Conjunctions are the glue that holds sentences and paragraphs together, enabling us to create complex and nuanced expressions. Among these, conjunctions that begin with the letter ‘W’ play a vital role in establishing relationships between ideas, indicating time, cause, condition, or contrast.
Mastering these conjunctions is essential for anyone seeking to improve their writing and speaking skills in English. This article provides a comprehensive overview of Conjunctions Starting With W, exploring their definitions, usages, and common pitfalls.
Whether you’re a student, a professional, or simply an English enthusiast, this guide will equip you with the knowledge and practice you need to use these conjunctions effectively.
This article is designed for English language learners of all levels, from beginners to advanced speakers. By understanding the functions and nuances of these conjunctions, you can significantly enhance your ability to communicate clearly and precisely.
The examples and exercises included will help you solidify your understanding and boost your confidence in using these words correctly.
Contents
ToggleDefinition of Conjunctions
A conjunction is a word that connects words, phrases, or clauses in a sentence. Conjunctions serve as essential tools for creating complex sentences and conveying relationships between different parts of a text. They help to establish a smooth flow of ideas and avoid the disjointedness that would result from using only simple sentences. Conjunctions can indicate a variety of relationships, including addition, contrast, cause and effect, and time.
Conjunctions are typically classified into three main types: coordinating conjunctions, subordinating conjunctions, and correlative conjunctions. Coordinating conjunctions (e.g., and, but, or, so) connect words, phrases, or independent clauses of equal grammatical rank. Subordinating conjunctions (e.g., because, although, if, since) introduce dependent clauses, which cannot stand alone as sentences. Correlative conjunctions (e.g., both…and, either…or, neither…nor) are used in pairs to connect elements of equal grammatical rank.
The conjunctions starting with ‘W’ that we will focus on in this article are primarily subordinating conjunctions. They introduce dependent clauses and establish relationships of time, place, condition, or contrast between the dependent clause and the independent clause. Understanding the specific function of each of these conjunctions is crucial for using them correctly and effectively.
Structural Breakdown
Conjunctions starting with ‘W’ typically introduce a dependent clause, which is then connected to an independent clause to form a complex sentence. The order of these clauses can sometimes be reversed, but this often requires the use of a comma.
The basic structure is as follows:
1. Dependent Clause + Comma (if it precedes the independent clause) + Independent Clause
2. Independent Clause + Dependent Clause
For example, consider the conjunction “when.” In the sentence “When it rains, I take my umbrella,” the dependent clause “When it rains” comes first and is followed by a comma. The independent clause “I take my umbrella” completes the sentence.
If we reverse the order, the sentence becomes “I take my umbrella when it rains,” and no comma is needed.
Understanding the role of dependent and independent clauses is key to using these conjunctions correctly. The dependent clause provides context or additional information, while the independent clause expresses the main idea of the sentence.
The conjunction acts as the bridge between these two clauses, indicating the specific relationship between them.
Types of Conjunctions Starting with ‘W’
There are several conjunctions starting with ‘W’ that are commonly used in English. Each has a specific meaning and usage, which we will explore in detail below.
When
When is a subordinating conjunction that indicates time. It is used to describe an event or action that occurs at a specific point in time or during a particular period. It can introduce either a specific moment or a more extended duration.
Example: When the sun sets, the stars appear.
Whenever
Whenever is a subordinating conjunction that also indicates time, but it implies a recurring or habitual action. It means “every time” or “at any time” that something happens.
Example: Whenever I feel stressed, I go for a walk.
Where
Where is a subordinating conjunction that indicates location or place. It is used to describe the location in which something happens or exists.
Example: I like to visit the park where the flowers bloom.
Whereas
Whereas is a subordinating conjunction used to introduce a statement that contrasts with or differs from a previous statement. It is often used in formal writing and legal documents.
Example: Whereas John prefers coffee, Mary prefers tea.
Wherever
Wherever is a subordinating conjunction that indicates any place or location. It means “in any place that” or “every place that.”
Example: You can sit wherever you like.
While
While is a subordinating conjunction that can indicate time or contrast. When indicating time, it means “during the time that” or “as long as.” When indicating contrast, it means “although” or “whereas.”
Example (Time): While I was studying, my brother was watching TV.
Example (Contrast): While some people enjoy summer, others prefer winter.
Whether
Whether is a subordinating conjunction that indicates a condition or choice between two possibilities. It is often used in indirect questions.
Example: I don’t know whether I should go to the party.
Examples of Conjunctions Starting with W
To further illustrate the usage of these conjunctions, here are several examples categorized by the specific conjunction.
Examples with “When”
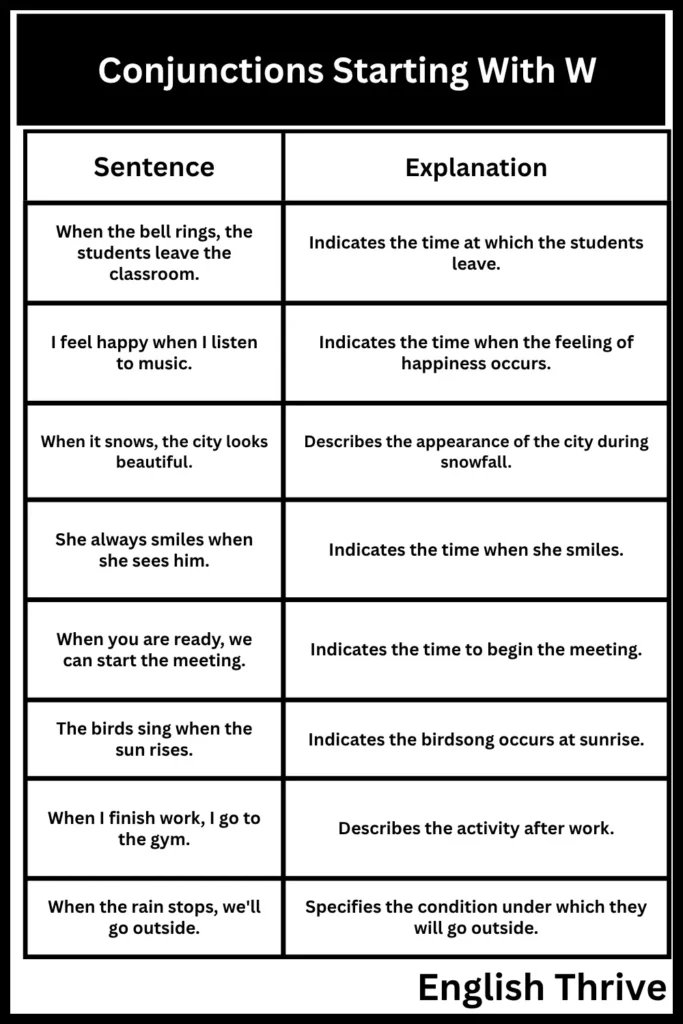
The following table provides examples of sentences using the conjunction “when” to denote time.
| Sentence | Explanation |
|---|---|
| When the bell rings, the students leave the classroom. | Indicates the time at which the students leave. |
| I feel happy when I listen to music. | Indicates the time when the feeling of happiness occurs. |
| When it snows, the city looks beautiful. | Describes the appearance of the city during snowfall. |
| She always smiles when she sees him. | Indicates the time when she smiles. |
| When you are ready, we can start the meeting. | Indicates the time to begin the meeting. |
| The birds sing when the sun rises. | Indicates the birdsong occurs at sunrise. |
| When I finish work, I go to the gym. | Describes the activity after work. |
| When the rain stops, we’ll go outside. | Specifies the condition under which they will go outside. |
| He gets nervous when he speaks in public. | Describes when he feels nervous. |
| When you visit Rome, you should see the Colosseum. | Recommends an activity during a visit to Rome. |
| When I was a child, I loved to read fairy tales. | Recalls a past fondness for reading. |
| When the power goes out, we light candles. | Describes a routine during a power outage. |
| She calls her mother when she needs advice. | Indicates when she seeks her mother’s counsel. |
| When the movie starts, please be quiet. | Requests silence once the movie begins. |
| We celebrate our anniversary when spring arrives. | States the time of their anniversary celebration. |
| When the cake is ready, take it out of the oven. | Instructs when to remove the cake. |
| The flowers bloom when the weather warms up. | Describes when the flowers bloom. |
| When he travels, he always takes his camera. | Indicates a habit during travel. |
| When I am tired, I drink coffee. | Describes a response to feeling tired. |
| When you are lost, ask for directions. | Advises what to do when lost. |
| When the music plays, they start dancing. | Describes a trigger for dancing. |
| When the store opens, the customers rush in. | Depicts the scene when the store opens. |
| When I have free time, I enjoy painting. | Indicates a hobby during free time. |
| When she feels lonely, she calls her friends. | Describes a reaction to loneliness. |
| When you exercise, you feel better. | Explains the effect of exercising. |
Examples with “Whenever”
The table below gives examples of sentences employing the conjunction “whenever” to indicate a recurring event.
| Sentence | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Whenever I visit my grandmother, she makes me cookies. | Indicates a recurring action of making cookies. |
| Whenever the phone rings, the dog barks. | Describes a habitual reaction of the dog. |
| Whenever she travels, she sends me a postcard. | Indicates a recurring action during her travels. |
| Whenever I feel overwhelmed, I take a deep breath. | Describes a habitual response to feeling overwhelmed. |
| Whenever he sees a stray animal, he tries to help it. | Indicates a recurring action of helping stray animals. |
| Whenever the sun shines, we go to the beach. | Describes a recurring activity during sunny weather. |
| Whenever she has time, she practices yoga. | Indicates a recurring habit of practicing yoga. |
| Whenever I cook, I listen to music. | Describes simultaneous activities. |
| Whenever he is bored, he reads a book. | Indicates a recurring solution to boredom. |
| Whenever the baby cries, the mother picks him up. | Describes a recurring response to the baby’s cries. |
| Whenever I go to that cafe, I order the same drink. | Indicates a consistent choice at the cafe. |
| Whenever she feels sad, she watches a comedy movie. | Describes a recurring remedy for sadness. |
| Whenever he is stressed, he goes for a run. | Indicates a recurring method for stress relief. |
| Whenever the weather is nice, we have a picnic. | Describes a recurring activity during good weather. |
| Whenever I need inspiration, I visit an art museum. | Indicates a recurring source of inspiration. |
| Whenever she feels tired, she takes a nap. | Describes a recurring response to tiredness. |
| Whenever he is confused, he asks for help. | Indicates a recurring strategy for dealing with confusion. |
| Whenever the flowers bloom, the garden looks beautiful. | Describes a recurring transformation of the garden. |
| Whenever I travel to a new city, I try the local cuisine. | Indicates a recurring culinary exploration during travels. |
| Whenever she has a problem, she talks to her sister. | Describes a recurring source of support. |
| Whenever he is late, he apologizes profusely. | Indicates a consistent behavior when tardy. |
| Whenever the children are quiet, I know they are up to something. | Describes a suspicion based on their silence. |
| Whenever I crave something sweet, I bake cookies. | Indicates a recurring response to a sweet craving. |
| Whenever she feels overwhelmed, she meditates. | Describes a regular practice for managing stress. |
| Whenever he needs to concentrate, he puts on headphones. | Indicates a recurring aid for focus. |
Examples with “Where” and “Wherever”
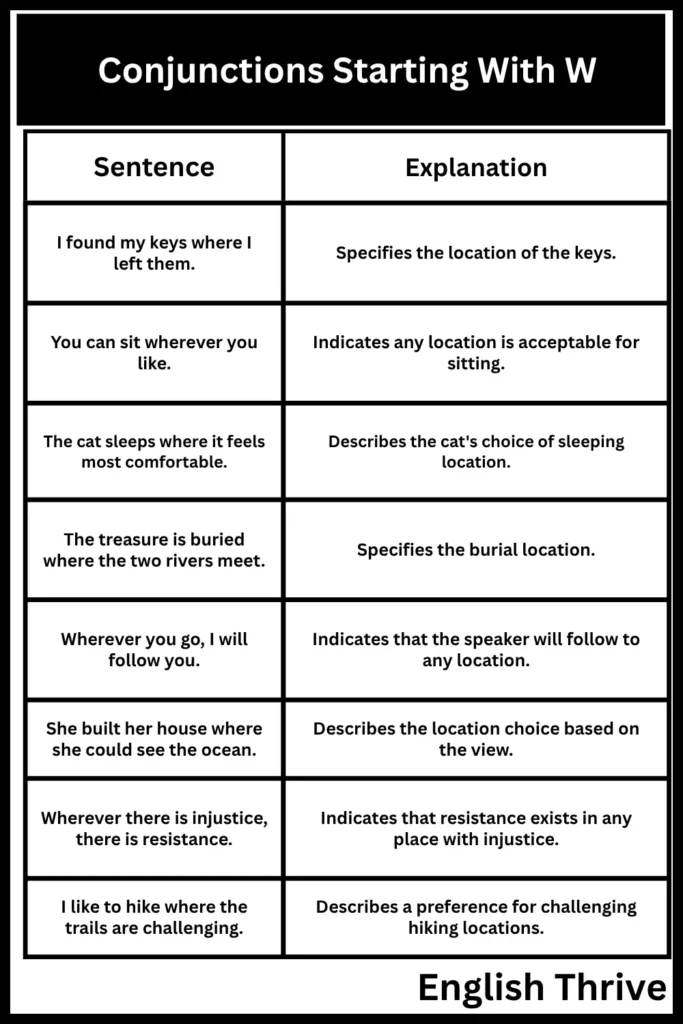
The following table illustrates the use of “where” to specify a location and “wherever” to indicate any location.
| Sentence | Explanation |
|---|---|
| I found my keys where I left them. | Specifies the location of the keys. |
| You can sit wherever you like. | Indicates any location is acceptable for sitting. |
| The cat sleeps where it feels most comfortable. | Describes the cat’s choice of sleeping location. |
| The treasure is buried where the two rivers meet. | Specifies the burial location. |
| Wherever you go, I will follow you. | Indicates that the speaker will follow to any location. |
| She built her house where she could see the ocean. | Describes the location choice based on the view. |
| Wherever there is injustice, there is resistance. | Indicates that resistance exists in any place with injustice. |
| I like to hike where the trails are challenging. | Describes a preference for challenging hiking locations. |
| Wherever he travels, he learns about the local culture. | Indicates that learning about cultures is part of his travel routine, regardless of the place. |
| The birds build their nests where they can find shelter. | Describes the bird’s choice of nesting location. |
| I always feel at peace where nature surrounds me. | Indicates that nature is source of peace. |
| Wherever she goes, she makes new friends. | Indicates that making friends occurs in any location. |
| The best ideas come to me where I least expect them. | Describes the unexpected locations of inspiration. |
| Wherever there is kindness, there is hope. | Indicates that hope exists in any place with kindness. |
| She likes to paint where the light is perfect. | Describes a preference for well-lit painting locations. |
| Wherever he works, he gives his best effort. | Indicates that he always tries hard, regardless of the workplace. |
| The children love to play where there is a playground. | Describes a preference for locations with playgrounds. |
| Wherever she lives, she makes it feel like home. | Indicates that she makes any place feel comfortable. |
| I feel inspired where creativity is celebrated. | Indicates that creativity inspires. |
| Wherever he finds himself, he tries to make a positive impact. | Indicates that he makes a positive impact wherever he goes. |
| The flowers always bloom beautifully where they are well cared for. | Describes the conditions under which the flowers bloom. |
| Wherever she teaches, her students excel. | Indicates that her students excel wherever she teaches. |
| I like to read where it’s quiet and peaceful. | Describes a preference for peaceful reading locations. |
| Wherever he goes, he carries his favorite book. | Indicates a habit of bringing his favorite book to any location. |
| The animals find food where the vegetation is lush. | Describes where the animals find food. |
Examples with “While” and “Whereas”
The following table shows examples of sentences using “while” to denote time or contrast, and “whereas” to introduce a contrast.
| Sentence | Explanation |
|---|---|
| While I was cooking, he was cleaning. | Indicates simultaneous activities. |
| While some people enjoy the beach, others prefer the mountains. | Introduces a contrast in preferences. |
| Whereas my brother loves to read, I prefer to watch movies. | Contrasts the speaker’s preference with their brother’s. |
| While the team played well, they still lost the game. | Indicates a contrast between performance and outcome. |
| Whereas she is outgoing, he is quite reserved. | Contrasts two different personalities. |
| While he studied hard, he didn’t pass the exam. | Indicates a contrast between effort and result. |
| Whereas the first proposal was rejected, the second was accepted. | Contrasts two different outcomes for proposals. |
| While the city is exciting, it can also be stressful. | Indicates a contrast in the city’s characteristics. |
| Whereas the rich have many options, the poor have few. | Contrasts the options available to different economic classes. |
| While I prefer coffee, my wife prefers tea. | Introduces a contrast between the speaker’s and their wife’s preferences. |
| Whereas some people are early risers, others are night owls. | Contrasts two different sleep schedules. |
| While the car is old, it still runs well. | Indicates a contrast between the car’s age and performance. |
| Whereas the weather is warm here, it is cold back home. | Contrasts the weather in two different locations. |
| While the food was delicious, the service was slow. | Indicates a contrast between the food quality and the service. |
| Whereas the book is fiction, it is based on real events. | Contrasts the book’s genre with its basis in reality. |
| While the project was challenging, it was also rewarding. | Indicates a contrast between difficulty and satisfaction. |
| Whereas the painting is modern, it draws inspiration from classical art. | Contrasts the painting’s style with its inspiration. |
| While he is quiet, he is very observant. | Indicates a contrast between his demeanor and his attentiveness. |
| Whereas the city is crowded, the countryside is peaceful. | Contrasts the qualities of urban and rural areas. |
| While the task is simple, it requires careful attention. | Indicates a contrast between the task’s simplicity and the attention it requires. |
| Whereas some believe in fate, others believe in free will. | Contrasts two different philosophical viewpoints. |
| While the room was small, it felt cozy. | Indicates a contrast between size and atmosphere. |
| Whereas the original plan failed, the revised plan succeeded. | Contrasts the outcomes of two different plans. |
| While the path was steep, the view was worth it. | Indicates a contrast between difficulty and reward. |
| Whereas some prefer to work alone, others thrive in a team. | Contrasts two different working styles. |
Examples with “Whether”
The following table provides examples of sentences employing the conjunction “whether” to express a condition or choice.
| Sentence | Explanation |
|---|---|
| I don’t know whether I should laugh or cry. | Indicates a choice between two emotional responses. |
| She asked me whether I had finished the report. | Introduces an indirect question. |
| Whether you like it or not, you have to go to school. | Indicates that attendance is mandatory, regardless of preference. |
| I’m not sure whether he will come to the party. | Expresses uncertainty about his attendance. |
| Whether it rains or shines, we will have the picnic. | Indicates that the picnic will proceed regardless of the weather. |
| He couldn’t decide whether to stay or leave. | Indicates a difficult choice between two options. |
| Whether she agrees or disagrees, the decision has been made. | Indicates that the decision is final, regardless of her opinion. |
| I’m wondering whether I should apply for the job. | Expresses uncertainty about applying for the job. |
| Whether you win or lose, it’s important to participate. | Indicates that participation is valuable regardless of the outcome. |
| She is unsure whether to trust him. | Expresses uncertainty about trusting him. |
| Whether he likes it or not, he has to follow the rules. | Indicates that following the rules is mandatory, regardless of preference. |
| I’m curious whether they will accept our offer. | Expresses curiosity about the offer’s acceptance. |
| Whether you succeed or fail, you should be proud of your effort. | Indicates that effort is valuable regardless of the outcome. |
| She is debating whether to tell him the truth. | Expresses internal conflict about telling the truth. |
| Whether it’s easy or difficult, we must complete the task. | Indicates that task completion is mandatory, regardless of difficulty. |
| I’m trying to determine whether the information is accurate. | Expresses an effort to verify information. |
| Whether you agree with me or not, I respect your opinion. | Indicates respect for differing opinions. |
| She is contemplating whether to move to a new city. | Expresses consideration of moving. |
| Whether the plan works or not, we will learn from the experience. | Indicates that learning will occur regardless of the plan’s success. |
| I’m investigating whether there is a better solution. | Expresses investigation of alternative solutions. |
| Whether you are rich or poor, everyone deserves respect. | Indicates that respect is universal, regardless of economic status. |
| She is deciding whether to invest in the stock market. | Expresses consideration of investing. |
| Whether it’s a success or a failure, it will be a learning experience. | Indicates that learning will occur regardless of the outcome. |
| I’m skeptical whether they will deliver on their promises. | Expresses doubt about fulfilling the promises. |
| Whether you are young or old, you can always learn something new. | Indicates that learning is always possible, regardless of age. |
Usage Rules
The correct usage of conjunctions starting with ‘W’ depends on understanding their specific meanings and the relationships they establish between clauses. Here are some key rules to keep in mind:
- Comma Usage: When the dependent clause introduced by the conjunction comes before the independent clause, a comma is usually required. For example, “When it rains, I stay inside.” However, if the independent clause comes first, the comma is typically omitted: “I stay inside when it rains.”
- Tense Consistency: Ensure that the tenses in the dependent and independent clauses are logically consistent. For example, “When I was young, I used to play outside” (both past tenses).
- Contextual Appropriateness: Choose the conjunction that best reflects the intended relationship between the clauses. For example, use “when” for time, “where” for location, “whereas” for contrast, and “whether” for choice.
- Formal vs. Informal: Be aware that some conjunctions, such as “whereas,” are more formal and are typically used in academic or legal writing.
Common Mistakes
Here are some common mistakes to avoid when using conjunctions starting with ‘W’:
- Incorrect Comma Placement: Misplacing or omitting commas can disrupt the flow of the sentence and change its meaning.
- Incorrect: I go to the park when I have time.
- Correct: When I have time, I go to the park.
- Using “Where” Instead of “When”: Confusing these two conjunctions is a common error. “Where” refers to location, while “when” refers to time.
- Incorrect: I met her where I was studying abroad.
- Correct: I met her when I was studying abroad.
- Misusing “While” for “Whereas”: Although both can indicate contrast, “whereas” is more formal and introduces a direct contrast between two specific statements. “While” can also indicate time.
- Incorrect: While John likes football, whereas Mary likes tennis.
- Correct: Whereas John likes football, Mary likes tennis.
- Incorrect Use of “Whether” with “If”: “Whether” is used to express a choice between two possibilities, whereas “if” introduces a conditional clause.
- Incorrect: I don’t know if I should laugh or cry.
- Correct: I don’t know whether I should laugh or cry.
Practice Exercises: Conjunctions Starting With W
Test your understanding of conjunctions starting with ‘W’ with the following exercises. Choose the correct conjunction to complete each sentence.
Exercise 1: Fill in the Blanks
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| 1. ______ I go, I always take my camera. | Wherever |
| 2. I will call you ______ I arrive. | When |
| 3. ______ some people prefer summer, others prefer winter. | While |
| 4. She asked me ______ I was coming to the party. | Whether |
| 5. I always feel happy ______ I am with my friends. | When |
| 6. You can sit ______ you want. | Wherever |
| 7. ______ I’m cooking, I like to listen to music. | While |
| 8. I don’t know ______ to go left or right. | Whether |
| 9. ______ I’m feeling stressed, I take a break. | Whenever |
| 10. I lost my keys ______ I was walking in the park. | When |
Exercise 2: Correct the Errors
Identify and correct the errors in the following sentences.
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| 1. I will see you where I am free. | I will see you when I am free. |
| 2. When I finish my work I will go home. | When I finish my work, I will go home. |
| 3. Whereas he likes to read if she prefers to watch TV. | Whereas he likes to read, she prefers to watch TV. |
| 4. I don’t know if or not I should go. | I don’t know whether or not I should go. |
| 5. Wherever I am happy, I sing. | Whenever I am happy, I sing. |
| 6. While she is tired but she keeps working. | While she is tired, she keeps working. |
| 7. You can find me when the library. | You can find me where the library is. |
| 8. Whenever I eat I feel happy. | Whenever I eat, I feel happy. |
| 9. Weather you like it or not, you have to do it. | Whether you like it or not, you have to do it. |
| 10. When I was young where I lived in a small town. | When I was young, I lived in a small town. |
Exercise 3: Sentence Combining
Combine the following pairs of sentences using the appropriate conjunction starting with ‘W’.
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| 1. The sun sets. The birds stop singing. | When the sun sets, the birds stop singing. |
| 2. I feel stressed. I go for a walk. | Whenever I feel stressed, I go for a walk. |
| 3. I left my keys. They were on the table. | I left my keys where they were on the table. |
| 4. John likes coffee. Mary prefers tea. | Whereas John likes coffee, Mary prefers tea. |
| 5. You go. I will be there. | Wherever you go, I will be there. |
| 6. I was studying. My brother was watching TV. | While I was studying, my brother was watching TV. |
| 7. I should go to the party. I am not sure. | I am not sure whether I should go to the party. |
| 8. The rain stops. We will go outside. | When the rain stops, we will go outside. |
| 9. I need advice. I call my mother. | Whenever I need advice, I call my mother. |
| 10. She travels. She always takes her camera. | Whenever she travels, she always takes her camera. |
Advanced Topics
For advanced learners, it’s important to understand the nuances and subtle differences in usage among these conjunctions. This includes recognizing their use in complex sentence structures, idiomatic expressions, and literary contexts.
For instance, the conjunction “while” can sometimes be used to express concession, similar to “although,” but with a slightly different emphasis. Additionally, the choice between “whether” and “if” in certain contexts can be a matter of style and formality.
Advanced learners should also pay attention to the historical evolution of these conjunctions and their changing roles in the English language. Studying examples from different periods of literature can provide valuable insights into the versatility and adaptability of these words.
Furthermore, exploring how these conjunctions are used in different dialects of English can enhance one’s understanding of their regional variations and idiomatic usages.
FAQs About Conjunctions Starting With W
What is the difference between “when” and “whenever”?
“When” refers to a specific point in time or a particular instance, while “whenever” implies a recurring or habitual action. For example, “When the bell rings, the class is over” refers to a specific instance, whereas “Whenever I feel tired, I take a nap” refers to a recurring action.
Can “while” and “whereas” be used interchangeably?
No, “while” and “whereas” cannot always be used interchangeably. “Whereas” is more formal and is used to introduce a direct contrast between two specific statements.
“While” can indicate time or a more general contrast.
Is it always necessary to use a comma after a clause beginning with “when”?
A comma is usually required when the clause beginning with “when” comes before the independent clause. For example, “When it rains, I stay inside.” However, if the independent clause comes first, the comma is typically omitted: “I stay inside when it rains.”
How do I know whether to use “whether” or “if”?
“Whether” is used to express a choice between two possibilities, while “if” introduces a conditional clause. In indirect questions, “whether” is generally preferred.
For example, “I don’t know whether I should go” (choice) vs. “If it rains, I will stay home” (condition).
Can “wherever” be used to refer to time instead of location?
No, “wherever” should only be used to refer to location. To refer to time, use “when” or “whenever.”
Conclusion
Mastering conjunctions that start with ‘W’ is crucial for constructing clear, coherent, and nuanced sentences in English. By understanding the specific meanings and usages of these conjunctions—when, whenever, where, whereas, wherever, while, and whether—you can significantly enhance your writing and speaking skills. Remember to pay attention to comma placement, tense consistency, and contextual appropriateness to avoid common mistakes. With practice and attention to detail, you can confidently and effectively use these conjunctions to express a wide range of relationships between ideas and create more sophisticated and compelling communication.