Similes are powerful tools in the English language that help create vivid imagery and meaningful comparisons. When used to describe a person, they add depth, nuance, and color to both writing and speech, making Similes For Describing Personality Traits especially effective and expressive.
Understanding how to effectively use similes to characterize individuals is essential for clear and engaging communication. This article delves into the art of crafting similes for people, exploring different types of traits and providing numerous examples and exercises to hone your skills.
Whether you’re a student, writer, or simply looking to improve your communication, this guide will equip you with the knowledge and practice you need to master the use of similes to describe personality.
This article will benefit anyone looking to enrich their descriptive writing, including ESL students, creative writers, and professionals aiming to improve their communication skills. We’ll cover everything from the basic definition of a simile to advanced techniques for crafting unique and impactful comparisons.
By the end of this guide, you’ll be able to confidently use similes to bring your characters and descriptions to life.
Contents
ToggleDefinition of Simile
A simile is a figure of speech that directly compares two different things using the words “like” or “as.” The purpose of a simile is to illuminate a characteristic of one thing by associating it with a more familiar or evocative quality of another. Similes are essential tools for writers and speakers because they allow for more descriptive and engaging language.
Similes belong to the broader category of figurative language, which includes metaphors, personification, and hyperbole. Unlike a metaphor, which states that one thing *is* another, a simile only suggests a resemblance.
This distinction is crucial for understanding the nuanced effects each figure of speech can create. Understanding the definition of a simile and how it differs from other related concepts is the first step to mastering their use.
By understanding the core elements of a simile, you can use it to add depth and vividness to your writing.
Structural Breakdown of Similes
Similes typically follow a simple structure: A is like/as B. Where A is the subject being described, and B is the object or concept it is being compared to.
Understanding the structural components of a simile allows you to craft them effectively and recognize them easily.
1. The Subject (A)
This is the person, object, or idea that you are trying to describe. It’s the focus of your comparison.
It should be clearly identified so the reader knows what you are trying to convey.
2. The Connector (like/as)
These words are the bridge that links the subject to the object of comparison. They signal that you are making a comparison, not stating an equivalence.
The choice between “like” and “as” is often stylistic, though “as” can sometimes imply a stronger degree of similarity.
3. The Object of Comparison (B)
This is the thing to which the subject is being compared. It should possess a quality that you want to highlight in the subject.
The more evocative and well-chosen this object is, the more effective the simile will be. This is the key element in creating a memorable impression on the reader.
For instance, in the simile “He is as brave as a lion,” “He” is the subject, “as” is the connector, and “a lion” is the object of comparison. The simile suggests that the person being described possesses the bravery commonly associated with lions.
Types of Similes
Similes can be categorized based on the type of comparison they make or the effect they aim to achieve. Understanding these categories can help you choose the most effective simile for your purpose.
1. Descriptive Similes
These similes focus on describing a physical attribute or characteristic. They aim to create a vivid image in the reader’s mind.
These are often the most straightforward and easily understood type of simile.
2. Emotional Similes
These similes convey a feeling or emotional state. They help the reader understand the emotional experience of the subject.
They are particularly effective for conveying complex or subtle emotions.
3. Behavioral Similes
These similes compare a person’s actions or behavior to something else. They provide insight into the person’s character or habits.
They can be used to highlight both positive and negative traits.
4. Exaggerated Similes
Also known as hyperbolic similes, these use exaggeration for emphasis or humor. They are not meant to be taken literally but rather to create a strong impression.
These similes are more playful and can add a lighthearted tone to your writing.
Examples of Similes for People
The following examples illustrate how similes can be used to describe different aspects of a person’s character, appearance, and behavior. The tables are organized by category for easy reference.
Each table includes a variety of examples to help you understand the range of possibilities.
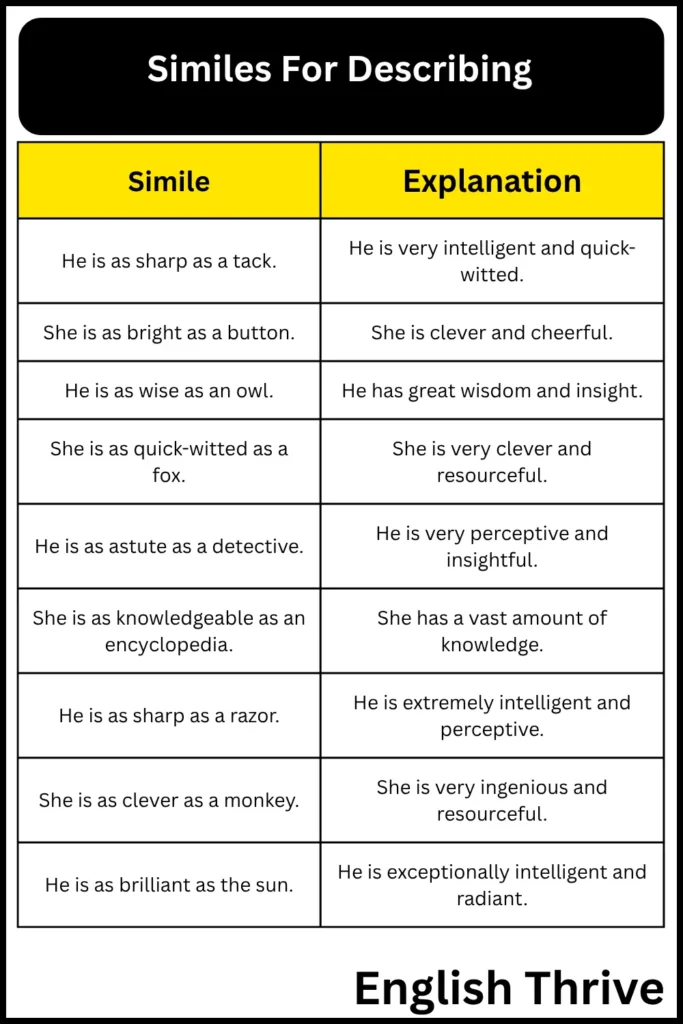
1. Similes for Intelligence and Wit
This table provides similes that describe a person’s intelligence, wit, and sharpness of mind. These examples help illustrate how similes can be used to convey intellectual characteristics.
| Simile | Explanation |
|---|---|
| He is as sharp as a tack. | He is very intelligent and quick-witted. |
| She is as bright as a button. | She is clever and cheerful. |
| He is as wise as an owl. | He has great wisdom and insight. |
| She is as quick-witted as a fox. | She is very clever and resourceful. |
| He is as astute as a detective. | He is very perceptive and insightful. |
| She is as knowledgeable as an encyclopedia. | She has a vast amount of knowledge. |
| He is as sharp as a razor. | He is extremely intelligent and perceptive. |
| She is as clever as a monkey. | She is very ingenious and resourceful. |
| He is as brilliant as the sun. | He is exceptionally intelligent and radiant. |
| She is as insightful as a philosopher. | She has deep understanding and wisdom. |
| He is as quick as a computer. | He processes information very rapidly. |
| She is as sharp-tongued as a viper. | She is witty but can also be cutting. |
| He is as cunning as a weasel. | He is sly and resourceful in achieving his goals. |
| She is as perceptive as an eagle. | She has excellent insight and awareness. |
| He is as strategic as a chess player. | He plans carefully and thinks ahead. |
| She is as analytical as a scientist. | She examines things logically and systematically. |
| He is as creative as an artist. | He is imaginative and innovative. |
| She is as eloquent as a poet. | She expresses herself beautifully and persuasively. |
| He is as resourceful as a scout. | He is able to find clever ways to overcome difficulties. |
| She is as inventive as an engineer. | She is skilled at creating new things and solutions. |
| He is as quick-thinking as a surgeon. | He is able to make fast and effective decisions under pressure. |
| She is as articulate as a lawyer. | She can express her ideas clearly and persuasively. |
| He is as knowledgeable as a professor. | He has a deep understanding of a particular subject. |
| She is as imaginative as a dreamer. | She is full of creative ideas and visions. |
 Similes For Describing Personality Traits
Similes For Describing Personality Traits
2. Similes for Appearance and Demeanor
This table showcases similes that describe a person’s physical appearance and general demeanor. These examples help illustrate how similes can be used to convey visual and behavioral characteristics.
| Simile | Explanation |
|---|---|
| He is as tall as a tree. | He is very tall. |
| She is as graceful as a swan. | She moves with elegance and poise. |
| He is as strong as an ox. | He is very physically strong. |
| She is as radiant as the sun. | She is beautiful and glowing. |
| He is as quiet as a mouse. | He is very shy and unobtrusive. |
| She is as gentle as a lamb. | She is kind and compassionate. |
| He is as fierce as a tiger. | He is aggressive and determined. |
| She is as delicate as a flower. | She is fragile and beautiful. |
| He is as imposing as a mountain. | He has a strong and impressive presence. |
| She is as serene as a lake. | She is calm and peaceful. |
| He is as rugged as a rock. | He has a strong, weathered appearance. |
| She is as light as a feather. | She is very graceful and delicate. |
| He is as round as a ball. | He is overweight or stout. |
| She is as pale as a ghost. | She is very pale, often due to illness or fear. |
| He is as sharp-dressed as a banker. | He is well-dressed and stylish. |
| She is as charming as a princess. | She is very attractive and charismatic. |
| He is as intimidating as a bouncer. | He is physically imposing and threatening. |
| She is as bubbly as champagne. | She is lively and enthusiastic. |
| He is as steady as a rock. | He is reliable and dependable. |
| She is as vibrant as a rainbow. | She is full of life and energy. |
| He is as mysterious as the night. | He is enigmatic and difficult to understand. |
| She is as radiant as the morning sun. | She is bright, cheerful, and beautiful. |
| He is as solid as an oak. | He is strong, sturdy, and reliable. |
| She is as ethereal as a dream. | She is delicate, graceful, and otherworldly. |
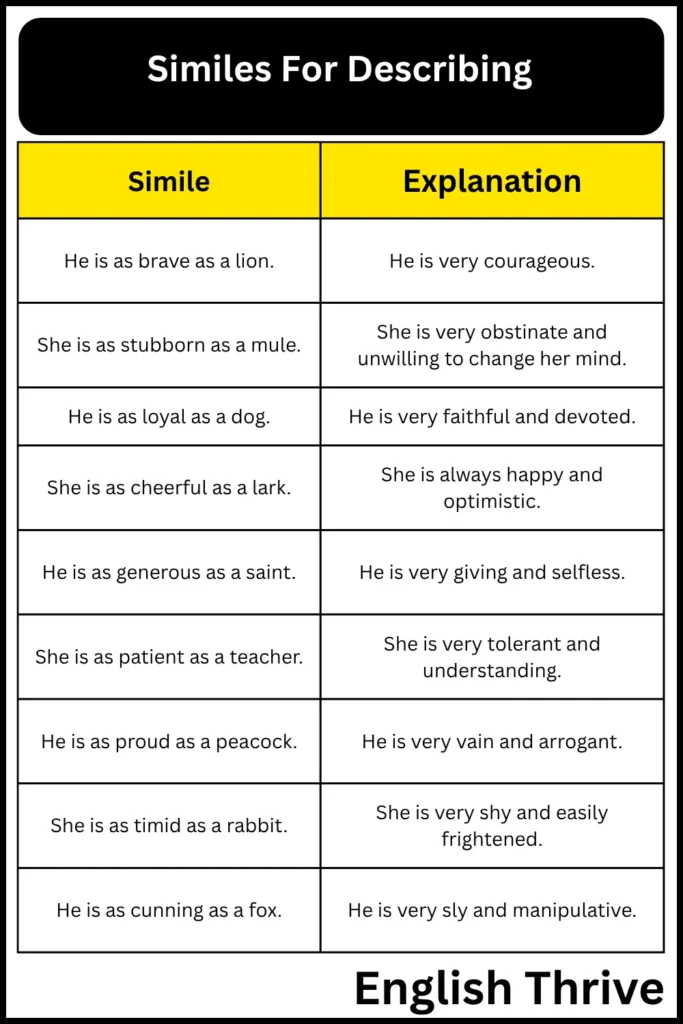
3. Similes for Personality and Character
This table offers similes that describe a person’s personality traits and character. These examples help illustrate how similes can be used to convey inner qualities.
| Simile | Explanation |
|---|---|
| He is as brave as a lion. | He is very courageous. |
| She is as stubborn as a mule. | She is very obstinate and unwilling to change her mind. |
| He is as loyal as a dog. | He is very faithful and devoted. |
| She is as cheerful as a lark. | She is always happy and optimistic. |
| He is as generous as a saint. | He is very giving and selfless. |
| She is as patient as a teacher. | She is very tolerant and understanding. |
| He is as proud as a peacock. | He is very vain and arrogant. |
| She is as timid as a rabbit. | She is very shy and easily frightened. |
| He is as cunning as a fox. | He is very sly and manipulative. |
| She is as wise as an owl. | She has great wisdom and insight. |
| He is as cold as ice. | He is emotionally distant and uncaring. |
| She is as warm as the sun. | She is friendly and welcoming. |
| He is as gentle as a breeze. | He is kind and considerate. |
| She is as fierce as a storm. | She is powerful and intense. |
| He is as determined as a bull. | He is very persistent and resolute. |
| She is as adaptable as a chameleon. | She can easily adjust to new situations. |
| He is as organized as a librarian. | He is very methodical and efficient. |
| She is as spontaneous as a child. | She is impulsive and carefree. |
| He is as calm as a monk. | He is very peaceful and composed. |
| She is as ambitious as an entrepreneur. | She is driven and determined to succeed. |
| He is as forgiving as a god. | He is always willing to pardon others. |
| She is as loyal as a soldier. | She is steadfast and dedicated to her principles. |
| He is as humble as a servant. | He is modest and unpretentious. |
| She is as optimistic as a dreamer. | She always looks on the bright side of things. |
4. Similes for Behavior and Actions
This table presents similes that describe a person’s typical behaviors and actions. These examples help illustrate how similes can be used to convey habits and tendencies.
| Simile | Explanation |
|---|---|
| He eats like a horse. | He eats a very large amount of food. |
| She sleeps like a log. | She sleeps very soundly. |
| He works like a beaver. | He works very hard and diligently. |
| She sings like an angel. | She sings beautifully. |
| He runs like the wind. | He runs very fast. |
| She fights like a wildcat. | She fights fiercely and aggressively. |
| He argues like a lawyer. | He argues skillfully and persuasively. |
| She gossips like a magpie. | She talks a lot, often about trivial matters. |
| He worries like a mother hen. | He worries excessively about others. |
| She spends money like water. | She spends money freely and carelessly. |
| He watches like a hawk. | He observes very carefully. |
| She plans like a general. | She makes very detailed and strategic plans. |
| He dances like a dream. | He dances gracefully and beautifully. |
| She swims like a fish. | She swims very well and effortlessly. |
| He drives like a maniac. | He drives recklessly and dangerously. |
| She learns like a sponge. | She absorbs information quickly and easily. |
| He leads like a shepherd. | He guides and protects his followers. |
| She follows like a shadow. | She is always present and supportive. |
| He roars like a lion. | He speaks loudly and powerfully. |
| She purrs like a kitten. | She speaks softly and contentedly. |
| He grumbles like a bear. | He complains frequently and irritably. |
| She chatters like a squirrel. | She talks rapidly and incessantly. |
| He struts like a peacock. | He walks proudly and arrogantly. |
| She sneaks like a cat. | She moves stealthily and quietly. |
Usage Rules for Similes
Using similes effectively requires understanding the rules that govern their construction and application. While similes offer creative freedom, adhering to certain guidelines ensures clarity and impact.
1. Clarity and Relevance
The comparison should be clear and easily understood. The object of comparison should have a quality that is readily associated with it and relevant to the subject being described.
Avoid obscure or confusing comparisons.
2. Originality
While common similes can be effective, strive for originality to make your writing more engaging and memorable. Overused similes can become clichés and lose their impact.
Think creatively to find fresh and insightful comparisons.
3. Appropriateness
The simile should be appropriate for the context and tone of your writing. A humorous simile might be out of place in a serious or formal setting.
Consider the audience and the overall message you are trying to convey.
4. Avoid Mixed Metaphors and Similes
Ensure that your similes are consistent and do not create conflicting images. Mixing metaphors and similes can lead to confusion and weaken your writing.
5. Use Sparingly
While similes can enhance your writing, overuse can make it feel forced and artificial. Use similes strategically to highlight key qualities and add depth to your descriptions, but avoid peppering your text with too many comparisons.
Common Mistakes When Using Similes
Even experienced writers can make mistakes when using similes. Recognizing these common errors can help you avoid them and improve the quality of your writing.
1. Clichés
Using overused similes, such as “as busy as a bee” or “as blind as a bat,” can make your writing sound unoriginal and uninspired. Strive to find fresh and unique comparisons.
| Incorrect (Cliché) | Correct (Original) |
|---|---|
| He was as busy as a bee. | He was as busy as a one-armed juggler. |
| She was as blind as a bat. | She was as blind as a mole in daylight. |
2. Illogical Comparisons
The comparison should make sense and be based on a shared quality between the subject and the object. Avoid comparisons that are nonsensical or contradictory.
| Incorrect (Illogical) | Correct (Logical) |
|---|---|
| He is as tall as an idea. | He is as tall as a skyscraper. |
| She is as loud as silence. | She is as quiet as a whisper. |
3. Overcomplicating
A simile should enhance clarity, not obscure it. Avoid using complex or obscure objects of comparison that require explanation.
| Incorrect (Overcomplicated) | Correct (Simple) |
|---|---|
| He is as complex as a fractal pattern. | He is as complex as a maze. |
| She is as ephemeral as quantum foam. | She is as fleeting as a dream. |
4. Misusing “Like” and “As”
Ensure you use “like” and “as” correctly. “Like” is a preposition and should be followed by a noun or pronoun, while “as” can be used as a conjunction to introduce a clause.
| Incorrect (Misused) | Correct (Properly Used) |
|---|---|
| He sings as a bird. | He sings like a bird. |
| She is intelligent like she is wise. | She is as intelligent as she is wise. |
Practice Exercises: Similes For Describing Personality Traits
Test your understanding of similes with the following exercises. Each exercise focuses on a different aspect of simile usage.
Answers are provided at the end of each exercise.
1. Identifying Similes
Identify the similes in the following sentences.
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| 1. The baby slept like a log. | slept like a log |
| 2. Her voice was as sweet as honey. | as sweet as honey |
| 3. He ran faster than a cheetah. | This sentence does not contain a simile. |
| 4. The news spread like wildfire. | spread like wildfire |
| 5. She is as brave as a lion. | as brave as a lion |
| 6. The old house stood silent as a tomb. | silent as a tomb |
| 7. He eats a lot of food every day. | This sentence does not contain a simile. |
| 8. The children played like puppies in the park. | played like puppies |
| 9. He is as stubborn as a mule. | as stubborn as a mule |
| 10. The snow fell softly like feathers. | like feathers |
2. Completing Similes
Complete the following similes with an appropriate comparison.
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| 1. He is as strong as ______. | an ox |
| 2. She is as graceful as ______. | a swan |
| 3. He is as quiet as ______. | a mouse |
| 4. She is as radiant as ______. | the sun |
| 5. He is as fierce as ______. | a tiger |
| 6. She is as delicate as ______. | a flower |
| 7. He is as imposing as ______. | a mountain |
| 8. She is as serene as ______. | a lake |
| 9. He is as rugged as ______. | a rock |
| 10. She is as light as ______. | a feather |
3. Creating Similes
Create similes to describe the following people based on the given traits.
| Trait | Example Simile |
|---|---|
| Courageous | He is as brave as a lion. |
| Stubborn | She is as stubborn as a mule. |
| Loyal | He is as loyal as a dog. |
| Cheerful | She is as cheerful as a lark. |
| Generous | He is as generous as a saint. |
| Patient | She is as patient as a teacher. |
| Proud | He is as proud as a peacock. |
| Timid | She is as timid as a rabbit. |
| Cunning | He is as cunning as a fox. |
| Wise | She is as wise as an owl. |
4. Correcting Incorrect Similes
Identify and correct the illogical or cliché similes in the following sentences.
| Incorrect Simile | Corrected Simile |
|---|---|
| 1. He is as busy as a bee. | He is as busy as a street vendor during rush hour. |
| 2. She is as blind as a bat. | She is as blind as a newborn kitten. |
| 3. He is as tall as an idea. | He is as tall as a redwood tree. |
| 4. She is as loud as silence. | She is as loud as a rock concert. |
| 5. He is as complex as a fractal pattern. | He is as complex as a human brain. |
| 6. She is as ephemeral as quantum foam. | She is as ephemeral as a soap bubble. |
| 7. He sings as a bird. | He sings like a bird. |
| 8. She is intelligent like she is wise. | She is as intelligent as she is wise. |
| 9. He is as fast as a snail. | He is as fast as a rocket. |
| 10. She is as strong as a feather. | She is as strong as an oak tree. |
Advanced Topics in Simile Usage
For advanced learners, delving deeper into the nuances of simile usage can further enhance your writing skills.
1. Subverting Expectations
Instead of using predictable comparisons, try subverting expectations by creating unexpected or ironic similes. This can add a layer of complexity and intrigue to your writing.
2. Extended Similes
Expand on a simile by developing it over several sentences or even paragraphs. This allows you to explore the comparison in greater detail and create a more vivid and lasting impression.
3. Similes in Poetry and Prose
Explore how similes are used differently in poetry and prose. In poetry, similes are often more lyrical and evocative, while in prose, they tend to be more functional and descriptive.
FAQs on Similes For Describing Personality Traits
Here are some frequently asked questions about similes.
Q1: What is the difference between a simile and a metaphor?
A: A simile compares two things using “like” or “as,” while a metaphor states that one thing *is* another. Similes suggest a resemblance, while metaphors imply a stronger equivalence.
Q2: Can a simile be a cliché?
A: Yes, overused similes can become clichés. To avoid this, strive for originality and find fresh, insightful comparisons.
Q3: How can I make my similes more creative?
A: Think outside the box and consider unexpected or unusual comparisons. Look for connections that are not immediately obvious but still relevant and meaningful.
Q4: Is it okay to use similes in formal writing?
A: Yes, but use them sparingly and ensure they are appropriate for the tone and context of your writing. Avoid overly casual or humorous similes in formal settings.
Q5: What is the purpose of using similes?
A: Similes add depth, color, and clarity to your writing by making comparisons that help readers understand and visualize your descriptions. They make your writing more engaging and memorable.
Q6: How do I avoid mixed metaphors and similes?
A: Ensure that your comparisons are consistent and do not create conflicting images. Avoid using metaphors and similes that contradict each other or create illogical combinations.
Q7: Can a simile use more than two things for comparison?
A: While the basic structure involves comparing two things, an extended simile can elaborate on the comparison with additional details and related elements, effectively broadening the scope.
Q8: What if I can’t think of a good simile?
A: Don’t force it. Sometimes, a direct description is more effective than a strained simile. Consider other figures of speech or descriptive techniques if you’re struggling to find a suitable comparison.
Conclusion: Similes For Describing Personality Traits
Mastering similes is an invaluable skill for anyone seeking to enhance their writing and communication. By understanding the structure, types, and usage rules of similes, you can craft vivid and engaging descriptions that bring your subjects to life.
Remember to strive for originality, avoid clichés, and use similes appropriately for the context and tone of your writing.
Continue practicing and experimenting with similes to hone your skills. The more you use them, the more natural and effective they will become.
With dedication and creativity, you can unlock the power of similes to transform your writing from ordinary to extraordinary. By following the guidelines and examples provided in this guide, you’ll be well on your way to becoming a simile master.