When expressing intensity or emphasis in English, the words So and Such serve as powerful tools that can transform ordinary statements into more impactful expressions. While they may seem interchangeable to many English learners, these two intensifiers follow distinct grammatical patterns and create subtly different meanings in conversation. Mastering their usage not only helps you move beyond repetitive expressions like “very” but also allows you to communicate with greater precision and emotional resonance.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the full range of applications for such and so, including their grammatical rules, practical examples, common phrases, and nuanced differences that even advanced English speakers sometimes miss. By understanding these distinctions, you’ll add sophisticated variety to your English expression and avoid common mistakes that might otherwise make your speech sound unnatural.
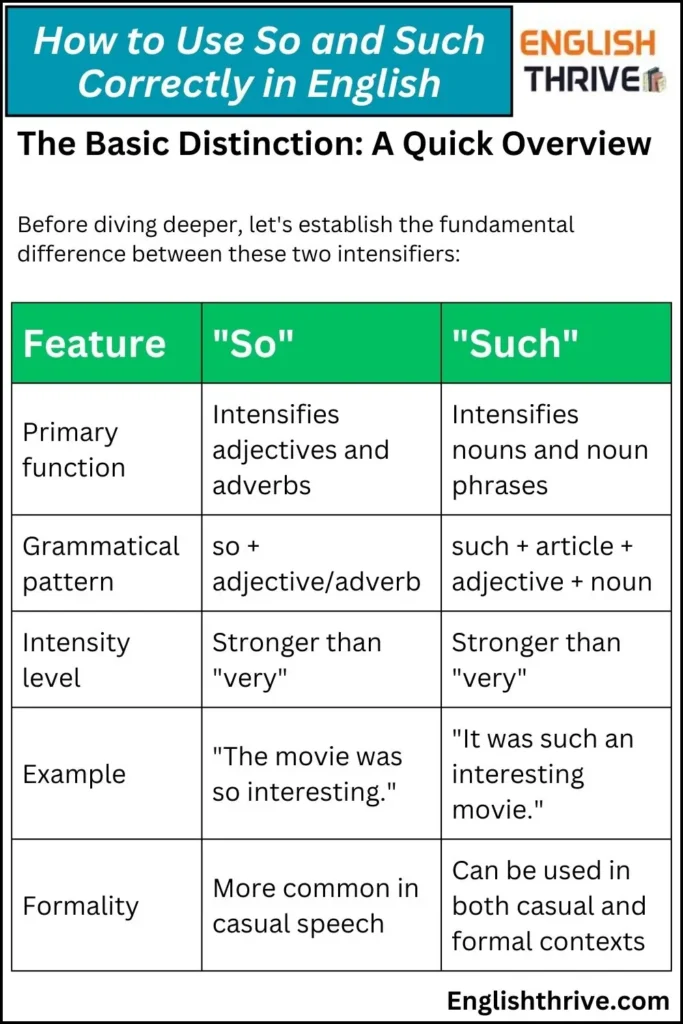
The Basic Distinction: A Quick Overview
Before diving deeper, let’s establish the fundamental difference between these two intensifiers:
| Feature | “So” | “Such” |
|---|---|---|
| Primary function | Intensifies adjectives and adverbs | Intensifies nouns and noun phrases |
| Grammatical pattern | so + adjective/adverb | such + article + adjective + noun |
| Intensity level | Stronger than “very” | Stronger than “very” |
| Example | “The movie was so interesting.” | “It was such an interesting movie.” |
| Formality | More common in casual speech | Can be used in both casual and formal contexts |
As you can see from this simple comparison, while both words serve as intensifiers, they operate on different grammatical elements within a sentence.
Using “So” Effectively
“So” with Adjectives
“So” functions as a powerful intensifier with adjectives, creating a stronger emphasis than the more basic “very.” When you want to express that something possesses a quality to an exceptional degree, “so” becomes your go-to intensifier.
Examples:
- “The coffee was so hot that I couldn’t drink it right away.”
- “Her explanation was so clear that everyone understood immediately.”
- “This puzzle is so difficult! I’ve been working on it for hours.”
- “The view from the mountain was so breathtaking.”
- “That documentary was so informative about climate change.”
Notice that “so” doesn’t merely indicate a high degree—it suggests an exceptional or noteworthy level that often provokes a reaction or consequence.
The Emotional Component of “So”
An important aspect that distinguishes “so” from “very” is its emotional weight. When you say something is “so beautiful” rather than “very beautiful,” you’re not just increasing the intensity—you’re adding an emotional response to your description. This makes “so” particularly effective in conversational English where expressing feelings is important.
This emotional component explains why “so” appears more frequently in casual speech than in formal writing. In academic or professional writing, emotional intensifiers are often avoided in favor of more precise, objective language.
“So” with Adverbs
Just as with adjectives, “so” intensifies adverbs to express manner, frequency, degree, or time to an exceptional level.
Examples:
- “She speaks so eloquently during presentations.”
- “The children ran so quickly that I couldn’t keep up.”
- “He plays the piano so beautifully that people often stop to listen.”
- “Why do you always arrive so late?”
- “The project was completed so efficiently that we finished ahead of schedule.”
The intensification of adverbs with “so” adds dynamism to descriptions of actions, making them more vivid and expressive.
“So” with Quantifiers
One of the most practical applications of “so” is with quantifiers like “many,” “much,” “few,” and “little.” This construction helps express surprise, concern, or emphasis about quantities.
Examples with countable nouns:
- “There were so many people at the concert that we couldn’t find seats.”
- “I have so few opportunities to practice my French these days.”
Examples with uncountable nouns:
- “There’s so much information to process before the exam.”
- “They showed so little interest in the proposal that we decided to revise it.”
This construction is especially useful for expressing contrast or unexpected quantities:
- “Why is there so much traffic today? It’s usually quiet on Sundays.”
- “There was so little food left that we had to order takeout.”
The “So… that…” Construction
This powerful structure expresses cause and effect, showing that the intensity of something leads directly to a specific result. It’s one of the most versatile and expressive constructions using “so.”
Examples:
- “The music was so loud that I couldn’t hear what you were saying.”
- “She was so well-prepared for the interview that they offered her the job immediately.”
- “The instructions were so complicated that I had to call customer service.”
- “The story was so moving that several people in the audience were in tears.”
- “The coffee was so strong that I couldn’t sleep that night.”
This construction doesn’t just describe—it tells a mini-story with both cause and effect, making it extremely useful in both speaking and writing.
Understanding “Such” in All Its Forms
“Such” with Noun Phrases
While “so” works with adjectives and adverbs, “such” is designed to intensify nouns and noun phrases. The most common pattern is “such + a/an + adjective + singular countable noun” or “such + adjective + plural/uncountable noun.“
Examples with singular countable nouns:
- “He’s such a talented musician that he can play any song after hearing it once.”
- “It was such an extraordinary experience that I’ll never forget it.”
- “She showed such a remarkable understanding of the problem.”
Examples with plural nouns:
- “They are such dedicated teachers that students love their classes.”
- “We faced such difficult challenges during the project.”
- “There were such heavy rains that the roads were flooded.”
Examples with uncountable nouns:
- “The speaker demonstrated such eloquence that the audience was captivated.”
- “The team showed such determination throughout the season.”
- “There was such chaos after the announcement that management had to intervene.”
The Subtle Art of Using “Such” in Formal Contexts
Unlike “so,” which tends to be more conversational, “such” can easily transition between casual and formal registers. In formal writing, “such” often carries more weight and authority than “so” constructions.
Formal examples:
- “Such considerations must be taken into account before proceeding with the investment.”
- “The committee has rejected such proposals in the past.”
- “Such evidence contradicts the initial hypothesis.”
This versatility makes “such” particularly valuable in academic, business, and legal contexts where precise intensification may be needed without sounding overly casual.
The “Such… that…” Construction
Similar to “so… that…” this construction creates a cause-effect relationship, but with a noun phrase as the intensified element.
Examples:
- “It was such a powerful storm that it knocked out electricity for days.”
- “They showed such impressive results that the company doubled their research budget.”
- “She has such extensive knowledge of the subject that everyone consults her.”
- “The company implemented such effective strategies that profits increased by 40%.”
- “He demonstrated such remarkable skills that he was immediately promoted.”
This construction creates a strong narrative flow while emphasizing the exceptional nature of the noun being described.
Comparative Analysis: “So and Such”
Understanding when to use “so” versus “such” becomes clearer when we transform sentences between the two forms:
| Using “So” | Using “Such” |
|---|---|
| The movie was so boring. | It was such a boring movie. |
| The news was so surprising. | It was such surprising news. |
| The children were so energetic. | They were such energetic children. |
| The solution is so simple. | It’s such a simple solution. |
| The explanation was so detailed. | It was such a detailed explanation. |
Notice that while both forms express intensity, the “such” construction often feels slightly more formal or emphatic because it intensifies the entire noun phrase rather than just the quality (adjective).
Grammar Traps to Avoid
Common mistakes often occur when English learners confuse the patterns for so and such:
❌ “It was so a good movie.” (Incorrect)
✓ “It was such a good movie.” (Correct)
❌ “She is such intelligent.” (Incorrect)
✓ “She is so intelligent.” (Correct)
❌ “The test was such difficult.” (Incorrect)
✓ “The test was so difficult.” (Correct)
❌ “They have so many good ideas.” (Correct)
❌ “They have such many good ideas.” (Incorrect)
Remember that “so” works with adjectives, adverbs, and quantifiers, while “such” works with nouns and noun phrases. Keeping this distinction clear will help you avoid these common errors.
Advanced Applications and Special Cases
Implied Results with So and Such
Both so and such can be used without an explicit “that” clause when the result is implied or understood:
- “The lecture was so boring!” (Implied: that I could hardly stay awake)
- “It was such a waste of time!” (Implied: that I regret attending)
These truncated forms are extremely common in casual speech, where the implied consequence is often communicated through tone or context.
Emphatic Questions and Exclamations
Both so and such create powerful emphatic questions and exclamations:
- “Why is she always so late?”
- “How can they be so insensitive?”
- “What such remarkable talent looks like!”
- “How could you make such a terrible mistake?”
These constructions add emotional weight to questions and can express surprise, frustration, admiration, or disbelief.
Final Thoughts
Mastering so and such is key to expressing intensity and emotion in English. These two intensifiers allow you to convey emphasis, surprise, and feelings in a way that simple words like “very” cannot. By understanding when to use “so” and when to use “such”, you’ll add sophistication and clarity to your speech and writing.
Practice these patterns in different contexts, and remember: “so” often goes with adjectives and adverbs, while “such” is typically used with nouns and noun phrases. With these tools in hand, you’ll be able to communicate with precision and emotional depth.
Meta Description: Learn how to use so and such correctly in English to express intensity and emotion. This guide provides examples, rules, and tips to help you master these powerful intensifiers.