Prepositions are essential components of English grammar, acting as bridges that connect nouns, pronouns, and phrases to other parts of a sentence. Mastering prepositions is crucial for constructing clear, accurate, and fluent sentences.
This article focuses specifically on prepositions that begin with the letter “P,” providing a detailed exploration of their meanings, usage, and common pitfalls. This guide will benefit English language learners of all levels, from beginners seeking to grasp the fundamentals to advanced speakers aiming to refine their precision and fluency.
Understanding these Prepositions Starting with P will significantly enhance your ability to express spatial relationships, temporal connections, and various other relationships between elements in a sentence. By studying their diverse applications and nuances, you can avoid common errors and communicate your ideas with greater clarity and confidence.
Contents
ToggleDefinition of Prepositions
A preposition is a word that connects a noun, pronoun, or noun phrase to other words in a sentence. It typically indicates the spatial, temporal, or logical relationship of the noun or pronoun to something else. Prepositions are essential for providing context and clarity in sentences.
Prepositions often express relationships of location (in, on, at), time (before, after, during), direction (to, from, toward), and manner (by, with, without). They are typically followed by a noun or pronoun, which is called the object of the preposition. The preposition and its object together form a prepositional phrase.
For instance, in the sentence “The book is on the table,” the word “on” is a preposition, “table” is its object, and “on the table” is the prepositional phrase.
Structural Breakdown of Prepositional Phrases
Understanding the structure of prepositional phrases is crucial for accurate grammar. A prepositional phrase consists of a preposition followed by its object. The object is usually a noun or pronoun, but it can also be a gerund (a verb ending in “-ing” that functions as a noun) or a noun clause.
The basic formula for a prepositional phrase is: Preposition + (Modifiers) + Object.
Here’s a breakdown of the components:
- Preposition: The word that introduces the phrase (e.g., in, on, at, to, from, with).
- Modifiers (optional): Words that describe the object (e.g., adjectives, adverbs).
- Object: The noun, pronoun, gerund, or noun clause that the preposition relates to the rest of the sentence.
Examples:
- In the morning (preposition + object)
- With great enthusiasm (preposition + modifier + object)
- Past the old oak tree (preposition + modifier + object)
Types of Prepositions
Prepositions can be categorized based on their meaning and function. Here are some common categories:
- Simple Prepositions: Single-word prepositions (e.g., in, on, at, to, from, with, by).
- Compound Prepositions: Prepositions consisting of two or more words (e.g., according to, because of, in spite of).
- Prepositions of Time: Indicate when something happens (e.g., at, on, in, before, after, during).
- Prepositions of Place: Indicate where something is located (e.g., in, on, at, under, over, between).
- Prepositions of Direction: Indicate movement or direction (e.g., to, from, toward, into, onto).
The prepositions starting with “P” that we will focus on in this article include: past, pending, per, plus, prior to, pursuant to. These prepositions exhibit a range of functions, primarily related to time, allowance, and legal contexts.
Examples of Prepositions Starting with P
This section provides detailed examples of each preposition starting with “P,” illustrating their usage in various contexts.
Past
The preposition “past” indicates movement beyond a specific point or a time beyond a specific moment.
Examples:
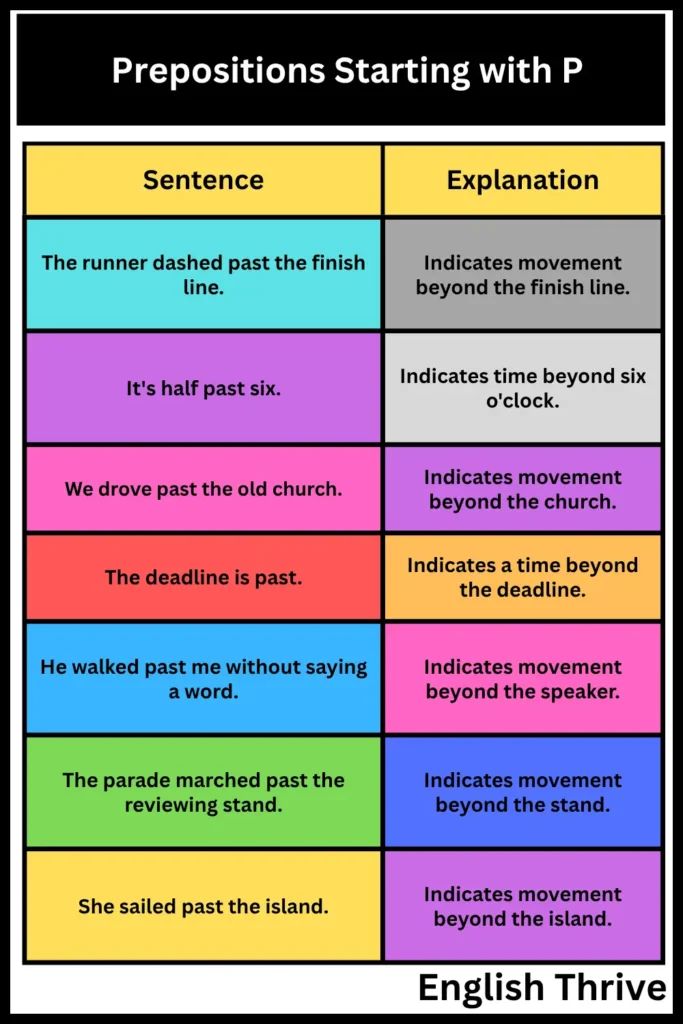
Here is a table with examples using “past” as a preposition:
| Sentence | Explanation |
|---|---|
| The runner dashed past the finish line. | Indicates movement beyond the finish line. |
| It’s half past six. | Indicates time beyond six o’clock. |
| We drove past the old church. | Indicates movement beyond the church. |
| The deadline is past. | Indicates a time beyond the deadline. |
| He walked past me without saying a word. | Indicates movement beyond the speaker. |
| The parade marched past the reviewing stand. | Indicates movement beyond the stand. |
| She sailed past the island. | Indicates movement beyond the island. |
| The train sped past the station. | Indicates movement beyond the station. |
| He’s well past his prime. | Indicates a time beyond his peak. |
| The expiration date is past due. | Indicates that the expiration date has passed. |
| I ran past my old school. | Indicates movement beyond the school. |
| The danger is past now. | Indicates that the dangerous time has ended. |
| The car zoomed past the slower traffic. | Indicates movement beyond the traffic. |
| We hiked past the waterfall. | Indicates movement beyond the waterfall. |
| The incident is now past. | Indicates the incident is over. |
| She glanced past the crowd. | Indicates looking beyond the crowd. |
| The years flew past. | Indicates time moving quickly. |
| He stepped past the security guard. | Indicates movement beyond the guard. |
| The storm has now blown past. | Indicates the storm has ended. |
| She waved as we drove past. | Indicates waving as we moved beyond her. |
| The memory is fading past. | Indicates the memory is fading into the past. |
| Let’s move past this disagreement. | Indicates moving beyond the disagreement. |
| We need to look past our differences. | Indicates looking beyond our differences. |
| The movie is set past the year 2050. | Indicates the movie is set in the future. |
| The soldiers marched past the monument. | Indicates movement beyond the monument. |
 Prepositions Starting with P
Prepositions Starting with P
Pending
The preposition “pending” means “while waiting for” or “until something happens.” It often refers to a decision, event, or resolution that is yet to occur.
Examples:
Here is a table with examples using “pending” as a preposition:
| Sentence | Explanation |
|---|---|
| The application is pending approval. | Waiting for approval. |
| The court case is pending a decision. | Waiting for a decision from the court. |
| Further action is pending review. | Waiting for a review to take place. |
| The contract is pending negotiation. | Waiting for negotiation to be completed. |
| His promotion is pending evaluation. | Waiting for an evaluation to occur. |
| The sale is pending completion of paperwork. | Waiting for the paperwork to be completed. |
| The offer is pending acceptance. | Waiting for the offer to be accepted. |
| The investigation is pending further evidence. | Waiting for more evidence to be presented. |
| Our vacation is pending confirmation. | Waiting for the vacation to be confirmed. |
| The legislation is pending a vote. | Waiting for a vote to be taken. |
| The shipment is pending customs clearance. | Waiting for customs to clear the shipment. |
| The project is pending funding. | Waiting for funding to be secured. |
| The merger is pending regulatory approval. | Waiting for approval from regulatory bodies. |
| The transfer is pending finalization. | Waiting for the transfer to be finalized. |
| The decision is pending further consideration. | Waiting for more consideration to be given. |
| The resolution is pending a meeting. | Waiting for a meeting to take place. |
| The agreement is pending signatures. | Waiting for the signatures to be obtained. |
| The announcement is pending official confirmation. | Waiting for official confirmation to be made. |
| The matter is pending legal advice. | Waiting for legal advice to be received. |
| The award is pending judging. | Waiting for the judging to be completed. |
| The event is pending final arrangements. | Waiting for final arrangements to be made. |
| The publication is pending editing. | Waiting for the editing process to be completed. |
| The release is pending distribution. | Waiting for the distribution to occur. |
| The upgrade is pending installation. | Waiting for the installation to take place. |
| The research is pending data analysis. | Waiting for the data analysis to be completed. |
Per
The preposition “per” means “for each” or “by means of.” It is often used to express rates, measurements, or methods.
Examples:
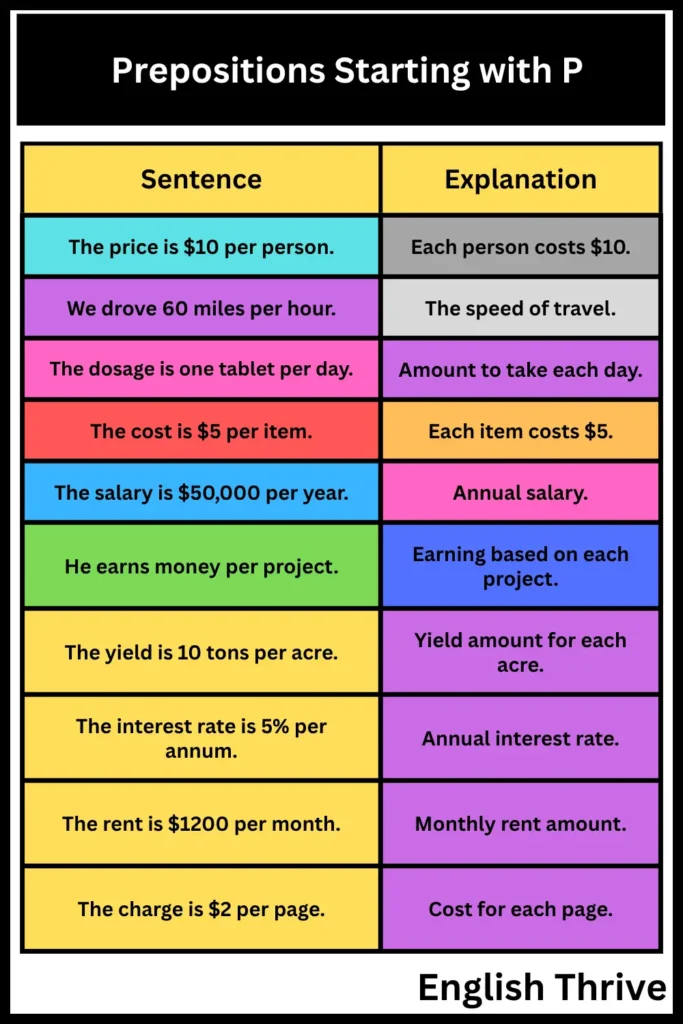
Here is a table with examples using “per” as a preposition:
| Sentence | Explanation |
|---|---|
| The price is $10 per person. | Each person costs $10. |
| We drove 60 miles per hour. | The speed of travel. |
| The dosage is one tablet per day. | Amount to take each day. |
| The cost is $5 per item. | Each item costs $5. |
| The salary is $50,000 per year. | Annual salary. |
| He earns money per project. | Earning based on each project. |
| The yield is 10 tons per acre. | Yield amount for each acre. |
| The interest rate is 5% per annum. | Annual interest rate. |
| The rent is $1200 per month. | Monthly rent amount. |
| The charge is $2 per page. | Cost for each page. |
| The output is 100 units per shift. | Units produced per shift. |
| The consumption is 10 liters per 100 kilometers. | Amount consumed per distance. |
| The tax is $1 per transaction. | Tax amount for each transaction. |
| The fee is $30 per session. | Cost for each session. |
| The rate is $15 per hour. | Hourly rate. |
| The allowance is $50 per week. | Weekly allowance amount. |
| The limit is 2 bags per person. | Limit amount for each person. |
| The allocation is 5 seats per department. | Seats allocated to each department. |
| The distribution is 20 flyers per street. | Flyers distributed to each street. |
| The frequency is 3 times per day. | Occurrences per day. |
| The resolution is 300 dots per inch. | Density of dots per inch. |
| The flow rate is 5 gallons per minute. | Amount flowing per minute. |
| The turnaround is 2 days per order. | Time taken per order. |
| The capacity is 1000 units per batch. | Units per batch. |
| The speed is 25 frames per second. | Frames displayed per second. |
 Prepositions Starting with P
Prepositions Starting with P
Plus
The preposition “plus” means “in addition to.” It is often used in mathematical contexts or to indicate an added element.
Examples:
Here is a table with examples using “plus” as a preposition:
| Sentence | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Two plus two equals four. | Mathematical addition. |
| The cost is $10 plus tax. | $10 plus the added tax. |
| He gets a salary plus commission. | Salary in addition to commission. |
| She has experience plus a great attitude. | Experience and a great attitude. |
| The package includes accommodation plus meals. | Accommodation and meals are included. |
| We offer a discount plus free shipping. | Discount and free shipping are offered. |
| The team has talent plus determination. | Talent and determination are present. |
| The job requires skills plus experience. | Skills and experience are needed. |
| The product features durability plus style. | Durability and style are featured. |
| The offer includes a bonus plus benefits. | Bonus and benefits are included. |
| The program provides support plus resources. | Support and resources are provided. |
| The project needs funding plus manpower. | Funding and manpower are needed. |
| The course offers lectures plus workshops. | Lectures and workshops are offered. |
| The event features music plus dance. | Music and dance are featured. |
| The service includes maintenance plus support. | Maintenance and support are included. |
| The system provides security plus efficiency. | Security and efficiency are provided. |
| The design incorporates functionality plus aesthetics. | Functionality and aesthetics are incorporated. |
| The solution provides reliability plus scalability. | Reliability and scalability are provided. |
| The building offers amenities plus convenience. | Amenities and convenience are offered. |
| The car has performance plus comfort. | Performance and comfort are present. |
| The recipe includes ingredients plus instructions. | Ingredients and instructions are included. |
| The game features strategy plus action. | Strategy and action are featured. |
| The book contains information plus insights. | Information and insights are contained. |
| The software provides tools plus features. | Tools and features are provided. |
| The vacation offers relaxation plus adventure. | Relaxation and adventure are offered. |
Prior To
The preposition “prior to” means “before” or “earlier than.” It indicates that something happens or exists before something else in time.
Examples:
Here is a table with examples using “prior to” as a preposition:
| Sentence | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Prior to the meeting, please review the agenda. | Before the meeting. |
| Prior to the invention of the car, people traveled by horse. | Before the car was invented. |
| Prior to his arrival, we set up the room. | Before he arrived. |
| Prior to the surgery, you must fast. | Before the surgery. |
| Prior to the concert, we grabbed dinner. | Before the concert. |
| Prior to the deadline, submit your work. | Before the deadline. |
| Prior to the event, we sent out invitations. | Before the event. |
| Prior to the trip, we made reservations. | Before the trip. |
| Prior to the launch, they tested the rocket. | Before the launch. |
| Prior to the exam, study the material. | Before the exam. |
| Prior to the decision, consider all options. | Before the decision. |
| Prior to the purchase, read the reviews. | Before the purchase. |
| Prior to the change, we sought approval. | Before the change. |
| Prior to the update, back up your data. | Before the update. |
| Prior to the sale, inspect the item. | Before the sale. |
| Prior to the start, prepare your equipment. | Before the start. |
| Prior to the release, review the document. | Before the release. |
| Prior to the interview, research the company. | Before the interview. |
| Prior to the experiment, gather the materials. | Before the experiment. |
| Prior to the installation, read the instructions. | Before the installation. |
| Prior to the meeting, distribute the reports. | Before the meeting. |
| Prior to the lecture, review the slides. | Before the lecture. |
| Prior to the workout, warm up your muscles. | Before the workout. |
| Prior to the presentation, practice your speech. | Before the presentation. |
| Prior to the journey, pack your bags. | Before the journey. |
Pursuant To
The preposition “pursuant to” means “in accordance with” or “in compliance with.” It is often used in legal or formal contexts to indicate that an action is being taken according to a specific rule, law, or agreement.
Examples:
Here is a table with examples using “pursuant to” as a preposition:
| Sentence | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Pursuant to the law, the company must comply with regulations. | In accordance with the law. |
| Pursuant to the agreement, we will proceed with the project. | In accordance with the agreement. |
| Pursuant to the court order, the assets were seized. | In accordance with the court order. |
| Pursuant to the policy, employees must wear badges. | In accordance with the policy. |
| Pursuant to the rules, the game was stopped. | In accordance with the rules. |
| Pursuant to the contract, payments are due monthly. | In accordance with the contract. |
| Pursuant to the guidelines, the report was formatted. | In accordance with the guidelines. |
| Pursuant to the statute, the claim was rejected. | In accordance with the statute. |
| Pursuant to the regulations, the facility was inspected. | In accordance with the regulations. |
| Pursuant to the mandate, the program was implemented. | In accordance with the mandate. |
| Pursuant to the directive, the changes were made. | In accordance with the directive. |
| Pursuant to the terms, the service was terminated. | In accordance with the terms. |
| Pursuant to the procedure, the request was processed. | In accordance with the procedure. |
| Pursuant to the resolution, the action was taken. | In accordance with the resolution. |
| Pursuant to the decree, the land was confiscated. | In accordance with the decree. |
| Pursuant to the protocol, the meeting was conducted. | In accordance with the protocol. |
| Pursuant to the legislation, the tax was imposed. | In accordance with the legislation. |
| Pursuant to the authorization, the funds were released. | In accordance with the authorization. |
| Pursuant to the instructions, the task was completed. | In accordance with the instructions. |
| Pursuant to the code, the system was designed. | In accordance with the code. |
| Pursuant to the standard, the product was tested. | In accordance with the standard. |
| Pursuant to the provision, the clause was enforced. | In accordance with the provision. |
| Pursuant to the warrant, the search was executed. | In accordance with the warrant. |
| Pursuant to the ruling, the judgment was issued. | In accordance with the ruling. |
| Pursuant to the agreement, the data was shared. | In accordance with the agreement. |
Usage Rules for Prepositions Starting with P
Proper preposition usage is crucial for clear and effective communication. Here are some key rules to keep in mind when using prepositions starting with “P”:
- “Past” vs. “Passed”: “Past” is a preposition indicating movement beyond or time beyond, while “passed” is the past tense of the verb “to pass.” For example: “We drove past the school” (preposition) vs. “We passed the school” (verb).
- “Pending” and Clarity: Ensure that the noun or event that is pending is clearly identified. For example, “The decision is pending review” is clearer than just “The decision is pending.”
- “Per” and Accuracy: Always use “per” to express rates or ratios. For instance, “$10 per hour” is correct; avoid using “a” or “an” in place of “per” in such contexts.
- “Plus” and Formal Writing: While “plus” is acceptable in informal contexts, consider using “in addition to” or “and” in more formal writing.
- “Prior To” and Conciseness: While grammatically correct, “prior to” can sometimes be replaced with the simpler “before” for conciseness, unless a more formal tone is desired.
- “Pursuant To” and Legal Contexts: “Pursuant to” is generally reserved for legal, formal, or official contexts. Avoid using it in casual conversation.
Common Mistakes with Prepositions Starting with P
Even experienced English speakers sometimes make mistakes with prepositions. Here are some common errors to watch out for:
| Incorrect | Correct | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| We passed by the store. | We drove past the store. | “Passed” is a verb. “Past” (preposition) is correct. |
| The application is pending of approval. | The application is pending approval. | The preposition “of” is unnecessary after “pending.” |
| $5 a person. | $5 per person. | “Per” is the correct preposition to indicate “for each.” |
| He has skills, plus also experience. | He has skills plus experience. | “Also” is redundant after “plus.” |
| Prior than the meeting. | Prior to the meeting. | The correct form is “prior to.” |
| Pursuant of the law. | Pursuant to the law. | The correct form is “pursuant to.” |
Practice Exercises :Prepositions Starting with P
Test your understanding of prepositions starting with “P” with these exercises.
Exercise 1: Fill in the Blanks
Fill in the blanks with the correct preposition (past, pending, per, plus, prior to, pursuant to).
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| 1. The train went _______ the station. | past |
| 2. The decision is _______ review. | pending |
| 3. The cost is $20 _______ ticket. | per |
| 4. She has talent _______ experience. | plus |
| 5. _______ the meeting, please read the report. | Prior to |
| 6. _______ the regulations, we must comply. | Pursuant to |
| 7. It’s ten minutes _______ four. | past |
| 8. The merger is _______ approval from the board. | pending |
| 9. The rate is $30 _______ hour. | per |
| 10. He has enthusiasm _______ dedication. | plus |
Exercise 2: Correct the Errors
Identify and correct the errors in the following sentences.
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| 1. We passed of the store. | We drove past the store. |
| 2. The application is pending of approval. | The application is pending approval. |
| 3. $10 a person. | $10 per person. |
| 4. She has skills, plus also experience. | She has skills plus experience. |
| 5. Prior than the concert, we had dinner. | Prior to the concert, we had dinner. |
| 6. Pursuant of the rules, the game was stopped. | Pursuant to the rules, the game was stopped. |
| 7. The deadline is passed. | The deadline is past. |
| 8. His promotion is pending of evaluation. | His promotion is pending evaluation. |
| 9. We traveled 50 miles an hour. | We traveled 50 miles per hour. |
| 10. The team has talent, plus also determination. | The team has talent plus determination. |
Advanced Topics in Preposition Usage
For advanced learners, here are some more complex aspects of preposition usage:
- Prepositional Stranding: This occurs when a preposition is separated from its object, often at the end of a sentence. While traditionally frowned upon, it is now widely accepted in modern English. For example: “Which school did you go to?”
- Multiple Prepositional Phrases: Sentences can contain multiple prepositional phrases, each modifying different parts of the sentence. Understanding how these phrases interact is crucial for complex sentence construction. For example: “The book on the table in the corner is mine.”
- Prepositions in Idiomatic Expressions: Many idiomatic expressions include specific prepositions that cannot be changed. Learning these expressions is essential for fluency. For example: “He is goodat playing the piano.”
FAQs About Prepositions Starting with P
Here are some frequently asked questions about prepositions, particularly those starting with “P”:
Q: Can “past” be used as something other than a preposition?
Yes, “past” can also be used as an adjective (e.g., “the past year”), a noun (e.g., “forget the past”), or an adverb (e.g., “he ran past”).
Q: Is it always necessary to use “prior to” instead of “before”?
No, “before” is often perfectly acceptable and more concise. “Prior to” is typically used in more formal contexts.
Q: When is it appropriate to use “pursuant to”?
“Pursuant to” is best used in legal, official, or formal contexts when indicating compliance with a rule, law, or agreement.
Q: Can “plus” always replace “and”?
While “plus” can sometimes replace “and” in informal contexts, it’s generally better to use “and” in formal writing to maintain a professional tone.
Q: What’s the difference between “pending” and “awaiting”?
“Pending” implies that something is waiting to happen or be decided, while “awaiting” simply means waiting for something. They are often interchangeable, but “pending” often suggests a more formal or official context.
Q: How can I improve my preposition usage in general?
Read widely, pay attention to how native speakers use prepositions, and practice using them in your own writing and speaking. Review grammar guides and do exercises to reinforce your understanding.
Conclusion: Prepositions Starting with P
Mastering prepositions, including those starting with “P,” is essential for clear, accurate, and effective communication in English. By understanding the nuances of words like past, pending, per, plus, prior to, and pursuant to, you can significantly enhance your language skills and avoid common errors.
Continue to practice and refine your understanding of these prepositions through reading, writing, and real-life conversations. With consistent effort, you’ll become more confident and proficient in your use of English.