If you’ve ever tried to improve your English, you’ve probably come across the term “parts of speech.” But what exactly does it mean? Simply put, parts of speech are the basic elements of language, which help us form sentences and express ideas clearly. By understanding parts of speech, you can create grammatically correct sentences and communicate more effectively.
In this article, we’ll explore into a detailed parts of speech chart with examples, breaking down each type with clear definitions, example words, and sentences so you can easily understand these important concepts.
Contents
ToggleWhat is Parts of Speech?
In English grammar, the term “parts of speech” refers to the categories that words are classified into based on their function in a sentence. These categories help us understand how words relate to each other and contribute to the overall meaning of a sentence. The basic parts of speech include nouns, pronouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, prepositions, conjunctions, interjections, determiners, and articles.
Types of Parts of Speech
There are traditionally eight core parts of speech, each serving a specific role in the structure of a sentence. Additionally, some consider determiners and articles as separate categories, expanding the parts of speech to ten. Here’s an overview:
- Noun
- Pronoun
- Verb
- Adjective
- Adverb
- Preposition
- Conjunction
- Interjection
- Determiner
- Article

Parts of Speech with Examples
Noun
A noun is a word that represents a person, place, thing, or idea.
- Example Words: dog, city, happiness, book, teacher, apple, car, house, love, music
- Example Sentences:
- The dog barked loudly.
- We visited the city last summer.
- Happiness is important in life.
- She read an interesting book.
- The teacher explained the lesson clearly.
- I ate an apple this morning.
- The car broke down on the way to work.
- They built a new house in the neighborhood.
- Love is a powerful emotion.
- Music brings joy to many people.
Pronoun
A pronoun replaces a noun in a sentence to avoid repetition.
- Example Words: he, she, it, they, we, you, who, what, mine, ours
- Example Sentences:
- He is my best friend.
- She loves to read.
- It is raining outside.
- They went to the movies yesterday.
- We are going to the beach.
- You should try this new recipe.
- Who is coming to the party?
- What is your favorite color?
- This book is mine.
- The house is ours now.
Adjective
An adjective describes or modifies a noun, providing more detail.
- Example Words: beautiful, tall, small, green, happy, blue, old, delicious, bright, soft
- Example Sentences:
- The beautiful flower bloomed in spring.
- He is a tall basketball player.
- The small cat ran across the yard.
- She wore a green dress to the party.
- The happy child smiled all day.
- The sky is blue today.
- The old house creaked in the wind.
- The cake tastes delicious.
- The bright light hurt my eyes.
- I bought a soft blanket for winter.
Adverb
An adverb modifies a verb, adjective, or another adverb. It provides more information about how, when, where, or to what extent something happens.
- Example Words: quickly, very, always, never, slowly, often, here, well, almost, extremely
- Example Sentences:
- She ran quickly to catch the bus.
- He is very talented at singing.
- They always arrive on time.
- She has never been to Japan.
- The car moved slowly through traffic.
- We often go for walks in the park.
- Please come here.
- She sings well.
- He almost missed the train.
- It is extremely cold outside.
Verb
A verb expresses an action, occurrence, or state of being.
- Example Words: run, jump, is, eat, sleep, write, talk, think, create, play
- Example Sentences:
- I run every morning to stay fit.
- He loves to jump on the trampoline.
- She is studying for her exams.
- They eat dinner at 7 p.m.
- I sleep eight hours every night.
- She likes to write in her journal.
- We can talk later about the details.
- He loves to think about new ideas.
- Artists create masterpieces.
- The children play outside after school.
Preposition
A preposition shows the relationship between a noun or pronoun and other words in a sentence.
- Example Words: in, on, under, above, beside, between, near, at, by, with
- Example Sentences:
- The cat is in the box.
- The book is on the table.
- The dog is hiding under the bed.
- The lamp is above the desk.
- The store is beside the post office.
- She sat between her two friends.
- The park is near my house.
- We will meet at the restaurant.
- He walked by the lake.
- I went to the movies with my friends.
Conjunction
A conjunction connects words, phrases, or clauses in a sentence.
- Example Words: and, but, or, because, so, yet, although, if, unless, while
- Example Sentences:
- I like pizza and pasta.
- He is tall, but she is taller.
- Do you want coffee or tea?
- I didn’t go to the party because I was sick.
- She was tired, so she went to bed early.
- It’s raining, yet we are going out.
- Although it’s late, I’ll still go.
- If you study, you will pass.
- I can’t help you unless you ask.
- She sang while playing the guitar.
Interjection
An interjection expresses a sudden feeling or reaction, often standing alone.
- Example Words: wow, ouch, hey, oh, ah, uh, hmm, yikes, hooray, oops
- Example Sentences:
- Wow, that’s amazing!
- Ouch, that hurt!
- Hey, wait for me!
- Oh, I forgot my keys.
- Ah, I see what you mean.
- Uh, I’m not sure about that.
- Hmm, that’s an interesting idea.
- Yikes, that was close!
- Hooray, we won the game!
- Oops, I dropped it.
Determiner
A determiner modifies a noun, giving more information about it. They often introduce noun phrases.
- Example Words: a, an, the, some, many, few, all, this, that, these
- Example Sentences:
- A dog is barking outside.
- She bought an apple.
- The book is on the shelf.
- Some people are coming to the event.
- Many students failed the test.
- Few people attended the meeting.
- All of the cookies are gone.
- This chair is uncomfortable.
- That restaurant serves great food.
- These shoes are new.
Article
Articles are a type of determiner used to specify a noun as something general or specific.
- Example Words: a, an, the
- Example Sentences:
- A car passed by.
- She ate an apple.
- The dog is sleeping.
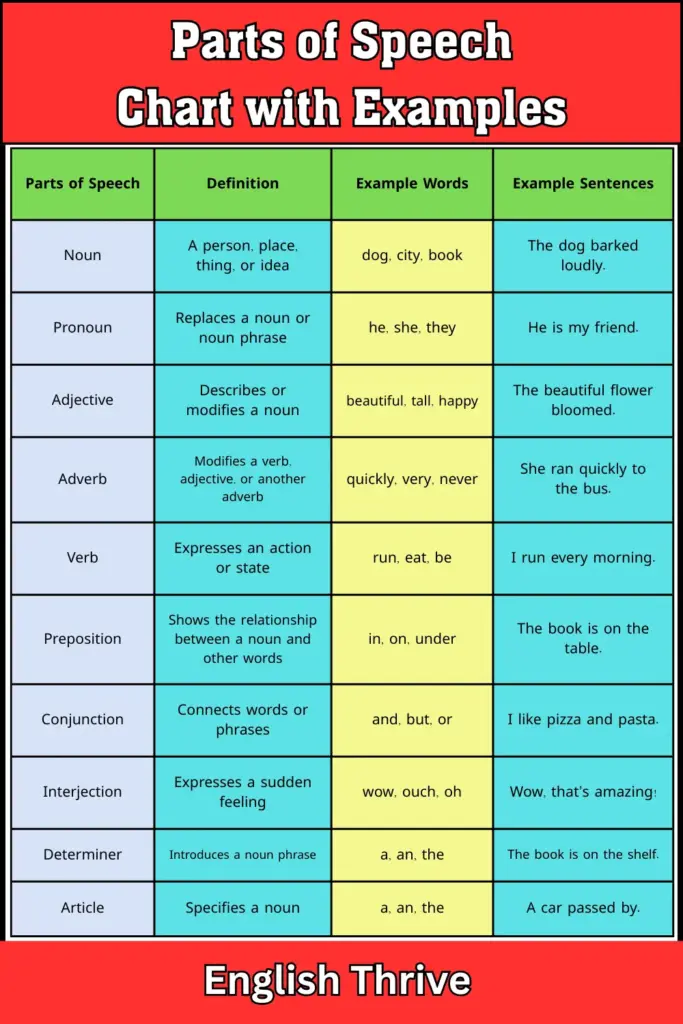
Parts of Speech Chart with Examples – 1
| Parts of Speech | Definition | Example Words | Example Sentences |
| Noun | A person, place, thing, or idea | dog, city, book | The dog barked loudly. |
| Pronoun | Replaces a noun or noun phrase | he, she, they | He is my friend. |
| Adjective | Describes or modifies a noun | beautiful, tall, happy | The beautiful flower bloomed. |
| Adverb | Modifies a verb, adjective, or another adverb | quickly, very, never | She ran quickly to the bus. |
| Verb | Expresses an action or state | run, eat, be | I run every morning. |
| Preposition | Shows the relationship between a noun and other words | in, on, under | The book is on the table. |
| Conjunction | Connects words or phrases | and, but, or | I like pizza and pasta. |
| Interjection | Expresses a sudden feeling | wow, ouch, oh | Wow, that’s amazing! |
| Determiner | Introduces a noun phrase | a, an, the | The book is on the shelf. |
| Article | Specifies a noun | a, an, the | A car passed by. |
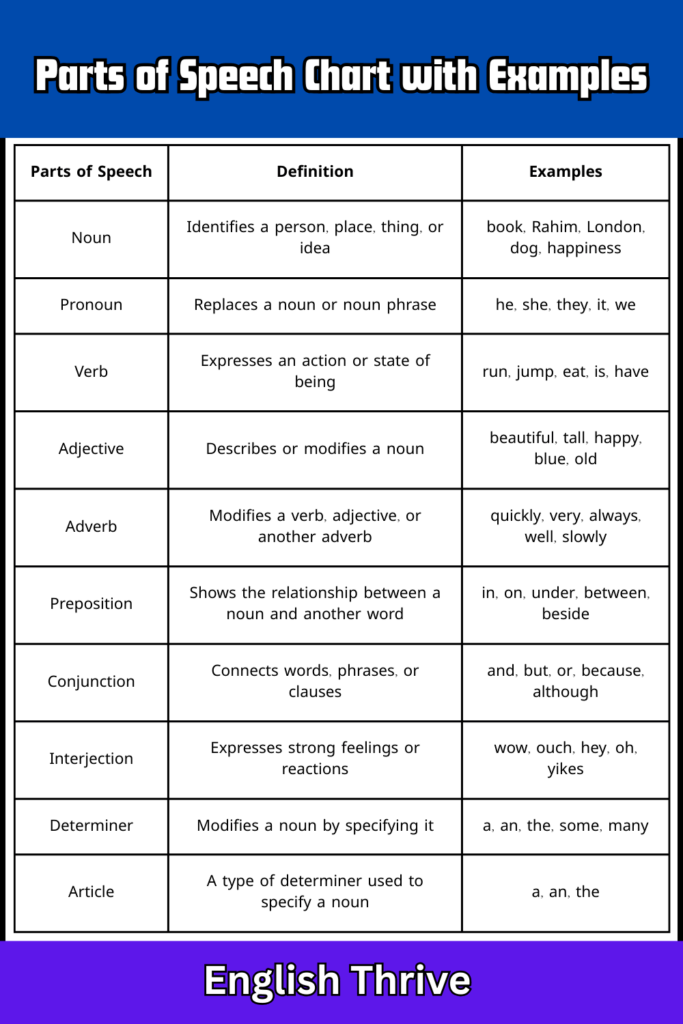
Parts of Speech Chart with Examples – 2
| Parts of Speech | Definition | Examples |
| Noun | Identifies a person, place, thing, or idea | book, Rahim, London, dog, happiness |
| Pronoun | Replaces a noun or noun phrase | he, she, they, it, we |
| Verb | Expresses an action or state of being | run, jump, eat, is, have |
| Adjective | Describes or modifies a noun | beautiful, tall, happy, blue, old |
| Adverb | Modifies a verb, adjective, or another adverb | quickly, very, always, well, slowly |
| Preposition | Shows the relationship between a noun and another word | in, on, under, between, beside |
| Conjunction | Connects words, phrases, or clauses | and, but, or, because, although |
| Interjection | Expresses strong feelings or reactions | wow, ouch, hey, oh, yikes |
| Determiner | Modifies a noun by specifying it | a, an, the, some, many |
| Article | A type of determiner used to specify a noun | a, an, the |
FAQs About Parts of Speech Chart with Examples
Which are the 8 parts of speech?
The 8 traditional parts of speech are: nouns, pronouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, prepositions, conjunctions, and interjections.
What are the 9 different parts of speech?
The 9 parts of speech often include the 8 basic parts plus determiners or articles as a separate category.
What is the 10th part of speech?
Some grammar experts include determiners and articles as a tenth category, depending on the classification.
What are adverbs?
Adverbs are words that modify verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs, providing more details about how, when, where, or to what extent something happens.
What are the types of nouns?
Nouns can be common or proper, countable or uncountable, abstract or concrete, among other classifications.
Final thoughts
I hope that this article covered everything about parts of speech chart with examples. If you keep practicing with charts and exerciser provided, then you will be able to identify and use parts of speech properly.

