Understanding science becomes much easier when you know the right words. 100 science words with meanings can help students, English learners, and beginners build strong scientific vocabulary without confusion. Science terms often look difficult, but when explained in simple language, they become easy to learn and remember.
This guide is designed to make science vocabulary clear, friendly, and useful for everyday learning.

Below is the list of 100 science words:
100 Science Words List
-
Acceleration
-
Adaptation
-
Atom
-
Atmosphere
-
Biology
-
Biomass
-
Catalyst
-
Cell
-
Chemical
-
Climate
-
Compound
-
Density
-
Diffusion
-
DNA
-
Ecosystem
-
Electricity
-
Energy
-
Evolution
-
Force
-
Fossil
-
Friction
-
Genetics
-
Gravity
-
Habitat
-
Heat
-
Hypothesis
-
Inertia
-
Insulator
-
Joule
-
Kinetic Energy
-
Latitude
-
Liquid
-
Magnetism
-
Mass
-
Matter
-
Molecule
-
Motion
-
Mutation
-
Nucleus
-
Nutrient
-
Organism
-
Oxygen
-
Photosynthesis
-
Physics
-
Pressure
-
Protein
-
Quantum
-
Radiation
-
Reaction
-
Respiration
-
Scientist
-
Sediment
-
Solution
-
Species
-
Speed
-
State of Matter
-
Temperature
-
Theory
-
Thermometer
-
Tectonic Plate
-
Tissue
-
Universe
-
Variable
-
Velocity
-
Volume
-
Wave
-
Wavelength
-
Weather
-
Weight
-
Work
-
Xylem
-
Yield
-
Zoology
-
Acid
-
Base
-
Carbon
-
Circuit
-
Conductor
-
Data
-
Element
-
Enzyme
-
Evaporation
-
Filtration
-
Gene
-
Ion
-
Mineral
-
Mixture
-
Observation
-
Orbit
-
Plasma
-
Reflection
-
Refraction
-
Renewable Energy
-
Satellite
-
Solar Energy
-
Sound
-
Spectrum
-
Substrate
-
Sustainability
-
Voltage
Now, the meanings of the 100 science words are given below:
Contents
Toggle100 Science Words With Meanings
- Acceleration—The rate at which an object changes its speed or direction.
- Adaptation—A feature that helps an organism survive in its environment.
- Atom—The smallest unit of matter.
- Atmosphere—The layer of gases surrounding the Earth.
- Biology – The study of living organisms.
- Biomass—Organic material used as a source of energy.
- Catalyst – A substance that speeds up a chemical reaction.
- Cell—The basic structural unit of all living things.
- Chemical – A substance with a specific composition.
- Climate—The average weather conditions of a place over time.
- Compound—A substance made of two or more elements chemically combined.
- Density—The amount of mass in a given volume.
- Diffusion—The movement of particles from high to low concentration.
- DNA—The molecule that carries genetic information.
- Ecosystem—A community of living organisms and their environment.
- Electricity—The flow of electric charge.
- Energy—the ability to do work or cause change.
- Evolution—The gradual change of organisms over time.
- Force—A push or pull that can change motion.
- Fossil—preserved remains of ancient plants or animals.
- Friction—A force that slows motion between surfaces in contact.
- Genetics—The study of heredity and traits.
- Gravity—the force that pulls objects toward each other.
- Habitat—The natural home of an organism.
- Heat—A form of energy that causes warmth.
- Hypothesis – A testable scientific prediction.
- Inertia—Resistance to change in motion.
- Insulator – A material that resists heat or electricity flow.
- Joule – A unit used to measure energy.
- Kinetic Energy – Energy possessed by a moving object.
- Latitude—Distance north or south of the equator.
- Liquid—A state of matter with fixed volume but no fixed shape.
- Magnetism—A force caused by magnetic fields.
- Mass—The amount of matter in an object.
- Matter—Anything that has mass and occupies space.
- Molecule—Two or more atoms bonded together.
- Motion—The movement of an object.
- Mutation—A change in genetic material.
- Nucleus – The center of an atom or cell.
- Nutrient—A substance needed for growth and health.
- Organism – Any living thing.
- Oxygen—A gas essential for respiration.
- Photosynthesis—the process by which plants make food using sunlight.
- Physics – The study of matter, energy, and forces.
- Pressure—Force applied over a surface area.
- Protein—a nutrient needed for growth and repair.
- Quantum—The smallest possible unit of energy.
- Radiation—Energy that travels in waves or particles.
- Reaction—A process where substances change chemically.
- Respiration—The process of releasing energy from food.
- Scientist—A person who studies science.
- Sediment—Small particles of rock or soil.
- Solution – A mixture where one substance dissolves in another.
- Species—A group of similar organisms that can reproduce.
- Speed—How fast something moves.
- State of Matter – The form matter takes, such as solid or liquid.
- Temperature—A measure of how hot or cold something is.
- Theory—A well-supported scientific explanation.
- Thermometer—An instrument used to measure temperature.
- Tectonic Plate—Large moving sections of Earth’s crust.
- Tissue—A group of similar cells working together.
- Universe—All of space, matter, and energy.
- Variable—A factor that can change in an experiment.
- Velocity—Speed in a specific direction.
- Volume—The amount of space an object occupies.
- Wave—A movement that transfers energy.
- Wavelength – Distance between wave peaks.
- Weather—Day-to-day atmospheric conditions.
- Weight—The force of gravity on an object.
- Work—Energy transferred by force.
- Xylem—Plant tissue that carries water.
- Yield—The amount produced in a process or reaction.
- Zoology – The study of animals.
- Acid—A substance with a low pH.
- Base—A substance with a high pH.
- Carbon—a key element found in living organisms.
- Circuit—A closed path for electricity to flow.
- Conductor – A material that allows electricity to pass through.
- Data – Collected information or facts.
- Element—A pure substance made of one type of atom.
- Enzyme – A protein that speeds up biological reactions.
- Evaporation—Liquid changing into gas.
- Filtration—separating solids from liquids.
- Gene—A unit of heredity.
- Ion—An atom with an electric charge.
- Mineral – A naturally occurring inorganic substance.
- Mixture—Two or more substances combined physically.
- Observation – Careful watching and recording of events.
- Orbit—The path an object follows around another object.
- Plasma—A high-energy state of matter.
- Reflection—Bouncing back of light or sound.
- Refraction—Bending of light through different materials.
- Renewable Energy – Energy from sources that can be replaced naturally.
- Satellite—An object that orbits a planet.
- Solar Energy—Energy from the sun.
- Sound—Energy produced by vibrations.
- Spectrum—A range of wavelengths or colors.
- Substrate—A substance acted upon by an enzyme.
- Sustainability—Using resources without harming the future.
- Voltage—The force that moves electric current.
Get the Free PDF: 100 Science Words with Meanings
FAQs: 100 science words with meanings
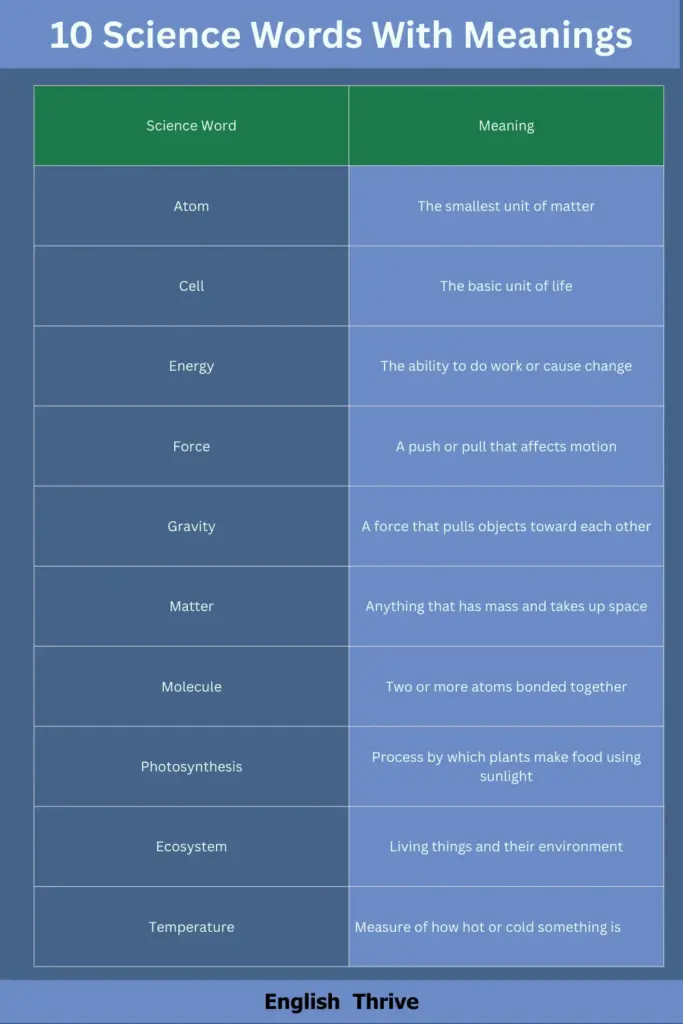
1. What are 10 science words with meaning?
| Science Word | Meaning |
|---|---|
| Atom | The smallest unit of matter |
| Cell | The basic unit of life |
| Energy | The ability to do work or cause change |
| Force | A push or pull that affects motion |
| Gravity | A force that pulls objects toward each other |
| Matter | Anything that has mass and takes up space |
| Molecule | Two or more atoms bonded together |
| Photosynthesis | Process by which plants make food using sunlight |
| Ecosystem | Living things and their environment |
| Temperature | Measure of how hot or cold something is |
2. What is science in 50 words?
Science is the systematic study of the natural world through observation, experiments, and evidence. It helps us understand how living and non-living things work, explains natural phenomena, and allows humans to solve problems, make discoveries, and improve daily life using facts and logical thinking.
3. What are the 4 meanings of science?
Science can be understood in four main ways:
- Science as knowledge—facts and information about the natural world.
- Science as a process—using observation and experiments to discover truth.
- Science as a subject—an academic field like biology, chemistry, or physics.
- Science as a way of thinking—logical, critical, and evidence-based reasoning.