Understanding science words that start with N is essential for anyone exploring scientific literature, discussions, or studies. These words appear frequently across various scientific fields, from biology and chemistry to physics and medicine, playing a key role in expanding your scientific vocabulary.
This article serves as a comprehensive guide to science words that start with N, offering clear definitions, usage examples, and grammatical context. Whether you’re a student, researcher, educator, or simply someone passionate about science, mastering these terms will significantly boost your understanding and communication skills in the scientific world.
Contents
ToggleDefinition of Science Words Starting with N
Science words starting with “N” are used across various scientific fields to describe phenomena, processes, substances, and concepts. Understanding these terms is essential for accurate interpretation and clear communication.
For example, in biology, “nucleus” refers to the central part of a cell containing genetic material, while in physics, it describes the core of an atom. In chemistry, “neutralization” refers to a reaction that neutralizes acidity or alkalinity.
These words can function as nouns, verbs, adjectives, or adverbs, depending on the context. For instance, “nucleate” can be a verb describing the formation of a nucleus or an adjective related to it. Context is key to understanding the precise meaning and function of these terms.
Structural Breakdown of Science Words
Many science words come from Latin or Greek roots, prefixes, and suffixes. Recognizing these components helps decode unfamiliar terms. For example, “nano-” means one billionth (10-9), as seen in “nanotechnology.” The suffix “-ase” often refers to enzymes, like “nuclease.”
Breaking down words like “neovascularization”—where “neo-” means new, “vascular” refers to blood vessels, and “-ization” indicates a process—can make even complex terms easier to understand. Familiarity with these patterns enhances your ability to grasp and retain scientific vocabulary.
Types and Categories of Science Words Starting with N
Science words starting with “N” can be categorized based on the scientific discipline in which they are commonly used. Here are some of the major categories:
Biology
Biological terms starting with “N” are essential for understanding life processes, organisms, and their interactions. These terms are used in fields such as genetics, cell biology, ecology, and zoology.
Examples include: Nucleus (the control center of a cell), Neuron (a nerve cell), Niche (an organism’s role in an ecosystem), Nematode (a type of worm), Natural selection (the process by which organisms better adapted to their environment tend to survive and reproduce), Nitrogen fixation (the conversion of atmospheric nitrogen into usable forms by bacteria), Nutrient (a substance that provides nourishment essential for growth and the maintenance of life), Natal (pertaining to birth).
Chemistry
Chemical terms starting with “N” are used to describe elements, compounds, reactions, and properties of matter. These terms are fundamental to understanding chemical processes and the composition of substances.
Examples include: Nitrogen (a chemical element), Noble gas (a group of inert gases), Neutralization (a chemical reaction between an acid and a base), Nucleophile (a chemical species that donates an electron pair to form a chemical bond), Nonpolar (describing a molecule with an even distribution of electron density), Normality (a measure of concentration), Naphtalene (an aromatic hydrocarbon), Nitrate (a salt or ester of nitric acid).
Physics
Physical terms starting with “N” are used to describe fundamental concepts, laws, and phenomena related to energy, matter, and their interactions. These terms are essential for understanding the physical world.
Examples include: Newton (the SI unit of force), Neutron (a subatomic particle with no charge), Nuclear fission (the splitting of an atomic nucleus), Nuclear fusion (the combining of atomic nuclei), Node (a point of zero amplitude in a wave), Normal force (the force exerted by a surface perpendicular to the object in contact with it), Navier-Stokes equations (equations describing the motion of viscous fluids), N-type semiconductor (a semiconductor doped with impurities that contribute free electrons).
Medicine
Medical terms starting with “N” are used to describe diseases, conditions, treatments, and anatomical structures related to human health. These terms are essential for medical professionals and healthcare providers.
Examples include: Nerve (a bundle of fibers that transmits signals between the brain and other parts of the body), Necrosis (the death of cells or tissues), Neoplasm (an abnormal growth of tissue), Neurotransmitter (a chemical messenger that transmits signals between nerve cells), Nodule (a small swelling or aggregation of cells in the body), Narcotic (a drug that relieves pain and induces sleep), Nasopharynx (the upper part of the throat behind the nose), Neonatal (relating to newborn infants).
Environmental Science
Environmental science terms starting with “N” are used to describe ecological processes, environmental issues, and conservation efforts. These terms are essential for understanding the natural world and human impact on it.
Examples include: Nitrogen cycle (the biogeochemical cycle that describes the transformation of nitrogen and nitrogen-containing compounds in nature), Natural resources (materials or substances such as minerals, forests, water, and fertile land that occur in nature and can be used for economic gain), Native species (a species that is indigenous to a given region or ecosystem), Nonrenewable resources (resources that cannot be readily replaced by natural means on a level equal to their consumption), Noise pollution (harmful or annoying levels of noise), Nutrient pollution (pollution caused by excessive nutrients, such as nitrogen and phosphorus, in water bodies), National park (a reserve of land, usually declared and owned by a national government, protected from most development), Net primary productivity (the rate at which an ecosystem accumulates energy or biomass, excluding the energy used by the producers for respiration).
Examples of Science Words Starting with N
Here are several tables providing examples of science words starting with “N,” categorized by their scientific discipline. Each table includes the word, its definition, and an example sentence illustrating its use.
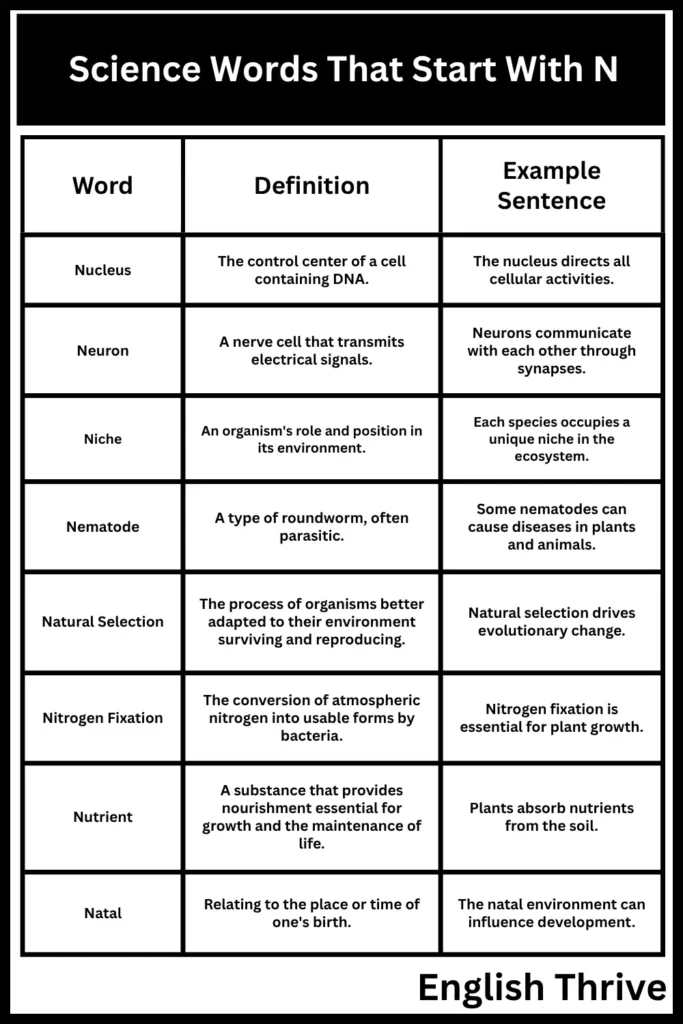
The following table provides examples of Biology words starting with N.
| Word | Definition | Example Sentence |
|---|---|---|
| Nucleus | The control center of a cell containing DNA. | The nucleus directs all cellular activities. |
| Neuron | A nerve cell that transmits electrical signals. | Neurons communicate with each other through synapses. |
| Niche | An organism’s role and position in its environment. | Each species occupies a unique niche in the ecosystem. |
| Nematode | A type of roundworm, often parasitic. | Some nematodes can cause diseases in plants and animals. |
| Natural Selection | The process of organisms better adapted to their environment surviving and reproducing. | Natural selection drives evolutionary change. |
| Nitrogen Fixation | The conversion of atmospheric nitrogen into usable forms by bacteria. | Nitrogen fixation is essential for plant growth. |
| Nutrient | A substance that provides nourishment essential for growth and the maintenance of life. | Plants absorb nutrients from the soil. |
| Natal | Relating to the place or time of one’s birth. | The natal environment can influence development. |
| Neurogenesis | The formation of new neurons in the brain. | Neurogenesis continues in some brain regions throughout adulthood. |
| Nuclease | An enzyme that cleaves nucleic acids. | Nucleases are important for DNA repair and replication. |
| Noncoding DNA | DNA sequences that do not encode proteins. | Noncoding DNA plays regulatory roles in gene expression. |
| Nymph | The immature form of some insects. | The nymph undergoes several molts before becoming an adult. |
| Node of Ranvier | A gap in the myelin sheath of a nerve cell. | The nodes of Ranvier facilitate rapid signal transmission. |
| Nocturnal | Active during the night. | Many animals are nocturnal to avoid predators. |
| Nacre | Also known as mother of pearl, a composite material produced by some mollusks. | The inside of the shell was lined with a beautiful nacre. |
| Nares | The nostrils or external openings of the nasal cavity. | Air enters the respiratory system through the nares. |
| Nanometer | A unit of length equal to one billionth of a meter, often used to measure very small biological structures. | Viruses are often measured in nanometers. |
| Necroptosis | A form of programmed cell death distinct from apoptosis. | Necroptosis can occur when apoptosis is blocked. |
| Nephron | The functional unit of the kidney, responsible for filtering blood and producing urine. | Each kidney contains millions of nephrons. |
| Neurula | An early stage in the development of a vertebrate embryo, characterized by the formation of the neural tube. | The neurula stage follows the gastrula stage in embryonic development. |
| Neutral mutation | A genetic mutation that has no effect on the fitness of an organism. | Many mutations are neutral mutations and do not affect phenotype. |
| Neuroglia | Also called glial cells, these are the support cells of the nervous system. | Neuroglia provide support and protection for neurons. |
| Notochord | A flexible rod-shaped structure that supports the body in the developing embryo of chordates. | The notochord is eventually replaced by the vertebral column in vertebrates. |
 Science Words That Start With N
Science Words That Start With N
The following table provides examples of Chemistry words starting with N.
| Word | Definition | Example Sentence |
|---|---|---|
| Nitrogen | A chemical element, symbol N, essential for life. | Nitrogen is a major component of the atmosphere. |
| Noble Gas | A group of inert gases with stable electron configurations. | Noble gases are used in lighting and other applications. |
| Neutralization | A chemical reaction between an acid and a base. | Neutralization reactions produce salt and water. |
| Nucleophile | A chemical species that donates an electron pair to form a chemical bond. | Nucleophiles are attracted to positive charges. |
| Nonpolar | Describing a molecule with an even distribution of electron density. | Nonpolar molecules are insoluble in water. |
| Normality | A measure of concentration, expressing the number of equivalents of solute per liter of solution. | The normality of the acid solution was precisely determined. |
| Naphthalene | A crystalline, aromatic, white solid hydrocarbon with formula C10H8. | Naphthalene is used in the production of mothballs. |
| Nitrate | A salt or ester of nitric acid, containing the NO3- anion. | Excess nitrates in water can cause pollution. |
| Nanomaterial | A material having structural components with at least one dimension in the size range of 1-100 nm. | Nanomaterials have unique properties due to their small size. |
| Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) | A spectroscopic technique used to observe local magnetic fields around atomic nuclei. | NMR can be used to determine the structure of molecules. |
| Nonmetal | An element that does not exhibit metallic properties. | Sulfur is a nonmetal. |
| Newtonian fluid | A fluid that has a constant viscosity, regardless of the shear rate. | Water is an example of a Newtonian fluid. |
| Nitrification | The biological oxidation of ammonia or ammonium to nitrite followed by the oxidation of nitrite to nitrate. | Nitrification is an important step in the nitrogen cycle. |
| Neutral compound | A compound that is neither acidic nor basic. | Water is a neutral compound. |
| Nanotube | A cylindrical molecule made of carbon atoms, with nanoscale dimensions. | Carbon nanotubes are used in various applications due to their strength and conductivity. |
| Neopentane | A highly branched alkane with five carbon atoms. | Neopentane is an isomer of pentane. |
| Nitride | A compound of nitrogen with a more electropositive element. | Silicon nitride is a hard, wear-resistant material. |
| Nitrous oxide | A colorless, non-flammable gas, commonly known as laughing gas. | Nitrous oxide is used as an anesthetic in dentistry. |
| Non-electrolyte | A substance that does not dissociate into ions when dissolved in water, and thus does not conduct electricity. | Sugar is a non-electrolyte. |
| Normal boiling point | The temperature at which a liquid boils under standard atmospheric pressure. | The normal boiling point of water is 100 degrees Celsius. |
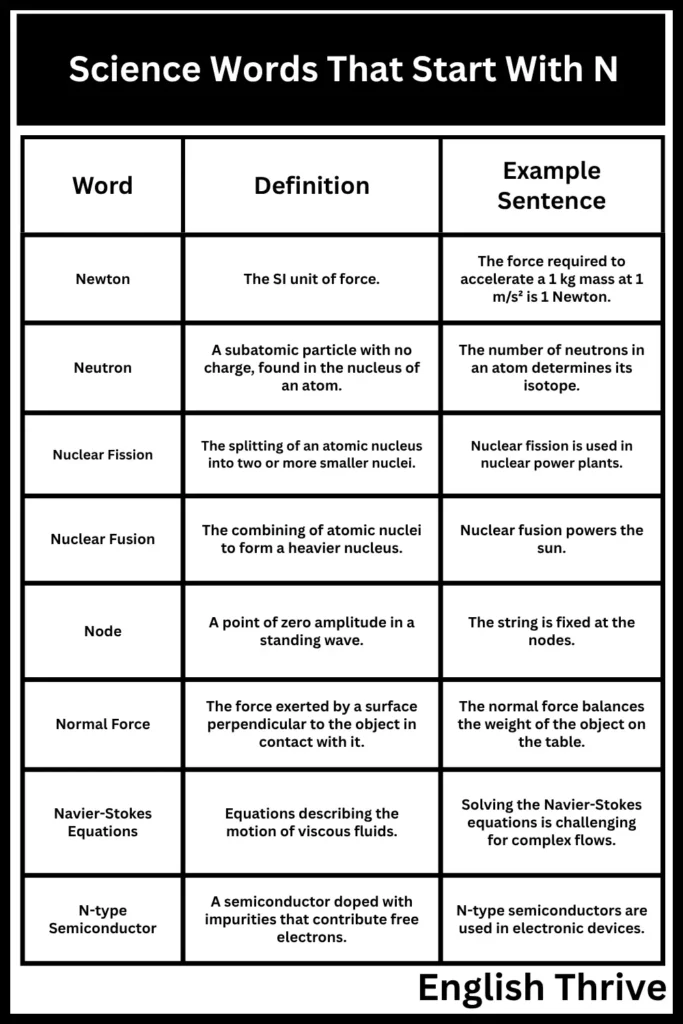
The following table provides examples of Physics words starting with N.
| Word | Definition | Example Sentence |
|---|---|---|
| Newton | The SI unit of force. | The force required to accelerate a 1 kg mass at 1 m/s² is 1 Newton. |
| Neutron | A subatomic particle with no charge, found in the nucleus of an atom. | The number of neutrons in an atom determines its isotope. |
| Nuclear Fission | The splitting of an atomic nucleus into two or more smaller nuclei. | Nuclear fission is used in nuclear power plants. |
| Nuclear Fusion | The combining of atomic nuclei to form a heavier nucleus. | Nuclear fusion powers the sun. |
| Node | A point of zero amplitude in a standing wave. | The string is fixed at the nodes. |
| Normal Force | The force exerted by a surface perpendicular to the object in contact with it. | The normal force balances the weight of the object on the table. |
| Navier-Stokes Equations | Equations describing the motion of viscous fluids. | Solving the Navier-Stokes equations is challenging for complex flows. |
| N-type Semiconductor | A semiconductor doped with impurities that contribute free electrons. | N-type semiconductors are used in electronic devices. |
| Nanophysics | The study of physical phenomena at the nanoscale. | Nanophysics deals with the properties of materials at the atomic level. |
| Nonlinear optics | The study of phenomena that occur when light interacts with matter in a nonlinear manner. | Nonlinear optics has applications in laser technology. |
| Nutation | A periodic variation in the inclination of the axis of a rotating object. | The Earth’s axis exhibits nutation. |
| Neutrino | A subatomic particle that is very similar to an electron, but has no electrical charge and a very small mass, which might even be zero. | Neutrinos are produced in nuclear reactions. |
| Nanoelectronics | The use of nanotechnology in electronic components. | Nanoelectronics allows for the creation of smaller and more efficient electronic devices. |
| Non-Euclidean geometry | A geometry that differs from Euclidean geometry in its axioms. | General relativity relies on non-Euclidean geometry. |
| Near field | The region close to an antenna or other radiating structure where the electromagnetic field is complex and does not behave like a propagating wave. | The properties of the near field are different from those of the far field. |
| Negative resistance | A property of some electronic circuits where an increase in voltage across the circuit results in a decrease in current through it. | Tunnel diodes exhibit negative resistance. |
| Nuclear force | The force that holds protons and neutrons together in the atomic nucleus. | The nuclear force is a strong, short-range force. |
| Noise | Unwanted or disturbing energy from erratic sources. | Noise can interfere with signal transmission. |
| Normal mode | A pattern of motion in which all parts of a system move sinusoidally with the same frequency and with a fixed phase relation. | Each normal mode has a characteristic frequency. |
| Navier Stokes equation | A set of nonlinear partial differential equations that describe the motion of viscous fluid substances. | The Navier-Stokes equation is fundamental to fluid dynamics. |
 Science Words That Start With N
Science Words That Start With N
The following table provides examples of Medicine words starting with N.
| Word | Definition | Example Sentence |
|---|---|---|
| Nerve | A bundle of fibers that transmits signals between the brain and other parts of the body. | The sciatic nerve is the largest nerve in the human body. |
| Necrosis | The death of cells or tissues. | Necrosis can result from injury or infection. |
| Neoplasm | An abnormal growth of tissue; a tumor. | A benign neoplasm is not cancerous. |
| Neurotransmitter | A chemical messenger that transmits signals between nerve cells. | Serotonin is a neurotransmitter that affects mood. |
| Nodule | A small swelling or aggregation of cells in the body. | The doctor found a nodule in the patient’s thyroid gland. |
| Narcotic | A drug that relieves pain and induces sleep. | Narcotics can be addictive. |
| Nasopharynx | The upper part of the throat behind the nose. | The nasopharynx connects the nasal cavity to the throat. |
| Neonatal | Relating to newborn infants. | The neonatal period is critical for development. |
| Nosocomial | Relating to a disease originating in a hospital. | Nosocomial infections can be a serious problem. |
| Neurology | The branch of medicine dealing with disorders of the nervous system. | The patient was referred to neurology for further evaluation. |
| Nutraceutical | A food or dietary supplement that is claimed to have health benefits. | Some people take nutraceuticals to improve their health. |
| Nystagmus | Involuntary rapid eye movements. | Nystagmus can be caused by various neurological conditions. |
| Nephrology | The branch of medicine dealing with the study of the function and diseases of the kidney. | The patient was referred to nephrology due to kidney problems. |
| Neuralgia | Intense, typically intermittent pain along the course of a nerve. | Trigeminal neuralgia causes severe facial pain. |
| Neurosis | A relatively mild mental disorder not caused by organic disease, involving symptoms of stress but not a radical loss of touch with reality. | The patient was diagnosed with anxiety neurosis. |
| Noninvasive | Not involving penetration of the skin or body. | The doctor recommended a noninvasive procedure. |
| Negative pressure wound therapy | A therapeutic technique using a vacuum dressing to promote healing in acute or chronic wounds and enhance healing of second and third degree burns. | The patient’s wound was treated with negative pressure wound therapy. |
| Nasogastric tube | A medical process involving the insertion of a plastic tube through the nose, past the throat, and down into the stomach. | The patient received feeding through a nasogastric tube. |
| Nociceptor | A sensory receptor for painful stimuli. | Nociceptors are activated by tissue damage. |
| Normocephalic | Having a normal-sized head. | The infant was normocephalic at birth. |
Usage Rules for Science Words
Using science words correctly requires attention to detail and an understanding of the specific context in which they are used. Here are some general usage rules:
- Be precise: Science words often have very specific meanings. Use them accurately to avoid ambiguity.
- Consider the context: The same word can have different meanings in different scientific disciplines.
- Use proper grammar: Ensure that the words are used correctly as nouns, verbs, adjectives, or adverbs.
- Follow scientific conventions: Adhere to established naming conventions and terminology standards.
For example, when discussing the nucleus, ensure you specify whether you are referring to the cell nucleus (biology) or the atomic nucleus (physics). Similarly, when using the term neutralization, clarify whether you are discussing a chemical reaction (chemistry) or a general process of rendering something ineffective.
Understanding the etymology of the word can also help in proper usage. Words derived from Greek or Latin roots often have specific connotations that can guide their application in scientific contexts.
For instance, the prefix “neo-” always indicates something new or recent, so a term like “neovascularization” inherently refers to the formation of new blood vessels, not the modification of existing ones.
Common Mistakes When Using Science Words Starting with N
Even experienced scientists can make mistakes when using scientific terminology. Here are some common errors to avoid:
| Incorrect | Correct | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| The neuron was dead due to necrosis. | The cell was dead due to necrosis. | Necrosis refers to cell or tissue death in general, not specifically neurons. |
| The titration resulted in a normalcy. | The titration resulted in a neutralization. | Normalcy is not a scientific term in this context; neutralization is the correct term. |
| The atom had too many neutrons, making it neutral. | The atom had too many neutrons, making it an isotope. | Excess neutrons create an isotope, not a neutral atom. |
| The doctor found a nose growth. | The doctor found a nasal neoplasm. | Neoplasm is the more precise term for an abnormal growth. |
| The plant needed more natural resources. | The plant needed more nutrients. | Nutrients are the specific resources that plants need for growth. |
| The process of natural selection made the animal nocturnal. | The process of natural selection favored nocturnal behavior in the animal. | Natural selection favors traits, it doesn’t “make” an animal something. |
| The scientist used a nometer to measure the substance. | The scientist used a nanometer to measure the substance. | Nanometer is a unit of length, there’s no such thing as a nometer. |
| The neural tube was not formed properly in the neonate. | The neural tube was not formed properly in the embryo. | The neural tube forms during the embryonic stage, not the neonatal stage. |
Practice Exercises
Test your understanding of science words starting with “N” with these exercises.
Exercise 1: Fill in the Blanks
Complete the following sentences with the appropriate science word starting with “N.”
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| The _______ is the control center of the cell. | Nucleus |
| _______ are chemical messengers that transmit signals between nerve cells. | Neurotransmitters |
| _______ is a chemical element essential for life and a major component of the atmosphere. | Nitrogen |
| _______ is the SI unit of force. | Newton |
| _______ is the death of cells or tissues. | Necrosis |
| The animal’s _______ helps it survive in its environment. | Niche |
| _______ are a group of inert gases with stable electron configurations. | Noble gases |
| _______ is a type of roundworm, often parasitic. | Nematode |
| _______ is an abnormal growth of tissue. | Neoplasm |
| The _______ cycle describes the transformation of nitrogen in nature. | Nitrogen |
Exercise 2: True or False
Indicate whether the following statements are true or false.
| Statement | Answer |
|---|---|
| A neuron is a type of plant cell. | False |
| Neutralization is a chemical reaction between an acid and a base. | True |
| Neutrons have a positive charge. | False |
| Nematodes are always beneficial to the environment. | False |
| Nuclear fusion is the splitting of an atomic nucleus. | False |
| Nitrogen is a noble gas. | False |
| Necrosis is the programmed cell death. | False |
| Neurotransmitters transmit signals between nerve cells. | True |
| Natural selection drives evolutionary change. | True |
| Nanomaterials have the same properties as their bulk counterparts. | False |
Exercise 3: Multiple Choice
Choose the best answer for each question.
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
Which of the following is the control center of a cell?
| Nucleus |
What is the SI unit of force?
| Newton |
Which process converts atmospheric nitrogen into usable forms by bacteria?
| Nitrogen fixation |
What term describes the death of cells or tissues?
| Necrosis |
Which of the following is a chemical messenger that transmits signals between nerve cells?
| Neurotransmitter |
Advanced Topics
For advanced learners, exploring the nuances of scientific terminology can be highly rewarding. Delving into the history and etymology of science words can provide a deeper understanding of their meanings and applications.
Furthermore, studying the specific naming conventions used in different scientific disciplines can enhance your ability to interpret complex scientific texts.
For example, in chemistry, the IUPAC (International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry) nomenclature provides a standardized system for naming chemical compounds. Understanding these rules allows you to systematically deduce the structure of a molecule from its name, and vice versa.
Similarly, in biology, the binomial nomenclature system (Genus species) is used to classify and name organisms, providing a universal framework for identifying and categorizing life forms.
Another advanced topic is the study of emerging terminology in cutting-edge scientific fields. As science advances, new concepts and technologies emerge, leading to the creation of new words and phrases.
Staying abreast of these developments requires continuous learning and engagement with the latest scientific literature. For instance, the field of nanotechnology has introduced a plethora of new terms, such as “quantum dot,” “graphene,” and “carbon nanotube,” which are essential for understanding the properties and applications of nanomaterials.
FAQs About Science Words That Start With N
What science word starts with N?
A science word that starts with “N” is “Newton.” It refers to Sir Isaac Newton, known for his laws of motion and universal gravitation, fundamental to physics.
Which word starts with N?
There are several words that start with “N,” such as “nature,” “nucleus,” “neuron,” and “nitrate.” These words are often used in various scientific fields.
What word starts with N in biology?
In biology, “nucleus” is a key word. It refers to the membrane-bound organelle in eukaryotic cells that contains the genetic material (DNA).
What starts with N in chemistry?
In chemistry, “nitrogen” is a prominent element that starts with “N.” It’s a vital element in compounds like ammonia and proteins and makes up a large part of Earth’s atmosphere.
What is N used for in science?
In science, “N” is commonly used to represent “Newton,” the unit of force in physics. It is also used for “nitrogen,” an essential element in various chemical and biological processes.
What is a 7 letter word with N?
A 7-letter word with “N” is “nitrogen.” This element plays a crucial role in life processes and chemical reactions, particularly in plant growth and the atmosphere.
Conclusion: Science Words That Start With N
Mastering science words starting with “N” is an important step in building a strong foundation in scientific literacy. By understanding the definitions, structural components, and usage rules of these terms, you can confidently navigate scientific texts and discussions.
This guide has provided a comprehensive overview of essential “N” words across various scientific disciplines, along with practice exercises to reinforce your learning. Remember to continue expanding your vocabulary and refining your understanding of scientific terminology as you delve deeper into the fascinating world of science.

