Have you ever wondered why some sentences flow like music while others sound jumbled? The secret lies in understanding the building blocks of language – the 8 parts of speech. Whether you’re writing your first story or preparing for an exam, mastering these fundamentals will transform your English skills. Let’s explore each part of speech with clear examples and easy-to-follow rules.
Contents
Toggle1. Nouns
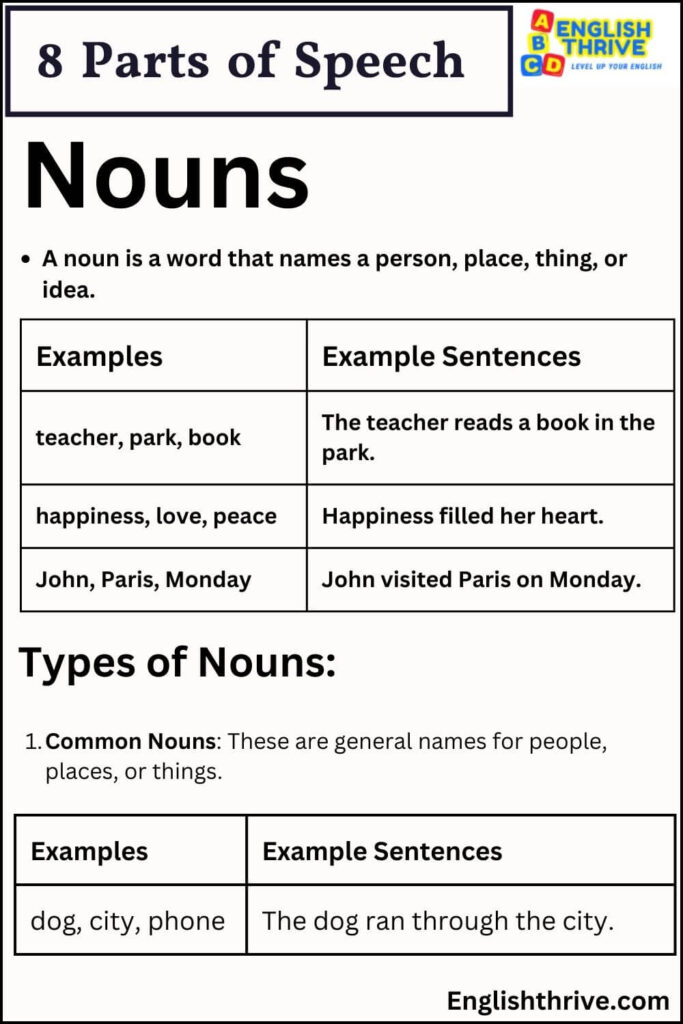
A noun is a word that names a person, place, thing, or idea.
| Examples | Example Sentences |
|---|---|
| teacher, park, book | The teacher reads a book in the park. |
| happiness, love, peace | Happiness filled her heart. |
| John, Paris, Monday | John visited Paris on Monday. |
Types of Nouns:
- Common Nouns: These are general names for people, places, or things.
| Examples | Example Sentences |
|---|---|
| dog, city, phone | The dog ran through the city. |
- Proper Nouns: Specific names of people, places, or things (always capitalized).
| Examples | Example Sentences |
|---|---|
| America, Toyota, Lisa | Lisa drives a Toyota in America. |
- Abstract Nouns : Names of ideas or qualities that cannot be touched.
| Examples | Example Sentences |
|---|---|
| beauty, courage, time | Her courage inspired everyone. |
- Collective Nouns : Names for groups of people or things.
| Examples | Example Sentences |
|---|---|
| team, family, herd | The team won the game. |
Rules for Using Nouns:
-
Countable vs. Uncountable
- Countable: can use ‘a’ or ‘an’ and have plural forms Example: a book, three books
- Uncountable: cannot be counted individually Example: water, music
-
Singular vs. Plural
- Regular: add ‘s’ or ‘es’ Example: dog → dogs, box → boxes
- Irregular: unique forms Example: child → children, foot → feet
2. Pronouns
A pronoun is a word that takes the place of a noun to avoid repetition.
| Examples | Example Sentences |
|---|---|
| he, she, it | He gave her the book, and it made her happy. |
| they, we, you | They visited us when we moved. |
Types of Pronouns:
- Personal Pronouns- Replace specific nouns (people or things).
| Subject | Object |
|---|---|
| I, you, he, she, it | me, you, him, her, it |
| we, they | us, them |
- Possessive Pronouns- Show ownership.
| Examples | Example Sentences |
|---|---|
| mine, yours, his, hers | This book is mine. |
| ours, theirs | The house is theirs. |
- Demonstrative Pronouns -Point to specific things.
| Examples | Example Sentences |
|---|---|
| this, that | This is my car. |
| these, those | Those are beautiful flowers. |
- Relative Pronouns -Connect parts of sentences.
| Examples | Example Sentences |
|---|---|
| who, whom, which | The person who called left a message. |
| that, whose | The book that you gave me is interesting. |
- Reflexive Pronouns- Show that the subject and object are the same.
| Examples | Example Sentences |
|---|---|
| myself, yourself, himself | He hurt himself while playing. |
| herself, itself, themselves | They taught themselves to cook. |
Rules for Using Pronouns:
- Agreement
- Pronouns must agree with their antecedents in number and gender Example: Sarah lost her book (not his book)
- Case
- Use subject pronouns for subjects Example: She and I went to the store (not Her and me)
- Use object pronouns for objects Example: Please give it to him and me (not he and I)
Practice Exercises:
Fill in the blanks with appropriate pronouns:
- John and _____ (I/me) went to the park.
- The book belongs to _____ (they/them).
- Mary hurt _____ (herself/himself) yesterday.
3. Verbs
A verb is a word that shows action or state of being.
| Examples | Example Sentences |
|---|---|
| run, sing, dance | Birds fly in the sky. |
| is, am, was | She is happy today. |
Types of Verbs:
- Action Verbs -Show physical or mental actions.
| Examples | Example Sentences |
|---|---|
| jump, read, think | Children play in the park. |
| write, speak, eat | She writes beautiful poems. |
- Linking Verbs- Connect the subject to additional information.
| Examples | Example Sentences |
|---|---|
| is, are, was, were | The sky is blue. |
| seem, appear, become | She became a doctor. |
- Helping (Auxiliary) -Verbs Help main verbs express tense or mood.
| Examples | Example Sentences |
|---|---|
| can, will, may | I will visit tomorrow. |
| have, had, do | They have finished work. |
- Regular and Irregular Verbs
Regular Verbs (add -ed):
| Present | Past | Example Sentence |
|---|---|---|
| walk | walked | I walked home yesterday. |
| talk | talked | We talked for hours. |
Irregular Verbs:
| Present | Past | Example Sentence |
|---|---|---|
| go | went | She went to school. |
| see | saw | They saw the movie. |
Rules for Using Verbs:
- Subject-Verb Agreement
- Singular subjects take singular verbs Example: He runs fast.
- Plural subjects take plural verbs Example: They run fast.
- Tense Consistency
- Maintain consistent tense throughout a paragraph Wrong: He runs to the store and bought bread. Correct: He ran to the store and bought bread.
Practice Exercises:
Complete these sentences with the correct form of verbs:
- The dog _____ (bark) loudly last night.
- They _____ (study) for their exam now.
- She _____ (go/gone) to the market yesterday.
4. Adjectives
An adjective describes or modifies a noun or pronoun.
| Examples | Example Sentences |
|---|---|
| tall, red, happy | The tall girl has a red balloon. |
| soft, cold, bright | The soft pillow feels nice. |
Types of Adjectives:
- Descriptive Adjectives -Describe qualities or features.
| Examples | Example Sentences |
|---|---|
| beautiful, smart, old | A beautiful garden grows here. |
| round, heavy, smooth | The smooth stone feels cool. |
- Quantitative Adjectives- Show amount or quantity.
| Examples | Example Sentences |
|---|---|
| many, few, three | I have three books. |
| some, several, much | Many people attended. |
- Demonstrative Adjectives -Point out specific things.
| Examples | Example Sentences |
|---|---|
| this, that | This car is mine. |
| these, those | Those flowers smell sweet. |
- Possessive Adjectives- Show ownership.
| Examples | Example Sentences |
|---|---|
| my, your, his, her | My phone is new. |
| our, their, its | Their house is big. |
Degrees of Comparison:
| Positive | Comparative | Superlative |
|---|---|---|
| tall | taller | tallest |
| happy | happier | happiest |
| good | better | best |
Rules for Using Adjectives:
- Order of Adjectives
- Follow the correct order: opinion, size, age, shape, color, origin, material, purpose Example: A beautiful small old round brown French wooden cooking spoon
- Comparative and Superlative Forms
- One syllable: add -er or -est Example: tall → taller → tallest
- Two or more syllables: use more/most Example: beautiful → more beautiful → most beautiful
Practice Exercises:
Add appropriate adjectives in these sentences:
- The _____ cat chased a _____ mouse.
- She wore a _____ dress to the _____ party.
- The _____ boy solved the _____ puzzle quickly.
5. Adverbs
An adverb modifies verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs.
| Examples | Example Sentences |
|---|---|
| quickly, softly, well | He runs quickly. |
| very, too, quite | She sings very well. |
Types of Adverbs:
- Adverbs of Manner- Show how something happens.
| Examples | Example Sentences |
|---|---|
| carefully, happily | She danced gracefully. |
| slowly, loudly | The child spoke softly. |
- Adverbs of Time- Tell when something happens.
| Examples | Example Sentences |
|---|---|
| now, yesterday, soon | We’ll leave tomorrow. |
| later, early, never | They arrived late. |
- Adverbs of Place- Indicate where something happens.
| Examples | Example Sentences |
|---|---|
| here, there, everywhere | The children played outside. |
| upstairs, nearby | Your book is here. |
- Adverbs of Frequency -Show how often something happens.
| Examples | Example Sentences |
|---|---|
| always, usually, often | She always studies hard. |
| sometimes, rarely, never | They rarely visit us. |
- Adverbs of Degree- Show how much or to what extent.
| Examples | Example Sentences |
|---|---|
| very, quite, rather | The soup is extremely hot. |
| too, almost, just | It’s quite cold today. |
Rules for Using Adverbs:
- Formation
- Many adverbs are formed by adding -ly to adjectives Example: quick → quickly careful → carefully
- Position
- Usually placed after the verb Example: She sings beautifully.
- Can also go at the beginning or end of sentences Example: Unfortunately, it rained. The children played happily.
Practice Exercises:
Complete these sentences with suitable adverbs:
- The tortoise moves _____ (slow/slowly).
- He _____ (frequent/frequently) visits his grandparents.
- The bird sang _____ (sweet/sweetly).
6. Prepositions
A preposition shows the relationship between nouns/pronouns and other words in a sentence.
| Examples | Example Sentences |
|---|---|
| in, on, at | The book is on the table. |
| under, over, between | The cat sleeps under the chair. |
Types of Prepositions:
- Prepositions of Place- Show location or position.
| Examples | Example Sentences |
|---|---|
| in, on, at, near | The phone is in my bag. |
| above, below, beside | Stand beside me. |
- Prepositions of Time- Show when something happens.
| Examples | Example Sentences |
|---|---|
| at, in, on | We meet at noon. |
| before, after, during | I’ll call you after dinner. |
- Prepositions of Movement- Show motion or direction.
| Examples | Example Sentences |
|---|---|
| to, from, across | Walk across the street. |
| through, into, out of | The train went through the tunnel. |
Common Preposition Combinations:
| Verb + Preposition | Example Sentences |
|---|---|
| agree with | I agree with your opinion. |
| depend on | Don’t depend on luck. |
Rules for Using Prepositions:
- Time Expressions
- at (specific time): at 3 o’clock
- on (days/dates): on Monday
- in (months/years/periods): in June, in 2024
- Place Expressions
- at (specific point): at home
- in (enclosed space): in the room
- on (surface): on the wall
Practice Exercises:
Fill in the blanks with appropriate prepositions:
- The keys are _____ the drawer.
- She arrives _____ 9 AM _____ Monday.
- The bird flew _____ the window.
7. Conjunctions
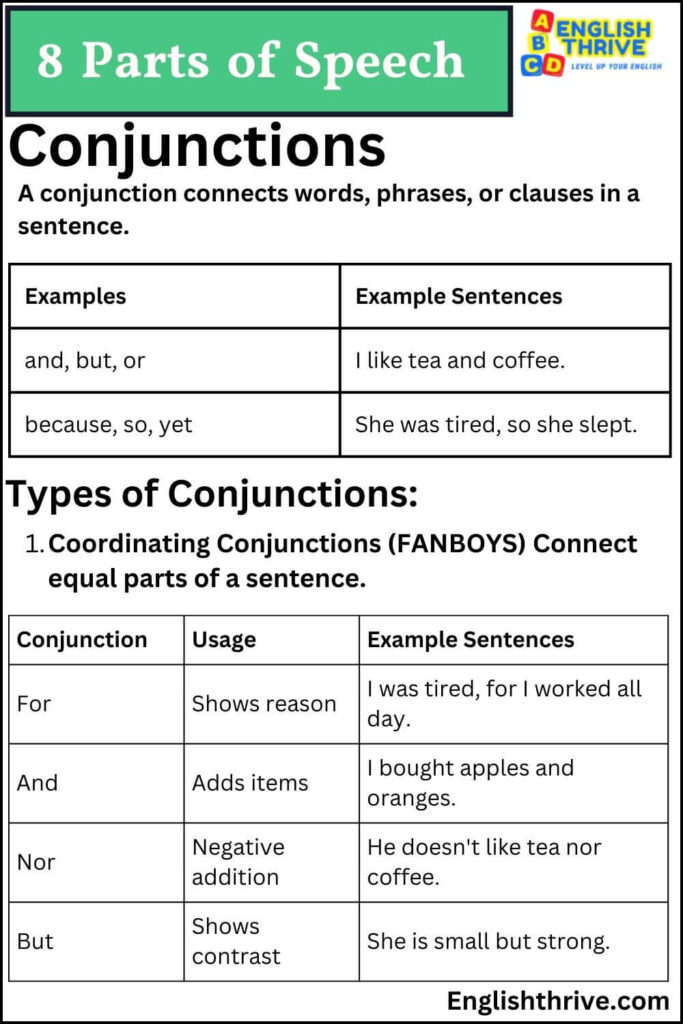
A conjunction connects words, phrases, or clauses in a sentence.
| Examples | Example Sentences |
|---|---|
| and, but, or | I like tea and coffee. |
| because, so, yet | She was tired, so she slept. |
Types of Conjunctions:
- Coordinating Conjunctions (FANBOYS)- Connect equal parts of a sentence.
| Conjunction | Usage | Example Sentences |
|---|---|---|
| For | Shows reason | I was tired, for I worked all day. |
| And | Adds items | I bought apples and oranges. |
| Nor | Negative addition | He doesn’t like tea nor coffee. |
| But | Shows contrast | She is small but strong. |
| Or | Shows choice | You can walk or take a bus. |
| Yet | Shows contrast | He was sick, yet he came to work. |
| So | Shows result | It rained, so we stayed home. |
- Subordinating Conjunctions- Connect dependent and independent clauses.
| Examples | Example Sentences |
|---|---|
| because, although | I stayed home because it rained. |
| unless, while | While I cook, you can set the table. |
- Correlative Conjunctions- Work in pairs.
| Pairs | Example Sentences |
|---|---|
| either…or | Either you go or I go. |
| both…and | She likes both cats and dogs. |
| neither…nor | He is neither rich nor poor. |
Rules for Using Conjunctions:
- Comma Usage
- Use comma before coordinating conjunctions connecting independent clauses Example: I like swimming, but I don’t like diving.
- Parallel Structure
- Keep similar grammatical forms when connecting items Example: He likes running and swimming (not: He likes running and to swim)
Practice Exercises:
Join these sentences using appropriate conjunctions:
- I like chocolate. I like vanilla. (and)
- She will come. She finishes work. (after)
- We can eat here. We can go to a restaurant. (either/or)
8. Interjections
An interjection is a word that expresses strong emotion or sudden feeling.
| Examples | Example Sentences |
|---|---|
| Oh!, Wow!, Ouch! | Wow! That’s amazing! |
| Hey!, Ah!, Hurrah! | Hurrah! We won the game! |
Types of Interjections:
- Strong Emotions Express intense feelings.
| Examples | Example Sentences |
|---|---|
| Yikes!, Ouch! | Yikes! That was close! |
| Hurrah!, Alas! | Alas! We lost the match. |
- Mild Emotions Express gentler feelings.
| Examples | Example Sentences |
|---|---|
| Well, Oh, Ah | Well, that’s interesting. |
| Hmm, Eh, Um | Hmm, let me think. |
Common Interjections and Their Meanings:
| Interjection | Emotion | Example Usage |
|---|---|---|
| Wow! | Amazement | Wow! Look at that sunset! |
| Oops! | Mistake | Oops! I dropped my phone. |
| Shh! | Request silence | Shh! The baby is sleeping. |
Rules for Using Interjections:
- Punctuation
- Strong emotions use exclamation marks Example: Ouch! That hurts!
- Mild emotions use commas Example: Well, I’m not sure.
- Usage Guidelines
- Use sparingly in formal writing
- More common in dialogue and informal writing
- Can stand alone or be part of a sentence
Practice Exercises:
Add appropriate interjections to these situations:
- _____ ! I won the lottery!
- _____ , I need to think about it.
- _____ ! Watch out for that car!
FAQs About Parts of Speech
1. How do you identify parts of speech in a sentence?
Consider the word’s function in the sentence. Ask questions like:
- Is it naming something? (Noun)
- Is it showing action? (Verb)
- Is it describing? (Adjective/Adverb)
- Is it connecting? (Conjunction)
- Is it showing relationship? (Preposition)
- Is it expressing emotion? (Interjection)
2. Can a word be multiple parts of speech?
Yes! Many words can function as different parts of speech depending on their use in a sentence. For example:
- “Fast” as adjective: The fast car
- “Fast” as adverb: He runs fast
3. Why are parts of speech important?
Understanding parts of speech helps in:
- Writing clearly and effectively
- Understanding sentence structure
- Learning other languages
- Improving communication skills
- Mastering grammar rules
4. What are the most common mistakes in using parts of speech?
Common mistakes include:
- Confusing adjectives and adverbs (quick vs quickly)
- Misusing pronouns (me vs I)
- Incorrect verb agreements
- Wrong preposition choices
- Using double negatives The key to avoiding these is understanding each part’s function and practicing regularly.
5. How can I practice identifying parts of speech?
Several effective methods include:
- Sentence diagramming
- Color-coding different parts in a text
- Playing grammar games
- Using online quizzes
- Reading actively and analyzing sentence structures
6. What is the role of parts of speech in sentence structure?
Parts of speech form the building blocks of sentences by:
- Creating meaningful relationships between words
- Establishing proper word order
- Conveying complete thoughts clearly
- Adding variety to expression
- Enabling complex communication
Comprehensive Practice Exercise
Complete the following paragraph by filling in appropriate words:
The _____ (adjective) cat _____ (verb) _____ (adverb) across the _____ (adjective) garden. _____ (preposition) the trees, birds _____ (verb) and _____ (conjunction) sang. “_____ (interjection)!” said the _____ (adjective) girl, watching _____ (pronoun) play.
Practice Exercise Answers
Pronouns Exercise Answers
| Question | Answer | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| John and _____ went to the park. | I | Subject pronoun needed |
| The book belongs to _____. | them | Object pronoun needed |
| Mary hurt _____ yesterday. | herself | Reflexive pronoun referring back to Mary |
Verbs Exercise Answers
| Question | Answer | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| The dog _____ loudly last night. | barked | Past tense needed |
| They _____ for their exam now. | are studying | Present continuous needed |
| She _____ to the market yesterday. | went | Irregular past tense |
Adjectives Exercise Answers
| Question | Answer | Example |
|---|---|---|
| The _____ cat chased a _____ mouse. | black, tiny | The black cat chased a tiny mouse. |
| She wore a _____ dress to the _____ party. | beautiful, formal | She wore a beautiful dress to the formal party. |
| The _____ boy solved the _____ puzzle quickly. | smart, difficult | The smart boy solved the difficult puzzle quickly. |
Prepositions Exercise Answers
| Question | Answer | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| The keys are _____ the drawer. | in | Location inside something |
| She arrives _____ 9 AM _____ Monday. | at, on | Time and day prepositions |
| The bird flew _____ the window. | through | Movement preposition |
Conjunctions Exercise Answers
| Question | Answer | Result |
|---|---|---|
| I like chocolate. I like vanilla. | I like chocolate and vanilla. | Using coordinating conjunction |
| She will come. She finishes work. | She will come after she finishes work. | Using subordinating conjunction |
| We can eat here. We can go to a restaurant. | We can either eat here or go to a restaurant. | Using correlative conjunctions |
Comprehensive Paragraph Exercise Answer
Original: The _____ (adjective) cat _____ (verb) _____ (adverb) across the _____ (adjective) garden. _____ (preposition) the trees, birds _____ (verb) and _____ (conjunction) sang. “_____ (interjection)!” said the _____ (adjective) girl, watching _____ (pronoun) play.
Complete Answer: The playful cat jumped gracefully across the sunny garden. Behind the trees, birds flew and sang. “Wow!” said the little girl, watching them play.