Understanding metaphors is crucial for mastering the nuances of the English language. Metaphors allow us to express complex emotions and ideas in a vivid and relatable way.
One common emotion often described metaphorically is fear. This article delves into the world of metaphors used to describe fear, providing a comprehensive overview of their types, structure, usage, and common mistakes.
Contents
ToggleDefinition of Metaphor and Its Role in Describing Fear
A metaphor is a figure of speech that directly compares two unrelated things. Unlike similes, which use “like” or “as” to make a comparison, metaphors state that one thing *is* another. This creates a vivid image or understanding by transferring qualities from one concept to another. Metaphors are essential in English because they allow for concise and impactful communication, adding depth and color to language.
In the context of fear, metaphors provide a powerful way to express the often overwhelming and intangible feeling. Instead of simply stating “I am scared,” a metaphor can paint a much more evocative picture: “My heart was a trapped bird” or “Fear was a cold hand on my spine.” These metaphors tap into shared human experiences and sensory details to convey the intensity and nature of the emotion.
Structural Breakdown of Metaphors for Scared
Metaphors for scared typically consist of two main elements: the tenor and the vehicle. The tenor is the subject being described (in this case, the feeling of fear or the person experiencing fear), and the vehicle is the object or concept used to represent it. The connection between the tenor and vehicle is based on shared characteristics or associations.
For example, in the metaphor “He was frozen with fear,” the tenor is “he” (the person experiencing fear), and the vehicle is “frozen.” The shared characteristic is the inability to move or react, which effectively conveys the paralyzing effect of fear. Understanding this structure helps in both interpreting and creating effective metaphors.
The effectiveness of a metaphor also relies on its context. The surrounding words, phrases, and the overall situation contribute to the meaning and impact of the metaphor. A metaphor that works well in one context might be confusing or ineffective in another. Careful consideration of the audience and the intended message is crucial.
Types and Categories of Metaphors for Scared
Metaphors for scared can be categorized based on the type of vehicle used to describe the feeling. Here are some common categories:
Animal Metaphors
Animal metaphors often draw on the instinctive reactions and vulnerability associated with animals to represent fear. These metaphors can evoke feelings of helplessness, panic, or being preyed upon.
Physical Sensation Metaphors
These metaphors use physical sensations like coldness, heat, pressure, or pain to describe the feeling of fear. They connect the abstract emotion to tangible experiences, making the fear more relatable and immediate.
Weather Metaphors
Weather metaphors utilize the power and unpredictability of natural phenomena to illustrate the overwhelming and uncontrollable nature of fear. They can convey a sense of impending doom or chaotic emotional turmoil.
Object Metaphors
Object metaphors use inanimate objects to represent the feeling of fear. These metaphors often focus on the object’s properties, such as fragility, confinement, or darkness, to convey the specific aspects of fear being experienced.
Motion Metaphors
Motion metaphors use movement or lack thereof to describe the experience of fear. These metaphors can illustrate the feeling of being overwhelmed, paralyzed, or propelled into action by fear.
Examples of Metaphors for Scared
Here are some examples of metaphors for ‘scared,’ organized by category:
Table 1: Animal Metaphors for Scared
| Metaphor | Explanation |
|---|---|
| He was a deer caught in headlights. | He was paralyzed by fear, unable to react. |
| She felt like a mouse cornered by a cat. | She felt trapped and vulnerable, with no escape. |
| His courage turned tail and ran. | His bravery disappeared, replaced by overwhelming fear. |
| They were like sheep being led to slaughter. | They felt helpless and doomed in the face of danger. |
| The fear gnawed at him like a rat. | The fear was persistent and destructive, eating away at his peace. |
| She was as timid as a newborn fawn. | She was extremely fearful and easily frightened. |
| He trembled like a leaf in the wind. | His body shook uncontrollably due to fear. |
| Her heart fluttered like a trapped bird. | Her heart beat rapidly and erratically due to anxiety. |
| He was a caged lion, pacing with fear. | He was restless and agitated, confined by his fear. |
| She felt like a lamb among wolves. | She felt vulnerable and surrounded by danger. |
| His fear was a snake coiling in his stomach. | The fear was constricting and unsettling, causing physical discomfort. |
| They scattered like cockroaches when the light turned on. | They fled quickly and in disarray due to sudden fear. |
| She was as skittish as a wild horse. | She was easily startled and prone to fear. |
| He felt like a lone wolf surrounded by hunters. | He felt isolated and threatened by unseen dangers. |
| Her fear was a spider spinning a web around her. | The fear was trapping and ensnaring, limiting her actions. |
| He was as quiet as a church mouse. | He was very quiet and timid due to fear. |
| She felt like a bird with clipped wings. | She felt helpless and unable to escape her fear. |
| His fear was a swarm of bees buzzing in his head. | The fear was overwhelming and chaotic, filling his thoughts. |
| They huddled together like penguins in a storm. | They sought comfort and safety in numbers due to fear. |
| She was as jumpy as a kangaroo. | She was very nervous and easily startled. |
| His fear was a vulture circling overhead. | The fear was a constant threat, looming over him. |
This table illustrates how metaphors using animals can effectively convey the feeling of fear through associations with vulnerability, panic, and helplessness.
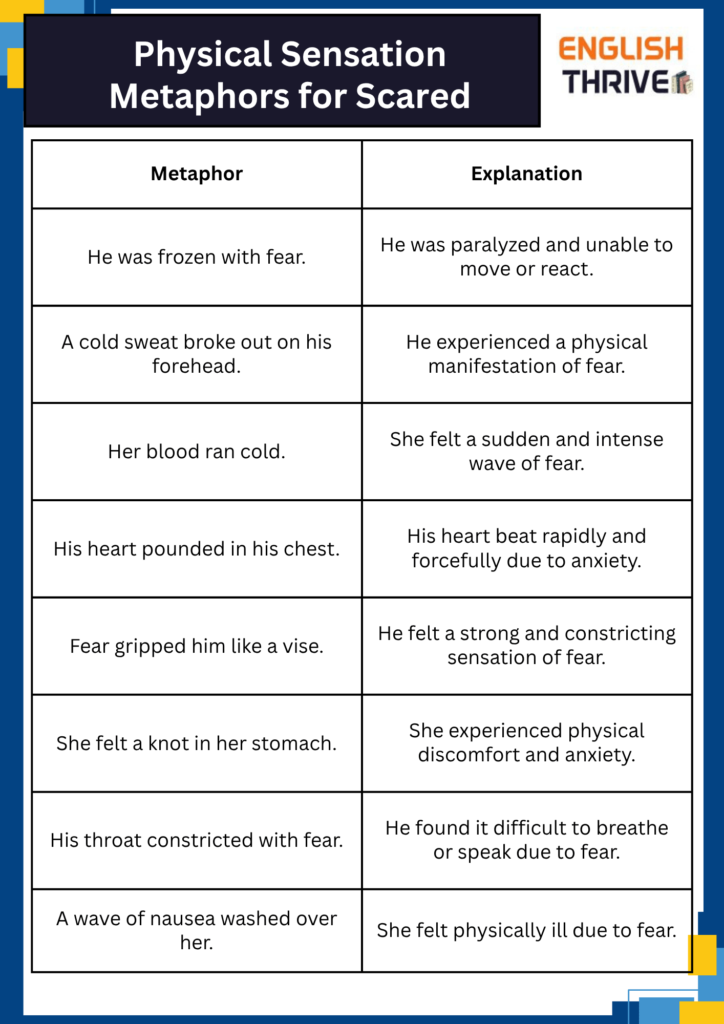
Table 2: Physical Sensation Metaphors for Scared
| Metaphor | Explanation |
|---|---|
| He was frozen with fear. | He was paralyzed and unable to move or react. |
| A cold sweat broke out on his forehead. | He experienced a physical manifestation of fear. |
| Her blood ran cold. | She felt a sudden and intense wave of fear. |
| His heart pounded in his chest. | His heart beat rapidly and forcefully due to anxiety. |
| Fear gripped him like a vise. | He felt a strong and constricting sensation of fear. |
| She felt a knot in her stomach. | She experienced physical discomfort and anxiety. |
| His throat constricted with fear. | He found it difficult to breathe or speak due to fear. |
| A wave of nausea washed over her. | She felt physically ill due to fear. |
| He felt a chill run down his spine. | He experienced a sudden and unsettling sensation of fear. |
| Her hands were clammy with fear. | Her hands were sweaty and cold due to anxiety. |
| He felt a lump in his throat. | He felt emotional and choked up with fear. |
| She felt lightheaded with fear. | She felt dizzy and faint due to anxiety. |
| His legs turned to jelly. | His legs felt weak and unstable due to fear. |
| She felt a burning sensation in her chest. | She experienced a physical manifestation of anxiety and fear. |
| He felt like his skin was crawling. | He experienced an unsettling and uncomfortable sensation of fear. |
| She felt a crushing weight on her chest. | She felt overwhelmed and suffocated by fear. |
| His muscles were tense with fear. | His body was rigid and strained due to anxiety. |
| She felt a prickling sensation on the back of her neck. | She experienced a heightened sense of awareness and fear. |
| He felt like his stomach was tied in knots. | He experienced intense physical discomfort and anxiety. |
| She felt a jolt of fear run through her. | She experienced a sudden and intense surge of fear. |
| He felt his heart skip a beat. | His heart beat irregularly due to fear. |
| She felt like she couldn’t catch her breath. | She had difficulty breathing due to anxiety. |
This table showcases how metaphors using physical sensations can effectively convey the feeling of fear by connecting it to tangible and relatable experiences.
Table 3: Weather Metaphors for Scared
| Metaphor | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Fear washed over him like a tidal wave. | He was overwhelmed by an immense and unstoppable wave of fear. |
| A storm of fear raged inside her. | She experienced intense and tumultuous emotions of fear. |
| He was caught in a whirlwind of panic. | He was swept up in a chaotic and disorienting state of fear. |
| Dark clouds of fear gathered in his mind. | Ominous and threatening thoughts of fear filled his mind. |
| A chilling wind of fear swept through the room. | A palpable sense of fear and unease spread throughout the room. |
| She was engulfed in a fog of fear. | She was disoriented and unable to think clearly due to fear. |
| He felt like he was drowning in a sea of fear. | He felt overwhelmed and suffocated by his fear. |
| A thunderclap of fear shook him to his core. | He experienced a sudden and shocking jolt of fear. |
| She was weathering a hurricane of anxiety. | She was enduring a period of intense and overwhelming anxiety. |
| He felt like he was standing in the eye of the storm. | He felt a brief moment of calm amidst the chaos of fear. |
| A drizzle of fear turned into a downpour. | A small amount of fear quickly escalated into an overwhelming amount. |
| She was blinded by a blizzard of fear. | She was unable to see or think clearly due to intense fear. |
| He felt like he was being struck by lightning. | He experienced a sudden and intense shock of fear. |
| She was caught in the crosswinds of her fears. | She was pulled in different directions by conflicting fears. |
| He felt like he was being buried alive in an avalanche of fear. | He felt completely overwhelmed and suffocated by his fear. |
| She was navigating through a dense fog of uncertainty and fear. | She was struggling to find her way through a confusing and frightening situation. |
| He felt the ground tremble beneath his feet. | He sensed an impending threat or danger. |
| She felt the sun disappear behind a wall of clouds. | She felt hope and optimism fade away due to fear. |
| He felt like he was adrift at sea in a storm. | He felt lost and helpless in the face of overwhelming fear. |
| She was bracing herself for the inevitable storm. | She was preparing for a difficult and frightening situation. |
This table demonstrates how weather metaphors can effectively convey the feeling of fear by drawing on the power and unpredictability of natural events.
Table 4: Object Metaphors for Scared
| Metaphor | Explanation |
|---|---|
| He felt like a fragile vase about to shatter. | He felt vulnerable and on the verge of breaking down. |
| Her courage was a flickering candle in the wind. | Her bravery was weak and could easily be extinguished. |
| Fear was a heavy chain dragging him down. | Fear was a burden that hindered his progress. |
| He felt like a puppet on strings, controlled by his fear. | He felt powerless and manipulated by his fear. |
| She felt trapped in a cage of her own making. | She felt confined and unable to escape her fears. |
| He was a tightly wound spring, ready to snap. | He was extremely tense and on the verge of losing control. |
| Her heart was a drum beating a frantic rhythm. | Her heart beat rapidly and erratically due to anxiety. |
| He felt like a ticking time bomb, about to explode. | He felt overwhelmed and on the verge of losing control. |
| She was a broken record, repeating her fears over and over. | She was obsessively dwelling on her fears. |
| He felt like a shadow lurking in the darkness. | He felt unseen and vulnerable, consumed by his fear. |
| She was a tightly closed book, afraid to reveal her vulnerabilities. | She was guarded and unwilling to share her fears. |
| He felt like a lone tree standing against a strong wind. | He felt isolated and vulnerable in the face of adversity. |
| She was a fragile glass, easily shattered by fear. | She was emotionally vulnerable and easily hurt. |
| He felt like a rusty lock, unable to open up and express his feelings. | He was emotionally closed off and unable to share his fears. |
| She was a tightly sealed jar, holding in all her fears. | She was suppressing her emotions and anxieties. |
| He felt like a worn-out tire, unable to keep going. | He felt exhausted and overwhelmed by his fears. |
| She was a tangled thread, unable to unravel her anxieties. | She felt confused and overwhelmed by her fears. |
| He felt like a deflated balloon, lacking energy and enthusiasm. | He felt drained and unmotivated due to fear. |
| She was a tightly coiled rope, ready to snap under pressure. | She was extremely tense and on the verge of losing control. |
| He felt like a broken mirror, unable to see himself clearly. | He felt distorted and lost due to fear. |
This table illustrates how object metaphors can effectively convey the feeling of fear by focusing on the object’s properties, such as fragility, confinement, or darkness.
Table 5: Motion Metaphors for Scared
| Metaphor | Explanation |
|---|---|
| He was running scared. | He was acting out of fear, trying to avoid danger. |
| Fear propelled her forward. | Fear motivated her to take action. |
| He was paralyzed by fear. | He was unable to move or react due to fear. |
| She was swept away by a wave of fear. | She was overwhelmed by an intense surge of fear. |
| He was sinking into a pit of despair. | He was becoming increasingly hopeless and fearful. |
| She was spiraling out of control. | She was losing control and becoming increasingly fearful. |
| He was treading water, struggling to stay afloat. | He was struggling to cope with his fears. |
| She was walking on eggshells. | She was being extremely cautious and careful due to fear. |
| He was skating on thin ice. | He was in a risky situation and could easily make a mistake. |
| She was climbing a mountain of fear. | She was facing a difficult and daunting challenge. |
| He was dodging bullets of anxiety. | He was trying to avoid stressful and frightening situations. |
| She was dancing with her demons. | She was confronting and grappling with her fears. |
| He was jumping through hoops of fear. | He was going to great lengths to avoid his fears. |
| She was tiptoeing around her anxieties. | She was carefully avoiding triggering her anxieties. |
| He was running in circles, trapped by his fears. | He was unable to escape his anxieties and fears. |
| She was building walls around her heart. | She was protecting herself from emotional pain and vulnerability. |
| He was digging himself into a hole of despair. | He was worsening his situation by giving in to his fears. |
| She was chasing shadows of her past. | She was haunted by past traumas and anxieties. |
| He was drifting aimlessly in a sea of uncertainty. | He felt lost and without direction due to fear. |
| She was hiding behind a mask of bravery. | She was concealing her fear and vulnerability. |
This table demonstrates how motion metaphors can effectively convey the experience of fear by illustrating the feeling of being overwhelmed, paralyzed, or propelled into action.
Usage Rules for Metaphors Describing Fear
When using metaphors to describe fear, it’s essential to follow certain guidelines to ensure clarity and impact:
- Choose relevant vehicles: Select objects or concepts that have a clear and logical connection to the feeling of fear. The association should be readily apparent to the audience.
- Maintain consistency: Avoid mixing metaphors or shifting between unrelated images. This can create confusion and weaken the impact of the metaphor.
- Consider the context: Ensure that the metaphor is appropriate for the tone and style of the writing or conversation. A highly dramatic metaphor might be out of place in a casual setting.
- Avoid clichés: Steer clear of overused metaphors that have lost their impact. Aim for originality and freshness in your imagery.
- Be mindful of your audience: Consider the cultural background and experiences of your audience when choosing metaphors. Some metaphors may not resonate with everyone.
Example of Consistent Metaphor Usage:
Correct: “Fear was a dark cloud hanging over him, casting a shadow on his every thought. The storm within him threatened to erupt at any moment.”
Incorrect: “Fear was a dark cloud hanging over him, but he decided to grab the bull by the horns and swim against the tide.” (Mixing unrelated metaphors)
Common Mistakes When Using Metaphors for Scared
Here are some common mistakes to avoid when using metaphors for scared:
- Using mixed metaphors: Combining unrelated images that create a confusing and illogical picture.
- Using clichés: Relying on overused metaphors that have lost their impact and originality.
- Being too literal: Creating metaphors that are too obvious or simplistic, failing to add depth or insight.
- Ignoring the context: Using metaphors that are inappropriate for the tone or audience.
- Overusing metaphors: Cluttering writing with too many metaphors, which can become distracting and overwhelming.
Table 6: Correct vs. Incorrect Metaphor Usage
| Incorrect | Correct | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| “He was scared as a cat on a hot tin roof, but he decided to bite the bullet.” | “He was as scared as a cat on a hot tin roof.” | Avoid mixing clichés. Choose one image and stick with it. |
| “Fear was like, you know, a bad thing.” | “Fear was a relentless pursuer, always one step behind him.” | Avoid vague or simplistic metaphors. Choose a specific and evocative image. |
| “The politician’s speech was a hurricane of fear.” (in a light-hearted blog post) | “The rollercoaster was a thrill ride, but I felt a flutter of fear as we climbed the first hill.” | Consider the context and tone. A dramatic metaphor might be inappropriate for a casual setting. |
| “He was scared, like, really scared.” | “He was a deer caught in headlights, paralyzed by fear.” | Avoid being too literal. A metaphor should add depth and insight. |
Practice Exercises
Test your understanding of metaphors for scared with these exercises:
Exercise 1: Identify the Metaphor
Identify the metaphor used to describe fear in each sentence.
Table 7: Practice Exercise 1
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| 1. Fear was a cold hand on her shoulder. | Fear was a cold hand |
| 2. He felt like a mouse trapped in a corner. | He felt like a mouse trapped in a corner |
| 3. The threat hung over them like a dark cloud. | threat hung over them like a dark cloud |
| 4. She was frozen to the spot with terror. | frozen to the spot |
| 5. His heart hammered against his ribs, a frantic drumbeat of fear. | heart hammered against his ribs, a frantic drumbeat of fear |
| 6. He was running scared after the incident. | running scared |
| 7. Her voice was a mere whisper of fear. | voice was a mere whisper |
| 8. A tidal wave of panic washed over him. | tidal wave of panic |
| 9. The fear was a knot tightening in her stomach. | fear was a knot tightening |
| 10. He was walking on eggshells around his boss. | walking on eggshells |
Exercise 2: Complete the Metaphor
Complete the following sentences with an appropriate metaphor for scared.
Table 8: Practice Exercise 2
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| 1. He was as ________ as a lamb. | He was as timid as a lamb. |
| 2. Fear was a ________ in his throat. | Fear was a lump in his throat. |
| 3. She felt like she was ________ in a sea of anxiety. | She felt like she was drowning in a sea of anxiety. |
| 4. The news hit him like a ________. | The news hit him like a thunderbolt. |
| 5. He felt ________ with fear. | He felt paralyzed with fear. |
| 6. Her mind was a ________ of worry. | Her mind was a whirlwind of worry. |
| 7. He was a ________ waiting to explode. | He was a time bomb waiting to explode. |
| 8. Fear was a ________ around his heart. | Fear was a vise around his heart. |
| 9. She felt like a ________ in the face of the challenge. | She felt like a pebble in the face of the challenge. |
| 10. The uncertainty cast a ________ over their future. | The uncertainty cast a shadow over their future. |
Exercise 3: Rewrite with a Metaphor
Rewrite the following sentences using a metaphor to describe the feeling of fear.
Table 9: Practice Exercise 3
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| 1. He was very scared when he heard the noise. | He was a deer caught in headlights when he heard the noise. |
| 2. She felt trapped and anxious about the situation. | She felt like a bird trapped in a cage, anxious about the situation. |
| 3. The thought of public speaking filled him with dread. | The thought of public speaking was a dark cloud looming over him. |
| 4. She was so afraid that she couldn’t move. | She was frozen solid with fear. |
| 5. They were running away because they were terrified. | They were running scared, trying to escape the terror. |
| 6. The fear made his heart beat very fast. | Fear turned his heart into a frantic drum. |
| 7. She was so nervous that she could barely speak. | Her voice was a mere whisper of fear. |
| 8. He was overwhelmed by a sudden feeling of panic. | A tidal wave of panic washed over him. |
| 9. The fear made her stomach hurt. | The fear was a knot tightening in her stomach. |
| 10. He was being very careful because he was afraid of making a mistake. | He was walking on eggshells, afraid of making a mistake. |
Advanced Topics: Extending and Combining Metaphors
For advanced learners, extending and combining metaphors can add layers of complexity and nuance to your writing. Extending a metaphor involves developing a single image over multiple sentences or paragraphs, exploring its various facets and implications.
Combining metaphors involves weaving together two or more related images to create a richer and more textured description.
Example of Extended Metaphor:
“Fear was a relentless hunter, always on his trail. It stalked him through the shadows, its eyes gleaming in the darkness.
He could hear its breath on the back of his neck, feel its presence in every creak and groan of the house. There was no escape, no sanctuary from its pursuit.”
Example of Combined Metaphors:
“Fear was a dark cloud that had settled over her, casting a long shadow on her hopes and dreams. It was a heavy chain, dragging her down into a pit of despair, where she struggled to breathe under the weight of her anxieties.”
FAQs About Metaphors for Scared
What is the difference between a metaphor and a simile?
A metaphor directly compares two unlike things by stating that one thing *is* another (e.g., “He is a lion”). A simile also compares two unlike things, but it uses “like” or “as” to make the comparison (e.g., “He is as brave as a lion”).
Why are metaphors important in writing?
Metaphors add depth, color, and vividness to writing. They help to create a stronger connection with the reader by using familiar images to convey abstract ideas or emotions. They also make writing more engaging and memorable.
How can I avoid using clichés in my metaphors?
To avoid clichés, try to think of original and unexpected ways to describe the feeling of fear. Consider using sensory details, personal experiences, or unusual combinations of objects and concepts. Read widely and pay attention to the metaphors used by other writers to inspire your own creativity.
Is it possible to overuse metaphors?
Yes, it is possible to overuse metaphors. Cluttering your writing with too many metaphors can become distracting and overwhelming for the reader. Use metaphors sparingly and strategically to maximize their impact.
How do I choose the right metaphor for a particular situation?
Consider the context, tone, and audience when choosing a metaphor. Select an image that is relevant, appropriate, and likely to resonate with your readers or listeners. Think about the specific aspects of fear that you want to convey and choose a metaphor that effectively captures those qualities.
What if my metaphor is misinterpreted?
Metaphors can sometimes be open to interpretation, but you can minimize the risk of misinterpretation by choosing clear and familiar images, providing sufficient context, and avoiding overly complex or obscure comparisons. If you’re concerned about potential confusion, you can also explain the intended meaning of the metaphor directly.
Can metaphors be used in spoken language, or are they only for writing?
Metaphors are commonly used in both spoken and written language. They can add color and expressiveness to everyday conversations, presentations, and speeches. However, it’s important to be mindful of your audience and choose metaphors that are appropriate for the situation.
How can I improve my ability to create effective metaphors?
Practice is key to improving your ability to create effective metaphors. Read widely, pay attention to the metaphors used by other writers, and experiment with different combinations of images and concepts. Ask for feedback from others on your metaphors and be willing to revise and refine your work.
Conclusion
Metaphors are powerful tools for expressing the complex emotion of fear. By understanding the different types of metaphors, following usage guidelines, and avoiding common mistakes, you can effectively use these figures of speech to add depth, color, and impact to your writing and communication.
Practice the exercises provided, and continue to explore the creative possibilities of metaphorical language to enhance your ability to convey the nuances of human experience.