the focus shifts to the object rather than the subject performing the action.
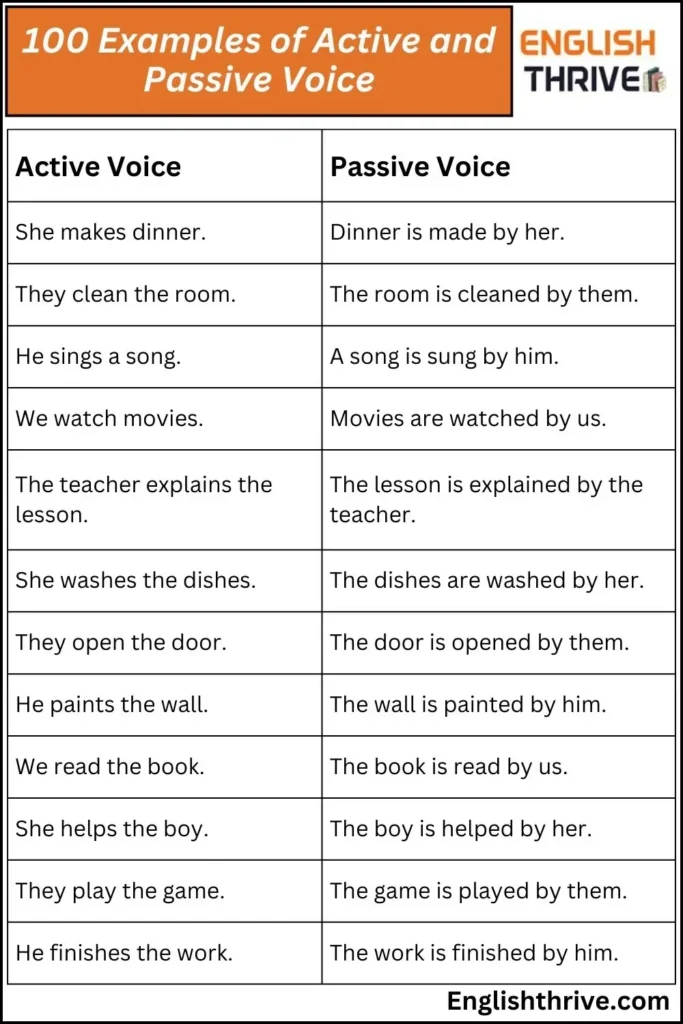
100 Examples of Active and Passive Voice
In this section, we’ll present 100 examples of active and passive voice to showcase the differences and help you practice using both voices. These examples cover a wide range of everyday actions, making it easier to recognize where and how active and passive voice are applied.
| Active Voice | Passive Voice |
|---|---|
| She makes dinner. | Dinner is made by her. |
| They clean the room. | The room is cleaned by them. |
| He sings a song. | A song is sung by him. |
| We watch movies. | Movies are watched by us. |
| The teacher explains the lesson. | The lesson is explained by the teacher. |
| She washes the dishes. | The dishes are washed by her. |
| They open the door. | The door is opened by them. |
| He paints the wall. | The wall is painted by him. |
| We read the book. | The book is read by us. |
| She helps the boy. | The boy is helped by her. |
| They play the game. | The game is played by them. |
| He finishes the work. | The work is finished by him. |
| We start the meeting. | The meeting is started by us. |
| She sends the email. | The email is sent by her. |
| They visit the park. | The park is visited by them. |
| He fixes the car. | The car is fixed by him. |
| We answer the question. | The question is answered by us. |
| She catches the ball. | The ball is caught by her. |
| They build the house. | The house is built by them. |
| He delivers the package. | The package is delivered by him. |
| We light the candle. | The candle is lit by us. |
| She waters the plants. | The plants are watered by her. |
| They write the story. | The story is written by them. |
| He teaches the class. | The class is taught by him. |
| We bake the cake. | The cake is baked by us. |
| She answers the phone. | The phone is answered by her. |
| They pack the bags. | The bags are packed by them. |
| He drives the car. | The car is driven by him. |
| We close the window. | The window is closed by us. |
| She decorates the room. | The room is decorated by her. |
| They solve the problem. | The problem is solved by them. |
| He repairs the bike. | The bike is repaired by him. |
| We organize the event. | The event is organized by us. |
| She buys the groceries. | The groceries are bought by her. |
| They sweep the floor. | The floor is swept by them. |
| He kicks the ball. | The ball is kicked by him. |
| We post the letter. | The letter is posted by us. |
| She folds the clothes. | The clothes are folded by her. |
| They record the video. | The video is recorded by them. |
| He catches the thief. | The thief is caught by him. |
| We fix the fence. | The fence is fixed by us. |
| She cooks the dinner. | The dinner is cooked by her. |
| They draw the picture. | The picture is drawn by them. |
| He mails the letter. | The letter is mailed by him. |
| We find the keys. | The keys are found by us. |
| She sells the car. | The car is sold by her. |
| They open the shop. | The shop is opened by them. |
| He meets the manager. | The manager is met by him. |
| We drive the truck. | The truck is driven by us. |
| She cleans the mirror. | The mirror is cleaned by her. |
| They arrange the chairs. | The chairs are arranged by them. |
| He repairs the watch. | The watch is repaired by him. |
| We lock the door. | The door is locked by us. |
| She sings the song. | The song is sung by her. |
| They deliver the mail. | The mail is delivered by them. |
| He lights the fire. | The fire is lit by him. |
| We enjoy the show. | The show is enjoyed by us. |
| She carries the bag. | The bag is carried by her. |
| They fill the forms. | The forms are filled by them. |
| He lifts the box. | The box is lifted by him. |
| We open the gate. | The gate is opened by us. |
| She buys the flowers. | The flowers are bought by her. |
| They drive the van. | The van is driven by them. |
| He reads the email. | The email is read by him. |
| We start the car. | The car is started by us. |
| She cooks the rice. | The rice is cooked by her. |
| They fix the pipe. | The pipe is fixed by them. |
| He trims the hedge. | The hedge is trimmed by him. |
| We polish the shoes. | The shoes are polished by us. |
| She arranges the flowers. | The flowers are arranged by her. |
| They update the report. | The report is updated by them. |
| He decorates the cake. | The cake is decorated by him. |
| We wash the clothes. | The clothes are washed by us. |
| She prints the document. | The document is printed by her. |
| They test the device. | The device is tested by them. |
| He washes the windows. | The windows are washed by him. |
| We repair the roof. | The roof is repaired by us. |
| She picks the flowers. | The flowers are picked by her. |
| They clean the pool. | The pool is cleaned by them. |
| He organizes the files. | The files are organized by him. |
| We wash the dishes. | The dishes are washed by us. |
| She writes the letter. | The letter is written by her. |
| They clean the windows. | The windows are cleaned by them. |
| He paints the house. | The house is painted by him. |
| We help the neighbors. | The neighbors are helped by us. |
| She studies the material. | The material is studied by her. |
| They decorate the room. | The room is decorated by them. |
| He builds the house. | The house is built by him. |
| We answer the questions. | The questions are answered by us. |
| She walks the dog. | The dog is walked by her. |
| They design the poster. | The poster is designed by them. |
| He drives the car. | The car is driven by him. |
| We open the box. | The box is opened by us. |
| She washes the car. | The car is washed by her. |
| They rent the apartment. | The apartment is rented by them. |
| He organizes the event. | The event is organized by him. |
| We clean the kitchen. | The kitchen is cleaned by us. |
| She answers the call. | The call is answered by her. |
| They set up the equipment. | The equipment is set up by them. |
| He cleans the house. | The house is cleaned by him. |
| We make the reservation. | The reservation is made by us. |
| She carries the groceries. | The groceries are carried by her. |
| They fix the roof. | The roof is fixed by them. |
| He prepares the meal. | The meal is prepared by him. |
| We play the game. | The game is played by us. |
| She answers the question. | The question is answered by her. |
| They repair the car. | The car is repaired by them. |
| He sends the letter. | The letter is sent by him. |
| We decorate the cake. | The cake is decorated by us. |
| She folds the clothes. | The clothes are folded by her. |
| They read the book. | The book is read by them. |
| He builds the wall. | The wall is built by him. |
| We order the supplies. | The supplies are ordered by us. |
| She explains the rules. | The rules are explained by her. |
| They prepare the report. | The report is prepared by them. |
| He teaches the lesson. | The lesson is taught by him. |
| We sing the song. | The song is sung by us. |
| She cleans the room. | The room is cleaned by her. |
| They give the gifts. | The gifts are given by them. |
| He fixes the bike. | The bike is fixed by him. |
| We close the door. | The door is closed by us. |
| She buys the gift. | The gift is bought by her. |
| They send the invitation. | The invitation is sent by them. |
| He writes the article. | The article is written by him. |
| We sweep the floor. | The floor is swept by us. |
| She prepares the agenda. | The agenda is prepared by her. |
| They make the decision. | The decision is made by them. |
| He teaches the class. | The class is taught by him. |
| We meet the deadline. | The deadline is met by us. |
| She plays the piano. | The piano is played by her. |
| They eat the cake. | The cake is eaten by them. |
| He starts the project. | The project is started by him. |
| We fix the computer. | The computer is fixed by us. |
| She organizes the schedule. | The schedule is organized by her. |
| They plan the event. | The event is planned by them. |
| He answers the email. | The email is answered by him. |
| We clean the yard. | The yard is cleaned by us. |
| She opens the window. | The window is opened by her. |
| They check the answers. | The answers are checked by them. |
| He carries the bag. | The bag is carried by him. |
| We check the list. | The list is checked by us. |
| She arranges the flowers. | The flowers are arranged by her. |
| They take the pictures. | The pictures are taken by them. |
| He prepares the presentation. | The presentation is prepared by him. |
| We finish the task. | The task is finished by us. |
| She sets the alarm. | The alarm is set by her. |
| They wash the dishes. | The dishes are washed by them. |
Active and Passive Voice in Different Tenses
Both active and passive voice can be used in different tenses, which allows for greater flexibility in expressing ideas. Here, we’ll break down how these voices function in the present, past, and future tenses.
Present Tense
- Active Voice: “She writes the report.”
- Passive Voice: “The report is written by her.”
In the present tense, the structure of both voices remains simple and easy to understand. The active voice focuses on the subject (she), while the passive voice emphasizes the object (the report).
Past Tense
- Active Voice: “He fixed the bike.”
- Passive Voice: “The bike was fixed by him.”
In the past tense, the verb is in its past form (fixed, written, etc.). The passive voice still maintains the same basic structure as in the present, but it shifts the focus from the subject to the object.
Future Tense
- Active Voice: “They will clean the room.”
- Passive Voice: “The room will be cleaned by them.”
In the future tense, passive voice uses “will be” followed by the past participle of the verb. Both voices convey actions that will happen later, but the focus differs.
Why Use Active and Passive Voice?
You may wonder: why not just use one voice consistently? Both active and passive voices serve different purposes, and their use depends on the message you want to convey. Here are a few key points to consider when choosing between active and passive voice:
Benefits of Active Voice
- Clarity: Active voice is generally clearer and easier to understand because the subject performs the action directly.
- Engagement: Sentences in active voice tend to be more dynamic and engaging, making them better suited for casual or persuasive writing.
- Brevity: Active voice sentences are typically shorter, which helps make writing more concise and direct.
Benefits of Passive Voice
- Focus on the Action: Passive voice shifts the focus to the action or the object rather than the subject, which can be useful when the action itself is more important.
- Formal Tone: Passive voice is often used in formal contexts where the agent is either unknown or irrelevant, as in scientific or legal writing.
- Avoiding Responsibility: Sometimes, passive voice is used to avoid assigning responsibility, which can be useful in situations like official statements or reports.
Common Mistakes in Using Active and Passive Voice
While understanding the difference between active and passive voice is important, it’s also crucial to be aware of common mistakes that people often make when using them. By avoiding these errors, you’ll be able to write more clearly and effectively.
Overuse of Passive Voice
One common mistake is the overuse of passive voice. While passive voice has its uses, overusing it can make your writing sound weak and vague. It can lead to longer sentences and a lack of clarity, making it harder for readers to follow your message.
- Mistake: “The report was written by me, and it was submitted by my team.”
- Improved: “I wrote the report and submitted it with my team.”
In the revised sentence, active voice is used to make the sentence clearer and more direct.
Confusing Active and Passive Voice Structures
Sometimes, people accidentally create a sentence structure that mixes active and passive voice, resulting in a confusing or grammatically incorrect sentence.
- Mistake: “The book is read by she.”
- Improved: “She reads the book.” (Active Voice)
The correct structure for passive voice requires the subject to be in the objective case, which in this case is “her,” not “she.” In passive voice, it should be “The book is read by her.”
Using Passive Voice When It’s Unnecessary
While passive voice can be effective in certain situations, it’s often unnecessary when the subject performing the action is clear and important. Choosing active voice instead of passive voice can improve the readability and effectiveness of your writing.
- Mistake: “A decision was made to hire new employees.”
- Improved: “We decided to hire new employees.”
In this example, the passive voice makes the sentence longer and less engaging. Using active voice makes the subject (we) clear and makes the sentence more direct.
How to Convert Active to Passive Voice
Knowing how to switch between active and passive voice is an essential skill for improving your writing style. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to convert sentences from active to passive voice and vice versa.
Converting Active Voice to Passive Voice
- Identify the subject, verb, and object in the sentence.
- Active voice: “The teacher explains the lesson.”
- Move the object of the active sentence to the subject position.
- “The lesson…”
- Change the verb into the past participle form and add a form of “to be” (is, was, etc.).
- “is explained”
- Add “by” and the original subject (if necessary).
- “The lesson is explained by the teacher.”
Now, you have successfully converted an active voice sentence into passive voice: “The lesson is explained by the teacher.”
Converting Passive Voice to Active Voice
- Identify the subject, verb, and object in the sentence.
- Passive voice: “The book is read by Mary.”
- Move the subject of the passive sentence to the object position.
- “Mary…”
- Change the verb back into its active form.
- “reads”
- Complete the sentence with the object.
- “Mary reads the book.”
Now, the passive voice sentence is converted to active voice: “Mary reads the book.”
Conclusion
Mastering the Examples of Active and Passive Voice is a crucial skill for anyone looking to improve their writing in English. Active voice allows for direct, clear communication, while passive voice can be useful in formal writing or when the action itself is the focus rather than the person performing it. By practicing and understanding when to use each voice, you can adjust your tone and style to fit various contexts—whether you’re writing an essay, crafting an email, or creating content for your business.
Remember, the key is to balance both voices effectively. Use active voice when clarity and engagement are a priority, and turn to passive voice when the action or result is more important than the subject performing the action.
With the 100 examples provided in this article, you now have a comprehensive understanding of active and passive voice, along with practical guidance on how to use them.