Ever caught yourself saying “I hurt me” instead of “I hurt myself”? You’re not alone! Understanding reflexive pronouns can be tricky, but they’re essential for clear communication.
Today, we’ll explore comprehensive reflexive pronouns lists with plenty of examples that’ll make mastering them a breeze. Let’s dive into these special pronouns that help us talk about actions we do to ourselves.
Contents
ToggleWhat Are Reflexive Pronouns?
Reflexive pronouns are special pronouns that end in “-self” (singular) or “-selves” (plural). Think of them as mirrors in grammar – they reflect the action back to the subject. When the person doing the action (subject) is the same as the person receiving the action (object), we use reflexive pronouns.
Basic Forms of Reflexive Pronouns
- Singular: myself, yourself, himself, herself, itself
- Plural: ourselves, yourselves, themselves
 39 Reflexive Pronouns Lists Definition Rules and Exercises
39 Reflexive Pronouns Lists Definition Rules and Exercises
Types of Reflexive Pronoun and Usage
1. True Reflexive Use
When the subject and object are the same:
- I taught myself to play guitar.
- She hurt herself while skating.
- The cat licked itself clean.
2. Emphatic Use
To emphasize who did the action:
- I myself checked the documents.
- The president himself attended the meeting.
- They built the house themselves.
3. Object of Preposition
When used after prepositions:
- She was proud of herself.
- They kept the secret to themselves.
- We did it by ourselves.
Common Rules for Using Reflexive Pronouns
Match with Subject
- Always match the reflexive pronoun with the subject:
- John hurt himself (not themselves)
- They helped themselves (not himself)
Avoid Unnecessary Use
- Don’t use reflexive pronouns when simple pronouns work:
- Incorrect: John and myself went to the store
- Correct: John and I went to the store
Distinguish from Intensive Pronouns
- Reflexive: The action reflects back to the subject
- Intensive: Adds emphasis to the subject
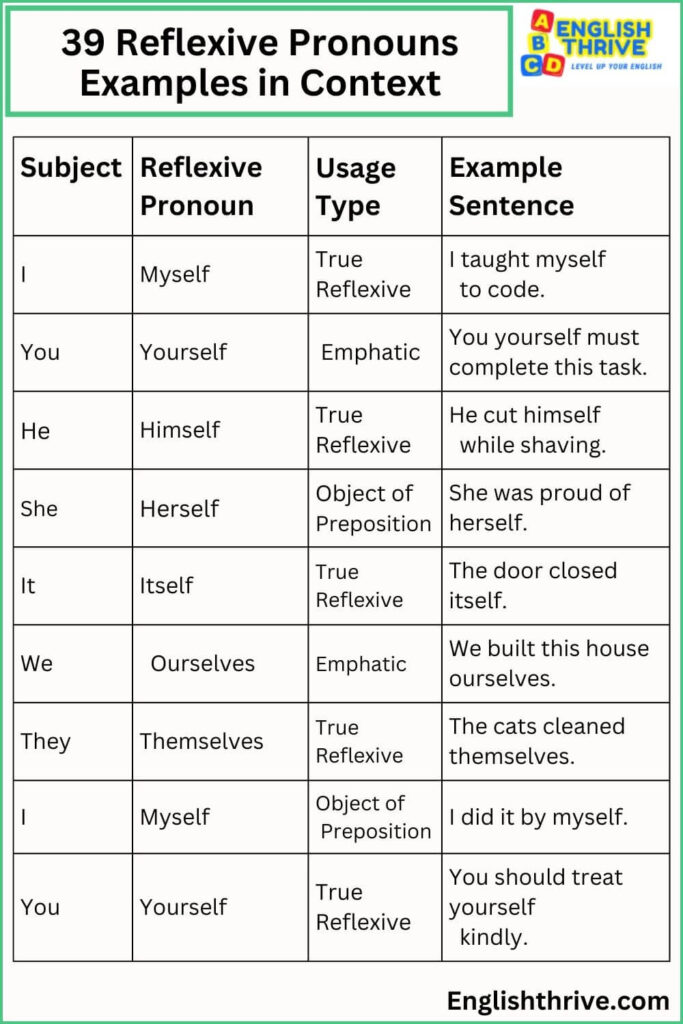
39 Reflexive Pronouns Examples
| Subject | Reflexive Pronoun | Usage Type | Example Sentence |
|---|---|---|---|
| I | Myself | True Reflexive | I taught myself to code. |
| You | Yourself | Emphatic | You yourself must complete this task. |
| He | Himself | True Reflexive | He cut himself while shaving. |
| She | Herself | Object of Preposition | She was proud of herself. |
| It | Itself | True Reflexive | The door closed itself. |
| We | Ourselves | Emphatic | We built this house ourselves. |
| They | Themselves | True Reflexive | The cats cleaned themselves. |
| I | Myself | Object of Preposition | I did it by myself. |
| You | Yourself | True Reflexive | You should treat yourself kindly. |
| He | Himself | Emphatic | The director himself approved the script. |
| She | Herself | True Reflexive | She prepared herself for the interview. |
| It | Itself | Emphatic | The problem itself wasn’t difficult. |
| We | Ourselves | Object of Preposition | We kept the secret to ourselves. |
| They | Themselves | Emphatic | The students themselves organized the event. |
| I | Myself | True Reflexive | I blamed myself for the mistake. |
| You | Yourself | Object of Preposition | You should be proud of yourself. |
| He | Himself | True Reflexive | He introduced himself to the class. |
| She | Herself | Emphatic | The queen herself attended the ceremony. |
| It | Itself | Object of Preposition | The system updates itself automatically. |
| We | Ourselves | True Reflexive | We found ourselves in a strange situation. |
 39 Reflexive Pronouns Lists
39 Reflexive Pronouns Lists
FAQ on Reflexive Pronouns Lists
1. How do you identify reflexive pronouns in a sentence?
Look for words ending in “-self” or “-selves” that refer back to the subject of the sentence. A reflexive pronoun is used when the subject and object are the same person or thing. For example, in “She dressed herself,” “herself” is a reflexive pronoun because “she” (the subject) is performing the action on “herself” (the same person).
2. What’s the difference between reflexive and intensive pronouns?
Reflexive pronouns are used when the subject and object are the same, while intensive pronouns emphasize the subject or antecedent. Here’s the difference:
- Reflexive: “I hurt myself” (action reflects back to subject)
- Intensive: “I myself will do it” (adds emphasis)
3. Can reflexive pronouns start a sentence?
Generally, reflexive pronouns don’t start sentences in standard English. Instead, use subject pronouns or nouns. For example:
- Incorrect: “Myself went to the store”
- Correct: “I went to the store”
4. When should you NOT use reflexive pronouns?
Avoid using reflexive pronouns:
- As subjects of sentences
- After prepositions when the action doesn’t reflect back
- In compound subjects or objects
- When a simple personal pronoun works better
5. How do reflexive pronouns work in compound subjects?
When using compound subjects, match the reflexive pronoun to all subjects involved:
- “John and I hurt ourselves” (not myself)
- “You and Tom can help yourselves” (not yourself)
Conclusion
Mastering reflexive pronouns lists doesn’t have to be complicated. Remember that they’re like mirrors, reflecting actions back to the subject. Practice using them in your daily conversations, and you’ll find they become natural tools for clear and precise communication. Keep this guide handy as you continue to improve your grammar skills.

