Prepositions are essential components of English grammar, serving as bridges that connect nouns, pronouns, and phrases to other parts of a sentence. Mastering prepositions enhances clarity, precision, and fluency in both writing and speech.
This article focuses specifically on Prepositions Starting With E, providing a detailed exploration of their meanings, usage, and common applications. Whether you are a beginner or an advanced learner, understanding these prepositions will significantly improve your command of the English language.
Contents
ToggleDefinition of Prepositions
A preposition is a word that connects a noun, pronoun, or noun phrase to other words in a sentence. It typically indicates the spatial, temporal, or logical relationship of the noun or pronoun to the rest of the sentence. Prepositions are crucial for creating clear and meaningful sentences, as they provide context and specify relationships between different elements. They often answer questions like “where,” “when,” “how,” or “why.”
Prepositions belong to a closed class of words, meaning that new prepositions are rarely added to the English language. They are typically followed by a noun or pronoun, which is called the object of the preposition. The preposition and its object together form a prepositional phrase.
Classification of Prepositions
Prepositions can be classified based on their structure and function. Structurally, they can be simple, compound, or phrasal.
Functionally, they can indicate location, time, direction, or other relationships.
- Simple Prepositions: These consist of a single word, such as in, on, at, and, of course, those starting with ‘E’ ( except).
- Compound Prepositions: These are formed by combining two or more words, such as according to, because of, and in front of.
- Phrasal Prepositions: These consist of a preposition and other words that function together as a single preposition, such as in spite of and due to.
Structural Breakdown
Understanding the structure of prepositional phrases is essential for correctly using prepositions. A prepositional phrase consists of a preposition followed by its object (a noun, pronoun, or noun phrase).
The object of the preposition is governed by the preposition, and the entire phrase functions as an adjective or adverb within the sentence.
The basic structure of a prepositional phrase is:
Preposition + (Modifier) + Object
For example:
- Except me (Except is the preposition, me is the object)
- Except for the rain (Except is the preposition, for the rain is the object)
The prepositional phrase can act as an adjective, modifying a noun or pronoun, or as an adverb, modifying a verb, adjective, or another adverb. This flexibility allows prepositional phrases to add detail and context to sentences.
Example as an Adjective: The book on the shelf is mine. (on the shelf modifies the noun book)
Example as an Adverb: He walked towards the park. (towards the park modifies the verb walked)
Categories of Prepositions Starting With E
While the number of prepositions starting with ‘E’ is relatively small, they each have distinct meanings and uses. The primary prepositions in this category include:
- Except
Except
The preposition except indicates exclusion or omission. It means “not including” or “excluding.” It specifies what or whom is being left out of a general statement or situation.
Example: Everyone passed the test except John.
Except for is a common variation that adds a slight emphasis or clarification to the exclusion.
Example: The movie was great except for the ending.
Examples of Prepositions Starting With ‘E’
To fully understand how to use prepositions starting with ‘E,’ it’s helpful to examine numerous examples in various contexts. Below are several tables illustrating the usage of ‘except’ and ‘except for’ in different sentences.
Each table offers a unique perspective on how these prepositions function, helping you grasp their nuances and applications.
Examples Using “Except”
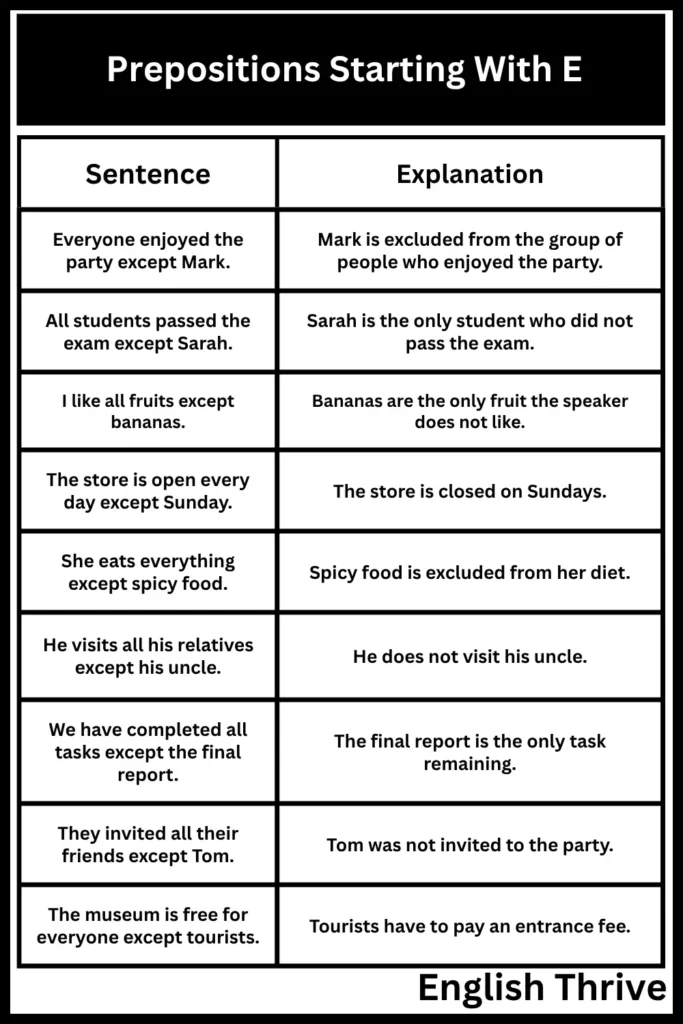
The following table provides examples of the preposition “except” used in different contexts. These examples highlight how “except” is used to indicate exclusion or omission.
| Sentence | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Everyone enjoyed the party except Mark. | Mark is excluded from the group of people who enjoyed the party. |
| All students passed the exam except Sarah. | Sarah is the only student who did not pass the exam. |
| I like all fruits except bananas. | Bananas are the only fruit the speaker does not like. |
| The store is open every day except Sunday. | The store is closed on Sundays. |
| She eats everything except spicy food. | Spicy food is excluded from her diet. |
| He visits all his relatives except his uncle. | He does not visit his uncle. |
| We have completed all tasks except the final report. | The final report is the only task remaining. |
| They invited all their friends except Tom. | Tom was not invited to the party. |
| The museum is free for everyone except tourists. | Tourists have to pay an entrance fee. |
| I’ve read all the books in this series except the last one. | The last book is the only one the speaker hasn’t read. |
| All the flowers are blooming except the roses. | The roses are not blooming. |
| Every question was easy except number five. | Question number five was difficult. |
| I use all the apps on my phone except this one. | This app is not used by the speaker. |
| He knows all the answers except the last one. | He does not know the last answer. |
| They cleaned the entire house except the attic. | The attic was not cleaned. |
| She likes all kinds of music except country. | Country music is not liked by her. |
| He watches all sports except golf. | Golf is not watched by him. |
| We visited all the countries in Europe except Spain. | Spain was not visited. |
| They fixed all the appliances except the dishwasher. | The dishwasher was not fixed. |
| She answered all the questions correctly except one. | One question was answered incorrectly. |
| I’ve tried every restaurant in town except that new Italian place. | The speaker has not tried the new Italian restaurant. |
| He remembers all his passwords except for his email. | He forgot his email password. |
| They packed everything for the trip except the sunscreen. | They forgot to pack the sunscreen. |
| She understood all the instructions except the final step. | She didn’t understand the final step. |
| He completed all his chores except mowing the lawn. | He didn’t mow the lawn. |
| We watered all the plants except the cactus. | The cactus was not watered. |
| They visited all the museums except the art gallery. | They didn’t visit the art gallery. |
| She wore all her jewelry except her necklace. | She didn’t wear her necklace. |
| He read all the articles except the last one. | He didn’t read the last article. |
 Prepositions Starting With E
Prepositions Starting With E
Examples Using “Except For”
The following table provides examples of the preposition “except for” used in different contexts. “Except for” often introduces a slight deviation or exception to a general statement.
| Sentence | Explanation |
|---|---|
| The movie was great except for the ending. | The ending of the movie was not as good as the rest. |
| The weather was perfect except for a little rain. | There was a small amount of rain, but otherwise, the weather was perfect. |
| The cake was delicious except for being slightly dry. | The cake was good, but it was a bit dry. |
| The room was clean except for the dust on the shelves. | The shelves were dusty, but the rest of the room was clean. |
| The trip was wonderful except for the long flight. | The flight was long and unpleasant, but the rest of the trip was great. |
| The presentation was excellent except for a few technical issues. | There were some technical problems, but the presentation was otherwise excellent. |
| The dinner was perfect except for the overcooked steak. | The steak was overcooked, but the rest of the dinner was perfect. |
| The concert was amazing except for the poor sound quality. | The sound quality was bad, but the concert was otherwise amazing. |
| The car is in good condition except for a few scratches. | There are some scratches on the car, but it is otherwise in good condition. |
| The garden is beautiful except for the weeds. | There are weeds in the garden, but it is otherwise beautiful. |
| The house is perfect except for the small kitchen. | The kitchen is small, but the rest of the house is perfect. |
| The project was successful except for the missed deadline. | The deadline was missed, but the project was otherwise successful. |
| The event was well-organized except for the seating arrangement. | The seating arrangement was not good, but the event was otherwise well-organized. |
| The article was informative except for a few grammatical errors. | There were some grammatical errors, but the article was otherwise informative. |
| The game was fun except for the bad refereeing. | The refereeing was bad, but the game was otherwise fun. |
| The service was excellent except for the slow delivery. | The delivery was slow, but the service was otherwise excellent. |
| The weather is warm except for the strong wind. | There is a strong wind, but the weather is otherwise warm. |
| The explanation was clear except for one confusing point. | One point was confusing, but the explanation was otherwise clear. |
| The party was great except for the loud music. | The music was loud, but the party was otherwise great. |
| The book was interesting except for the slow beginning. | The beginning was slow, but the book was otherwise interesting. |
| The presentation was flawless except for one minor typo. | There was one typo, but the presentation was otherwise flawless. |
| The meal was delicious except for the slightly burnt toast. | The toast was burnt, but the meal was otherwise delicious. |
| The hike was enjoyable except for the steep incline. | The incline was steep, but the hike was otherwise enjoyable. |
| The car ride was smooth except for one bumpy stretch of road. | There was one bumpy stretch of road, but the ride was otherwise smooth. |
| The interview went well except for one tricky question. | There was one tricky question, but the interview otherwise went well. |
| The garden is thriving except for a few persistent weeds. | There are a few weeds, but the garden is otherwise thriving. |
| The project is complete except for the final review. | The final review remains, but the project is otherwise complete. |
| The performance was captivating except for a brief technical glitch. | There was a glitch, but the performance was otherwise captivating. |
Except as a Conjunction
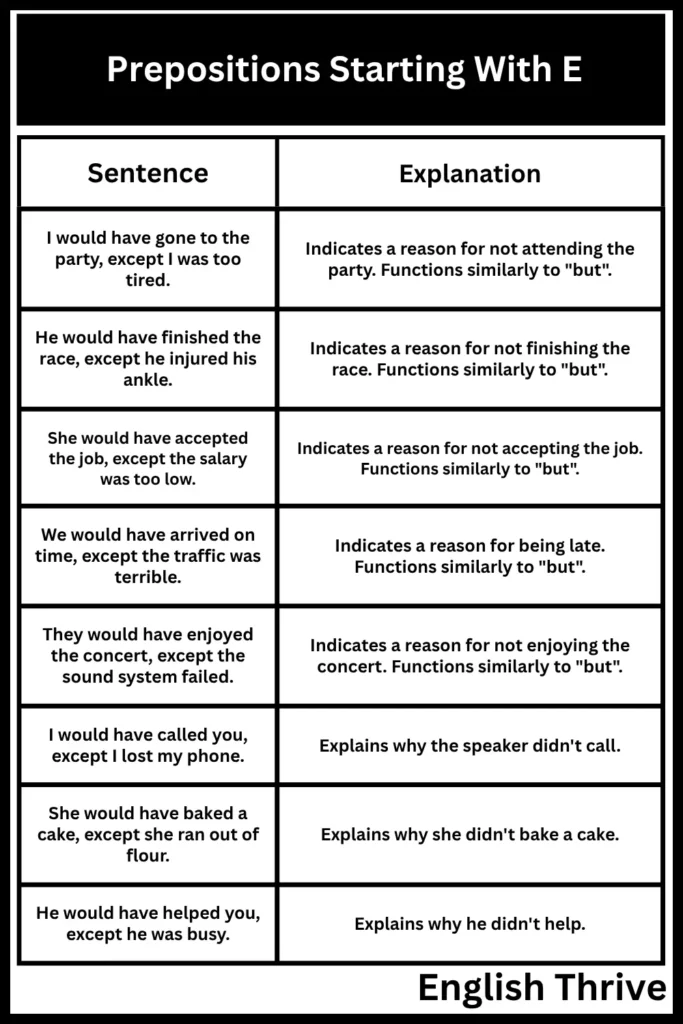
While primarily used as a preposition, “except” can also function as a conjunction. This table illustrates examples of “except” used as a conjunction.
| Sentence | Explanation |
|---|---|
| I would have gone to the party, except I was too tired. | Indicates a reason for not attending the party. Functions similarly to “but”. |
| He would have finished the race, except he injured his ankle. | Indicates a reason for not finishing the race. Functions similarly to “but”. |
| She would have accepted the job, except the salary was too low. | Indicates a reason for not accepting the job. Functions similarly to “but”. |
| We would have arrived on time, except the traffic was terrible. | Indicates a reason for being late. Functions similarly to “but”. |
| They would have enjoyed the concert, except the sound system failed. | Indicates a reason for not enjoying the concert. Functions similarly to “but”. |
| I would have called you, except I lost my phone. | Explains why the speaker didn’t call. |
| She would have baked a cake, except she ran out of flour. | Explains why she didn’t bake a cake. |
| He would have helped you, except he was busy. | Explains why he didn’t help. |
| We would have stayed longer, except we had an early flight. | Explains why they didn’t stay longer. |
| They would have joined us, except they had other plans. | Explains why they didn’t join. |
 Prepositions Starting With E
Prepositions Starting With E
Usage Rules
The use of prepositions, including those starting with ‘E’, follows specific rules that ensure clarity and grammatical correctness. Understanding these rules helps prevent common errors and improves overall language proficiency.
Rules for Using “Except”
- Exclusion: Use “except” to indicate that something or someone is excluded from a group or statement.
- Placement: “Except” typically comes before the noun or pronoun it excludes.
- Clarity: Ensure that the exclusion is clear and unambiguous.
Rules for Using “Except For”
- Emphasis: Use “except for” to emphasize a minor deviation or exception.
- Context: “Except for” often introduces a detail that contrasts with the general statement.
- Grammatical Structure: “Except for” is followed by a noun phrase.
Common Mistakes
Even experienced English speakers sometimes make mistakes when using prepositions. Being aware of these common errors can help you avoid them in your own writing and speech.
Common Mistakes with “Except”
| Incorrect | Correct | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| Everyone came to the party, include John. | Everyone came to the party except John. | “Include” is not used to exclude someone. |
| I like all the movies, but action. | I like all the movies except action movies. | “But” doesn’t function as a preposition of exclusion in this way. |
Common Mistakes with “Except For”
| Incorrect | Correct | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| The weather was good, except was raining. | The weather was good, except for the rain. | “Except for” requires a noun phrase, not a clause. |
| The food was delicious, except it was too spicy. | The food was delicious, except for the spiciness. | “Except for” requires a noun phrase, not a clause. |
Practice Exercises: Prepositions Starting With E
To reinforce your understanding of prepositions starting with ‘E’, complete the following practice exercises. These exercises cover various aspects of prepositional usage, including sentence completion and error correction.
Exercise 1: Fill in the Blanks
Complete the following sentences with the correct preposition (“except” or “except for”).
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| 1. I enjoy all sports _________ golf. | except |
| 2. The room was clean _________ the dust on the shelves. | except for |
| 3. Everyone passed the test _________ Mary. | except |
| 4. The movie was good _________ the ending. | except for |
| 5. She eats everything _________ seafood. | except |
| 6. The weather was perfect _________ a slight breeze. | except for |
| 7. He visits all his relatives _________ his uncle. | except |
| 8. The cake was delicious _________ being a little dry. | except for |
| 9. We have completed all tasks _________ the final review. | except |
| 10. The concert was amazing _________ the sound quality. | except for |
Exercise 2: Error Correction
Identify and correct the errors in the following sentences.
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| 1. All students attended, include John. | All students attended, except John. |
| 2. The house is perfect, except is small. | The house is perfect, except for the small size. |
| 3. I like all fruits, but bananas. | I like all fruits except bananas. |
| 4. The trip was great, except we had a flat tire. | The trip was great, except for the flat tire. |
| 5. She knows everyone, include him. | She knows everyone except him. |
| 6. The food was good, except was too salty. | The food was good, except for the saltiness. |
| 7. He reads all books, but mysteries. | He reads all books except mysteries. |
| 8. The presentation was excellent, except the projector didn’t work. | The presentation was excellent, except for the projector malfunction. |
| 9. They invited everyone, include her. | They invited everyone except her. |
| 10. The garden is beautiful, except have weeds. | The garden is beautiful, except for the weeds. |
Exercise 3: Sentence Completion
Complete the following sentences using “except” or “except for” and providing a logical ending.
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| 1. I enjoy all kinds of music _________. | I enjoy all kinds of music except country music. |
| 2. The day was perfect _________. | The day was perfect except for the strong wind. |
| 3. Everyone in the class passed _________. | Everyone in the class passed except for Tom. |
| 4. The meal was delicious _________. | The meal was delicious except for the overcooked vegetables. |
| 5. She has traveled to every continent _________. | She has traveled to every continent except Antarctica. |
| 6. The car runs smoothly _________. | The car runs smoothly except for a slight squeak in the brakes. |
| 7. He likes all subjects in school _________. | He likes all subjects in school except mathematics. |
| 8. The entire team played well _________. | The entire team played well except for a few minor mistakes. |
| 9. We visited all the museums in the city _________. | We visited all the museums in the city except the art museum. |
| 10. The software works perfectly _________. | The software works perfectly except for a small bug. |
Advanced Topics
For advanced learners, there are more complex aspects of prepositions that can be explored. These include idiomatic expressions, nuanced usages, and the historical evolution of prepositions.
Idiomatic Expressions
Prepositions often appear in idiomatic expressions, where the meaning of the phrase is not directly deducible from the individual words. Understanding these expressions requires familiarity and practice.
Example: He is exceptional at his job. (Here, “exceptional” is an adjective derived from “except,” but it doesn’t function as a prepositional phrase.)
Historical Evolution
The usage and meaning of prepositions have evolved over time. Studying the historical development of prepositions can provide deeper insights into their current usage and variations.
FAQs About Prepositions Starting With E
Here are some frequently asked questions about prepositions starting with ‘E’:
What is the difference between “except” and “except for”?
“Except” indicates a direct exclusion, while “except for” emphasizes a minor deviation or exception. “Except” is generally followed by a noun or pronoun, whereas “except for” is followed by a noun phrase that describes a specific detail that contrasts with a general statement.
Can “except” be used at the beginning of a sentence?
No, “except” is not typically used at the beginning of a sentence. However, you can restructure the sentence to use “except” correctly within the sentence.
Is it correct to say “Everyone except I”?
No, it should be “Everyone except me.” Prepositions take the objective case, so use “me” instead of “I.”
How can I improve my understanding of prepositions?
Practice regularly by reading, writing, and listening to English. Pay attention to how prepositions are used in different contexts and make note of any new usages you encounter. Use online resources and grammar guides to clarify any doubts.
Are there any other prepositions starting with ‘E’?
“Except” and “except for” are the primary prepositions that start with ‘E’. Other words may exist, but they are rarely used as prepositions in modern English.
Can ‘except’ function as a verb?
Yes, but this usage is rare and often formal. It means to exclude or leave out. For example: “These items are excepted from the list.” However, in most contexts, ‘except’ is used as a preposition or conjunction.
How do I choose between ‘except’ and ‘but’?
‘Except’ indicates exclusion from a group or statement, while ‘but’ introduces a contrast or exception to a general idea. Use ‘except’ when specifying what is not included, and ‘but’ when presenting a contrasting element.
Is it ever correct to omit the preposition ‘for’ after ‘except’?
Yes, it is correct to use “except” without “for” when directly excluding a noun or pronoun. For example, “Everyone came except John.” However, when introducing a more detailed exception or modifying phrase, “except for” is more appropriate, as in “The trip was great except for the weather.”
Conclusion: Prepositions Starting With E
Mastering prepositions starting with ‘E’ is crucial for enhancing your English language skills. By understanding the definitions, structural breakdowns, usage rules, and common mistakes associated with these prepositions, you can significantly improve your clarity and accuracy in both writing and speech.
Continuous practice and attention to detail will further solidify your knowledge and confidence in using these essential components of English grammar.
Remember to review the examples and practice exercises regularly to reinforce your learning. With consistent effort, you will be well on your way to mastering prepositions and achieving fluency in English.
Keep practicing, and you’ll find that using prepositions correctly becomes second nature!