Ever caught yourself writing “everyone should bring their books” and wondered if it’s correct? Common pronoun agreement errors can trip up even the best writers. Today, we’ll explore these tricky situations with clear examples and simple fixes. By understanding these common mistakes, you’ll write with more confidence and clarity.
Contents
ToggleUnderstanding Pronoun Agreement
Pronoun agreement means that pronouns must match their antecedents (the words they refer to) in number (singular or plural) and gender. Think of it like matching socks – they need to be from the same pair to work well together.

Types of Pronoun Agreement
1. Number Agreement
- Singular antecedents need singular pronouns
- Plural antecedents need plural pronouns
2. Gender Agreement
- Use masculine pronouns for male antecedents
- Use feminine pronouns for female antecedents
- Use neutral pronouns when gender is unknown or irrelevant
3. Person Agreement
- First person (I, we)
- Second person (you)
- Third person (he, she, it, they)
Most Common Agreement Issues
- Indefinite Pronouns
- Collective Nouns
- Multiple Antecedents
- Gender-Neutral References
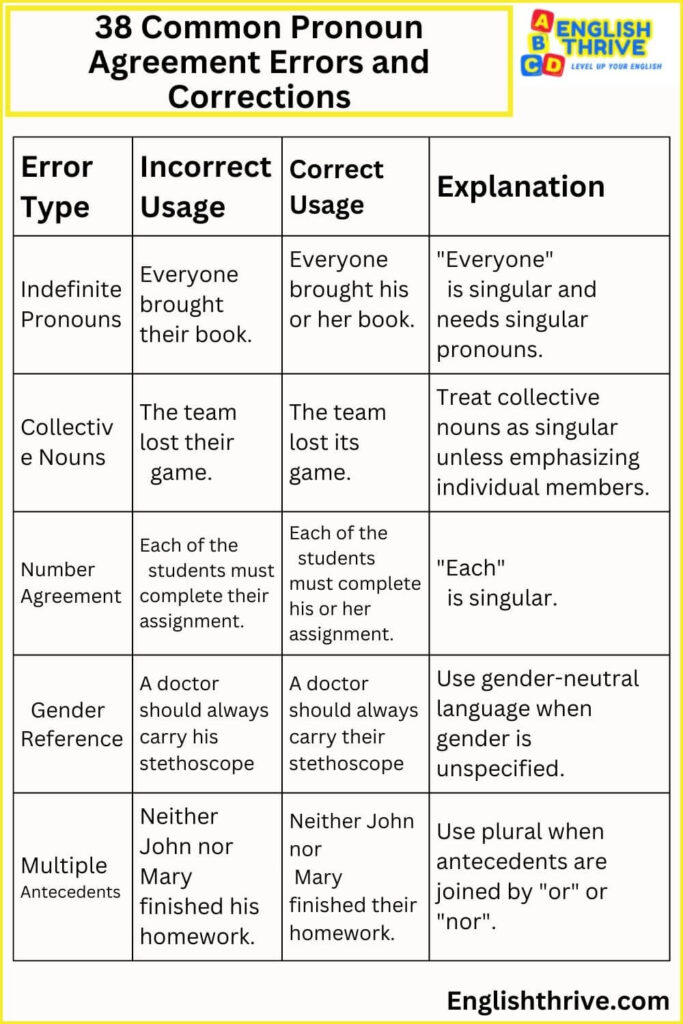
38 Common Pronoun Agreement Errors and Corrections
| Error Type | Incorrect Usage | Correct Usage | Explanation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Indefinite Pronouns | Everyone brought their book. | Everyone brought his or her book. | “Everyone” is singular and needs singular pronouns. |
| Collective Nouns | The team lost their game. | The team lost its game. | Treat collective nouns as singular unless emphasizing individual members. |
| Number Agreement | Each of the students must complete their assignment. | Each of the students must complete his or her assignment. | “Each” is singular. |
| Gender Reference | A doctor should always carry his stethoscope. | A doctor should always carry their stethoscope. | Use gender-neutral language when gender is unspecified. |
| Multiple Antecedents | Neither John nor Mary finished his homework. | Neither John nor Mary finished their homework. | Use plural when antecedents are joined by “or” or “nor”. |
| Indefinite Reference | This is what they said about it. | What they said about it is clear. | Avoid vague pronoun references. |
| Person Agreement | One should always do their best. | One should always do one’s best. | Maintain consistent person throughout. |
| Relative Pronouns | The book which I read was good. | The book that I read was good. | Use “that” for restrictive clauses. |
| Demonstrative Agreement | Those kind of movies are boring. | That kind of movie is boring. | Match demonstrative to noun number. |
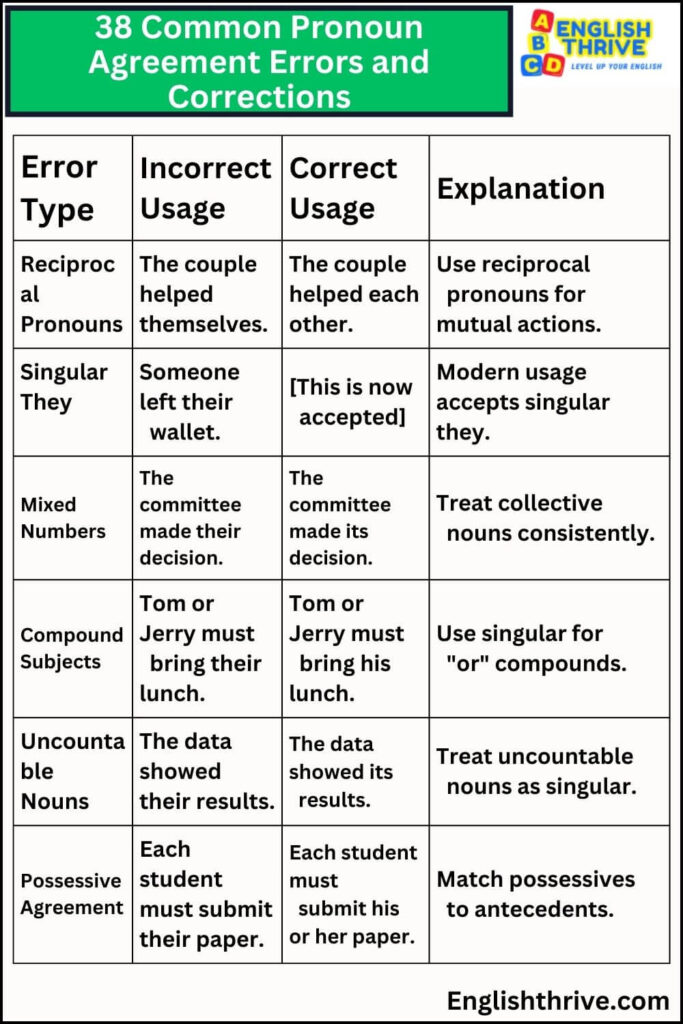
| Reciprocal Pronouns | The couple helped themselves. | The couple helped each other. | Use reciprocal pronouns for mutual actions. |
| Singular They | Someone left their wallet. | [This is now accepted] | Modern usage accepts singular they. |
| Mixed Numbers | The committee made their decision. | The committee made its decision. | Treat collective nouns consistently. |
| Compound Subjects | Tom or Jerry must bring their lunch. | Tom or Jerry must bring his lunch. | Use singular for “or” compounds. |
| Uncountable Nouns | The data showed their results. | The data showed its results. | Treat uncountable nouns as singular. |
| Possessive Agreement | Each student must submit their paper. | Each student must submit his or her paper. | Match possessives to antecedents. |
FAQ on Common Pronoun Agreement Errors
1. How do you identify pronoun agreement errors in writing?
To identify pronoun agreement errors, follow these steps:
- Find all pronouns in the text
- Locate their antecedents (what they refer to)
- Check if they match in:
- Number (singular/plural)
- Gender (masculine/feminine/neutral)
- Person (first/second/third)
- Verify that the reference is clear and unambiguous
2. Why is pronoun agreement important in writing?
Pronoun agreement is crucial because it:
- Ensures clarity and prevents confusion
- Makes writing more professional
- Helps readers follow your ideas easily
- Maintains grammatical correctness
- Reflects attention to detail
3. How do you handle gender-neutral pronoun agreement?
Modern approaches to gender-neutral pronoun agreement include:
- Using “they” as a singular pronoun
- Rewording to avoid pronoun usage
- Using both pronouns (he or she)
- Using alternative constructions
- Following style guide preferences
4. What are the rules for collective nouns and pronoun agreement?
Collective nouns require special attention:
- Treat as singular when the group acts as one unit
- Treat as plural when emphasizing individual members
- Be consistent throughout the document
- Consider regional differences (US vs. UK usage)
- Follow context clues for proper agreement
5. When is it acceptable to use “they” as a singular pronoun?
Using “they” as a singular pronoun is acceptable:
- When gender is unknown or irrelevant
- For non-binary individuals
- In informal writing
- When avoiding awkward “he/she” constructions
- Following modern style guides
Conclusion
Understanding common pronoun agreement errors helps you write more clearly and professionally. Remember to match your pronouns with their antecedents in number, gender, and person. Practice these examples, and you’ll find your writing becoming more precise and effective. Keep this guide handy as a reference while you continue improving your grammar skills.

