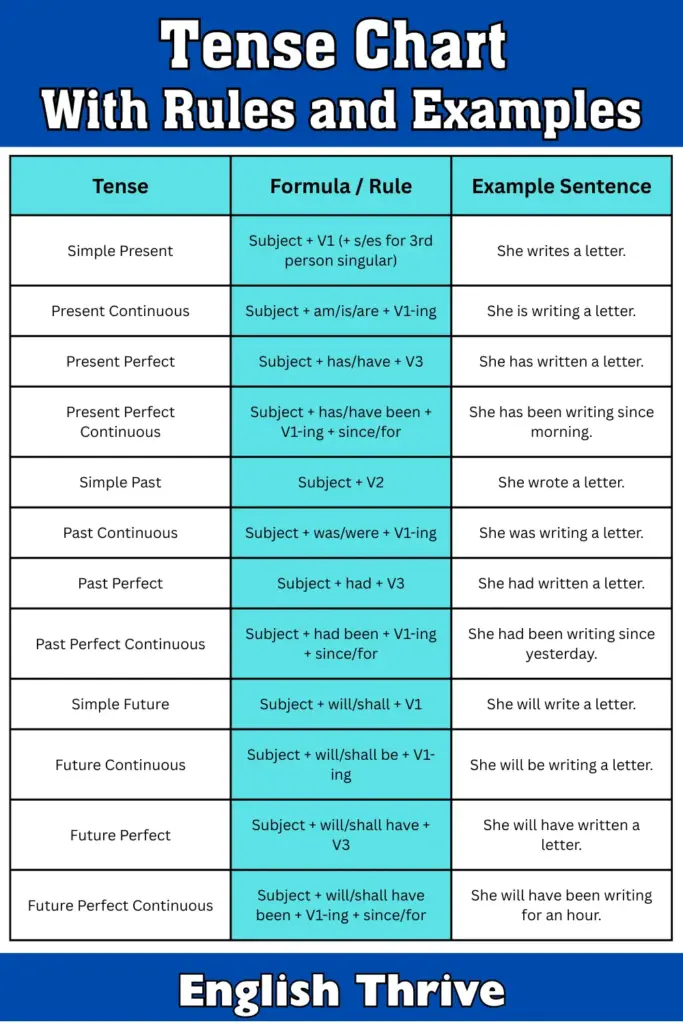
The tense chart with rules and examples serves as your guide to mastering English speaking and writing. Tenses are essential because they indicate when an action takes place – whether it’s in the past, present, or future. Once you understand tenses, your sentences will become clearer, making it easier for others to understand you.
In this guide, you’ll discover:
A simple chart that outlines 12 English tenses with simple rules and examples.
Clear explanations of the present, past, and future tenses.
A handy PDF that you can download and refer to anytime for quick practice.
Whether you’re just starting your English journey or looking to boost your confidence in conversation, this tense chart will guide you every step of the way.
Contents
ToggleWhat Are Tenses in English Grammar?
In grammar, tense is the form of a verb that shows the time of an action or event. The correct use of tenses ensures your sentences make sense and convey the right meaning.
There are three main tenses in English:
- Present Tense – talks about actions happening now.
- Past Tense – talks about actions that already happened.
- Future Tense – talks about actions that will happen.
Each of these has four aspects: Simple, Continuous, Perfect, and Perfect Continuous — giving us 12 tenses in total.
Tense Chart With Rules and Examples
Here’s a quick-reference tense chart showing all 12 tenses with their formulas and examples:
| Tense | Formula / Rule | Example Sentence |
|---|---|---|
| Simple Present | Subject + V1 (+ s/es for 3rd person singular) | She writes a letter. |
| Present Continuous | Subject + am/is/are + V1-ing | She is writing a letter. |
| Present Perfect | Subject + has/have + V3 | She has written a letter. |
| Present Perfect Continuous | Subject + has/have been + V1-ing + since/for | She has been writing since morning. |
| Simple Past | Subject + V2 | She wrote a letter. |
| Past Continuous | Subject + was/were + V1-ing | She was writing a letter. |
| Past Perfect | Subject + had + V3 | She had written a letter. |
| Past Perfect Continuous | Subject + had been + V1-ing + since/for | She had been writing since yesterday. |
| Simple Future | Subject + will/shall + V1 | She will write a letter. |
| Future Continuous | Subject + will/shall be + V1-ing | She will be writing a letter. |
| Future Perfect | Subject + will/shall have + V3 | She will have written a letter. |
| Future Perfect Continuous | Subject + will/shall have been + V1-ing + since/for | She will have been writing for an hour. |
Present Tense Chart and Rules
The Present Tense is used to describe actions that are happening now, actions that happen regularly, or facts that are always true.
There are four types of present tense:
1) Simple Present Tense
Formula:
Subject + Base Verb (V1) / Base Verb + s/es (3rd person singular)
Usage:
- For habits and routines: I drink coffee every morning.
- For universal truths: The sun rises in the east.
- For fixed schedules: The train leaves at 9 a.m.
Examples:
- He goes to the gym daily.
- They play football every weekend.
Common Mistake: Forgetting to add s/es for third-person singular subjects.
Wrong: She go to school every day.
Correct: She goes to school every day.
2) Present Continuous Tense
Formula:
Subject + am/is/are + Verb (V1) + ing
Usage:
- For actions happening right now: She is studying.
- For temporary situations: I am living in New York for a month.
- For planned future actions: We are meeting tomorrow.
Examples:
- I am reading a book.
- They are playing cricket in the park.
Common Mistake: Using stative verbs (e.g., know, like) in continuous form.
Wrong: I am knowing the answer.
Correct: I know the answer.
3) Present Perfect Tense
Formula:
Subject + has/have + Past Participle (V3)
Usage:
- For actions completed at an unspecified time: I have visited London.
- For life experiences: She has never seen snow.
- For actions that started in the past and continue: He has worked here since 2018.
Examples:
- I have finished my homework.
- She has read three books this week.
Common Mistake: Confusing past simple with present perfect.
Wrong: I have seen him yesterday.
Correct: I saw him yesterday. (Use past simple with specific time.)
4) Present Perfect Continuous Tense
Formula:
Subject + has/have been + Verb (V1) + ing + since/for
Usage:
- For actions started in the past and continuing now: I have been studying for two hours.
- For recent continuous activities: She has been running, so she is tired.
Examples:
- We have been waiting for you since 5 p.m.
- He has been working here for three years.
Common Mistake: Forgetting been in the formula.
Wrong: I have working here for three years.
Correct: I have been working here for three years.
Past Tense Chart and Rules
The Past Tense is used to describe actions or events that have already happened.
There are four types of past tense:
1) Simple Past Tense
Formula:
Subject + Verb (V2)
Usage:
- For completed actions at a specific time in the past: She visited Paris last year.
- For sequences of past events: He entered the room, sat down, and started reading.
Examples:
- We watched a movie last night.
- He played football yesterday.
Common Mistake: Using V1 instead of V2.
Wrong: I go to school yesterday.
Correct: I went to school yesterday.
2) Past Continuous Tense
Formula:
Subject + was/were + Verb (V1) + ing
Usage:
- For actions happening at a specific moment in the past: They were playing football at 5 p.m.
- For background actions in stories: It was raining when I woke up.
Examples:
- She was reading a book when I called.
- We were having dinner at that time.
Common Mistake: Mixing past simple and past continuous incorrectly.
Wrong: When I arrived, they play football.
Correct: When I arrived, they were playing football.
3) Past Perfect Tense
Formula:
Subject + had + Past Participle (V3)
Usage:
- For actions completed before another past action: I had finished my homework before she came.
- For emphasizing the order of past events.
Examples:
- They had left before the train arrived.
- She had cooked dinner before we got home.
Common Mistake: Using past simple instead of past perfect in sequences.
Wrong: I finished my work before she came. (Not wrong, but less precise)
Correct: I had finished my work before she came. (Shows clear order)
4) Past Perfect Continuous Tense
Formula:
Subject + had been + Verb (V1) + ing + since/for
Usage:
- For ongoing actions in the past that continued until another past action: I had been studying for two hours before the power went out.
- For showing cause of something in the past: She was tired because she had been working all day.
Examples:
- They had been waiting for an hour before the bus arrived.
- He had been living in New York for five years before moving to London.
Common Mistake: Forgetting the “been” part.
Wrong: I had working there for three years.
Correct: I had been working there for three years.
Future Tense Chart and Rules
The Future Tense is used to describe actions or events that have not yet happened but will occur later.
There are four types of future tense:
1) Simple Future Tense
Formula:
Subject + will/shall + Verb (V1)
Usage:
- For predictions: It will rain tomorrow.
- For promises or offers: I will help you with your homework.
- For decisions made at the moment of speaking: I’ll have tea instead of coffee.
Examples:
- We will visit London next month.
- She will join the meeting at 10 a.m.
Common Mistake: Forgetting to use “will” before the base verb.
Wrong: I go to the party tonight.
correct: I will go to the party tonight.
2) Future Continuous Tense
Formula:
Subject + will/shall + be + Verb (V1) + ing
Usage:
- For actions in progress at a specific future time: This time tomorrow, I will be flying to Dubai.
- For polite questions about plans: Will you be attending the conference?
Examples:
- He will be working late tonight.
- They will be traveling during the holidays.
Common Mistake: Using simple future instead of continuous for actions in progress.
Wrong: I will work at 5 p.m. tomorrow.
correct: I will be working at 5 p.m. tomorrow.
3) Future Perfect Tense
Formula:
Subject + will/shall + have + Past Participle (V3)
Usage:
- For actions completed before a specific time in the future: By next week, I will have finished this project.
Examples:
- She will have completed her degree by 2026.
- They will have built the bridge before the rainy season starts.
Common Mistake: Forgetting “have” in the formula.
Wrong: I will finished my work by tomorrow.
Correct: I will have finished my work by tomorrow.

4) Future Perfect Continuous Tense
Formula:
Subject + will/shall + have been + Verb (V1) + ing + since/for
Usage:
- For actions continuing up to a specific future point: By December, I will have been working here for 10 years.
Examples:
- She will have been studying English for five years by the time she graduates.
- They will have been traveling for a month when they return home.
Common Mistake: Dropping “been” from the structure.
Wrong: I will have working here for five years.
Correct: I will have been working here for five years.
Quick Reference: Downloadable Tense Chart PDF
Common Mistakes in Using Tenses
Many learners mix up tenses, leading to unclear sentences. Here are the most frequent mistakes and how to fix them:
| Mistake | Why It’s Wrong | Correct Form |
|---|---|---|
| I am knowing the answer. | Stative verbs don’t take continuous form. | I know the answer. |
| I have seen him yesterday. | Present perfect not used with specific past time. | I saw him yesterday. |
| She go to school daily. | Third-person singular needs “s/es”. | She goes to school daily. |
| They was playing football. | “They” requires plural past form “were”. | They were playing football. |
| I will finished my homework. | Missing “have” in future perfect tense. | I will have finished my homework. |
Exercises: Tense Chart With Rules and Examples
A. Fill in the blanks with the correct tense form:
- She ________ (read) a book when I called her yesterday.
- By this time next week, we ________ (complete) the project.
- I ________ (study) English for three years.
- They ________ (play) football at 5 p.m. yesterday.
- He ________ (visit) Paris last summer.
B. Correct the mistakes:
- I have been know him for years.
- We was going to the park when it rained.
- She write a letter yesterday.
- He will have working here for a year next month.
- They have finished their homework yesterday.
Here’s the answer sheet for your “Tense Chart With Rules and Examples” exercises.
Answer Sheet
A. Fill in the blanks with the correct tense form
- She was reading a book when I called her yesterday. (Past Continuous)
- By this time next week, we will have completed the project. (Future Perfect)
- I have been studying English for three years. (Present Perfect Continuous)
- They were playing football at 5 p.m. yesterday. (Past Continuous)
- He visited Paris last summer. (Simple Past)
B. Correct the mistakes
- Wrong: I have been know him for years.
Correct: I have known him for years. (Present Perfect) - Wrong: We was going to the park when it rained.
Correct: We were going to the park when it rained. (Past Continuous) - Wrong: She write a letter yesterday.
Correct: She wrote a letter yesterday. (Simple Past) - Wrong: He will have working here for a year next month.
Correct: He will have been working here for a year next month. (Future Perfect Continuous) - Wrong: They have finished their homework yesterday.
Correct: They finished their homework yesterday. (Simple Past)
FAQs about Tense Chart With Rules and Examples
What is a tense chart in grammar?
A tense chart is a table showing all 12 tenses, their formulas, and examples to help learners use correct verb forms in English.
How can I remember all 12 tenses easily?
Practice daily, use tense timelines, and group tenses by present, past, and future for better recall.
Which tense is used most in conversation?
The simple present tense is most common, as it’s used for routines, facts, and general statements.
What is the difference between perfect and perfect continuous tenses?
- Perfect tenses focus on completion of an action.
- Perfect continuous tenses focus on the duration of an ongoing action.
Conclusion
Learning all 12 tenses is an important step if you want to speak and write English with confidence. With this tense chart with rules and examples, you now have an easy-to-follow guide to help you understand when and how to use each tense.
Keep the free PDF handy for quick revision and try the exercises regularly. The more you practice, the more the tenses will feel natural in your everyday conversations and writing. Step by step, you will notice that your English is becoming clearer, smoother, and more fluent.