Understanding classroom-related vocabulary is essential for both students and teachers to facilitate effective communication and learning within the educational environment. This article provides a comprehensive guide to the words commonly used in classrooms, covering their definitions, usage, and practical examples.
Mastering this vocabulary will help learners of all levels navigate the classroom environment with confidence, participate actively in discussions, and understand instructions clearly. This guide is beneficial for ESL students, educators, and anyone interested in enhancing their understanding of educational terminology.
Contents
ToggleDefinition of Classroom Vocabulary
Classroom vocabulary encompasses all the words and phrases commonly used in an educational setting. This includes terms related to classroom objects, subjects, people, activities, instructions, and assessments.
Understanding classroom vocabulary is crucial for effective communication between teachers and students, facilitating a smooth learning process. This vocabulary is not limited to a single subject but spans across various disciplines and grade levels.
The function of classroom vocabulary is to provide a shared understanding of the concepts, instructions, and activities taking place within the classroom. It enables students to follow lessons, participate in discussions, and complete assignments successfully.
For teachers, it serves as a tool to effectively manage the classroom, deliver instructions, and assess student learning.
Contextually, classroom vocabulary is used in various situations, such as during lectures, group discussions, individual assignments, and assessments. It is also present in textbooks, handouts, and other learning materials.
The specific terms used may vary depending on the subject matter and the age group of the students.
Structural Breakdown of Classroom Vocabulary
Classroom vocabulary can be structurally broken down into several parts of speech, including nouns, verbs, adjectives, and adverbs. Nouns refer to objects, people, and concepts (e.g., desk, teacher, homework). Verbs describe actions and activities (e.g., to read, to write, to learn). Adjectives modify nouns and provide more information about them (e.g., difficult, easy, interesting). Adverbs modify verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs, providing information about how, when, where, or to what extent something is done (e.g., quickly, carefully, silently).
Understanding the grammatical structure of these words helps students use them correctly in sentences and comprehend their meaning in context. For instance, knowing that “assignment” is a noun allows students to identify it as a subject or object in a sentence.
Similarly, recognizing “explain” as a verb helps students understand that it describes an action.
Furthermore, many classroom-related terms are compound words or phrases, such as “textbook,” “group work,” and “pop quiz.” These terms combine two or more words to create a new meaning specific to the classroom environment. Recognizing these patterns enhances vocabulary acquisition and comprehension.
Types and Categories of Classroom Vocabulary
Classroom vocabulary can be categorized into several types based on their function and context. These categories include classroom objects, subjects and courses, people and roles, actions and activities, instructions and commands, assessment and evaluation, and academic terms.
Each category plays a distinct role in facilitating education and communication within the classroom.
Classroom Objects
This category includes physical items found in a classroom, such as desks, chairs, whiteboards, books, and computers. These objects are essential tools for teaching and learning.
Subjects and Courses
This category includes the names of academic disciplines and specific courses offered in schools and universities, such as mathematics, science, history, and English literature.
People and Roles
This category includes the titles and names of individuals involved in the educational process, such as teachers, students, principals, and teaching assistants. It also includes the roles they play within the classroom environment.
Actions and Activities
This category includes verbs and phrases that describe the actions and activities that take place in the classroom, such as reading, writing, listening, discussing, and presenting.
Instructions and Commands
This category includes the specific directions and commands given by teachers to students, such as “open your books,” “write your name,” and “listen carefully.”
Assessment and Evaluation
This category includes terms related to evaluating student learning, such as exams, quizzes, grades, and feedback.
Academic Terms
This category includes general terms used in academic contexts, such as “syllabus,” “curriculum,” “semester,” and “research.”
Examples of Classroom Vocabulary
To illustrate the different categories of classroom vocabulary, here are some examples organized into tables. These examples provide a clear understanding of how these words are used in context.
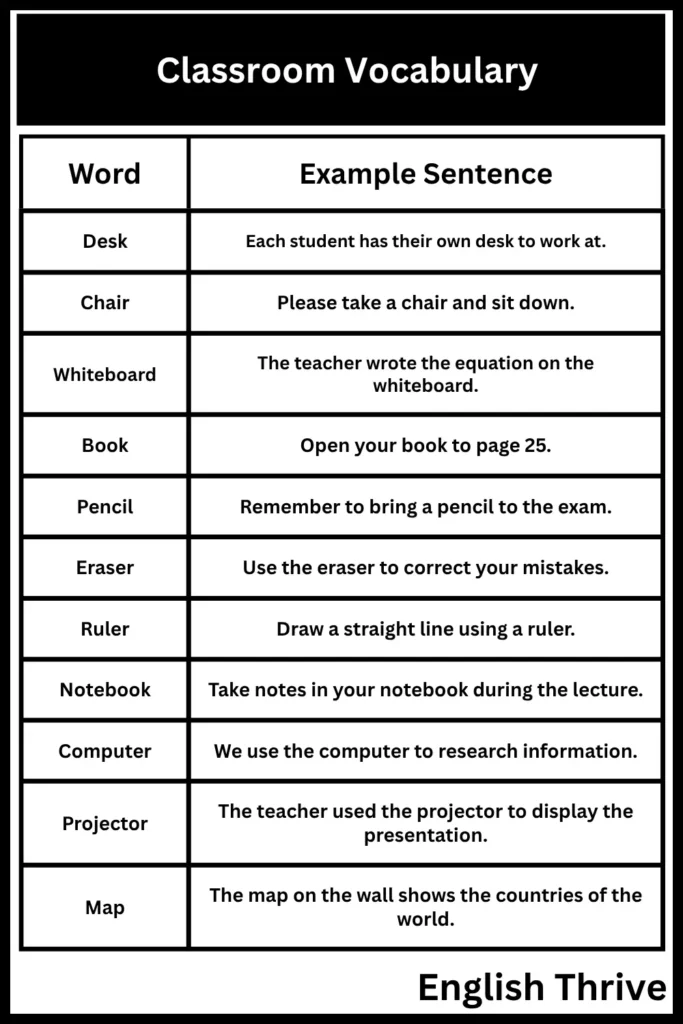
Classroom Objects Examples
The following table provides examples of common classroom objects, which are essential for the learning environment:
| Word | Example Sentence |
|---|---|
| Desk | Each student has their own desk to work at. |
| Chair | Please take a chair and sit down. |
| Whiteboard | The teacher wrote the equation on the whiteboard. |
| Book | Open your book to page 25. |
| Pencil | Remember to bring a pencil to the exam. |
| Eraser | Use the eraser to correct your mistakes. |
| Ruler | Draw a straight line using a ruler. |
| Notebook | Take notes in your notebook during the lecture. |
| Computer | We use the computer to research information. |
| Projector | The teacher used the projector to display the presentation. |
| Map | The map on the wall shows the countries of the world. |
| Globe | The globe helps us understand the Earth’s shape. |
| Calculator | You can use a calculator for these math problems. |
| Scissors | Be careful when using scissors. |
| Glue | Use glue to stick the paper together. |
| Markers | The teacher used colorful markers to draw on the whiteboard. |
| Textbook | The textbook contains all the information you need for the course. |
| Dictionary | Use a dictionary to look up the meaning of new words. |
| Backpack | Don’t forget to bring your backpack with all your books. |
| Pencil sharpener | Use the pencil sharpener to make your pencil pointy. |
| Highlighter | Use a highlighter to mark important information in the text. |
| Stapler | The teacher used a stapler to bind the papers together. |
| Paper | Write your answers on a piece of paper. |
Subjects and Courses Examples
The following table provides examples of common subjects and courses taught in schools:
| Word | Example Sentence |
|---|---|
| Mathematics | I enjoy solving problems in mathematics class. |
| Science | We conduct experiments in the science lab. |
| History | We learn about past events in history class. |
| English Literature | We read classic novels in English Literature. |
| Biology | Biology is the study of living organisms. |
| Chemistry | Chemistry involves the study of substances and their properties. |
| Physics | Physics explains the fundamental laws of the universe. |
| Geography | Geography teaches us about the Earth’s landscapes and cultures. |
| Art | I love expressing myself through art. |
| Music | Playing an instrument is a great part of music class. |
| Physical Education | We play sports in Physical Education. |
| Computer Science | Computer Science teaches us how to code and develop software. |
| Economics | Economics explains how societies manage their resources. |
| Psychology | Psychology studies the human mind and behavior. |
| Sociology | Sociology examines social structures and interactions. |
| Political Science | Political Science explores the theory and practice of politics. |
| Foreign Language | I am learning Spanish in my Foreign Language class. |
| Algebra | Algebra involves solving equations with unknown variables. |
| Calculus | Calculus is a branch of mathematics that deals with continuous change. |
| Geometry | Geometry involves the study of shapes and their properties. |
| Environmental Science | Environmental Science examines the interaction between humans and the environment. |
| Journalism | Journalism teaches the skills of reporting and writing news. |
| Philosophy | Philosophy explores fundamental questions about existence, knowledge, and ethics. |
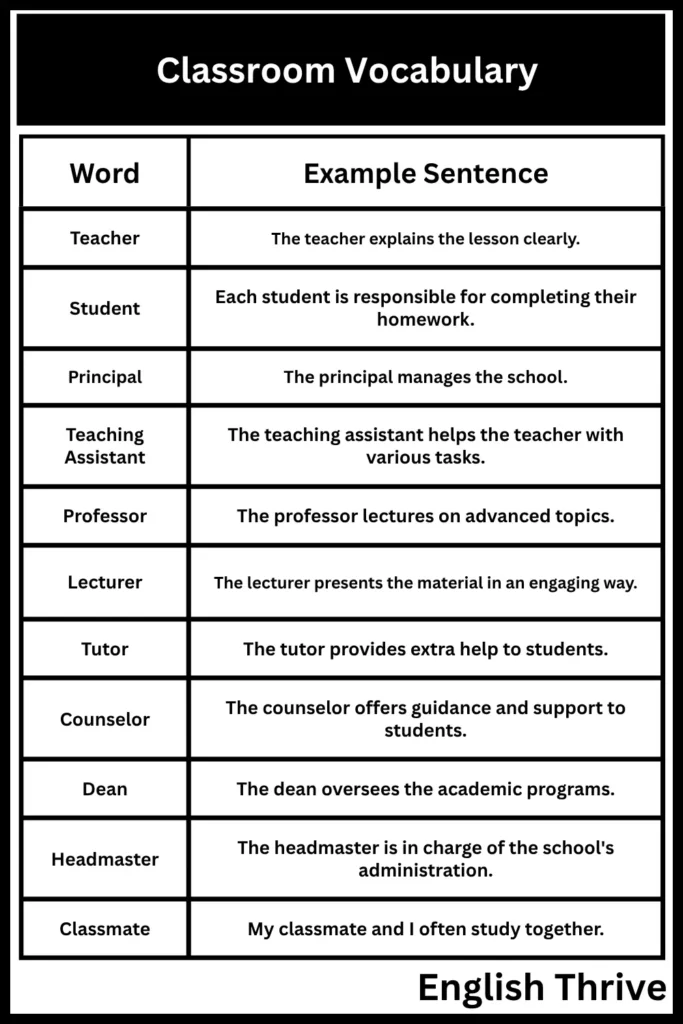
People and Roles Examples
The following table provides examples of the people involved in the classroom and their roles:
| Word | Example Sentence |
|---|---|
| Teacher | The teacher explains the lesson clearly. |
| Student | Each student is responsible for completing their homework. |
| Principal | The principal manages the school. |
| Teaching Assistant | The teaching assistant helps the teacher with various tasks. |
| Professor | The professor lectures on advanced topics. |
| Lecturer | The lecturer presents the material in an engaging way. |
| Tutor | The tutor provides extra help to students. |
| Counselor | The counselor offers guidance and support to students. |
| Dean | The dean oversees the academic programs. |
| Headmaster | The headmaster is in charge of the school’s administration. |
| Classmate | My classmate and I often study together. |
| Pupil | Each pupil is encouraged to participate in class. |
| Instructor | The instructor guides the students through the course. |
| Mentor | My mentor helps me with my career goals. |
| Advisor | The advisor helps students choose the right courses. |
| Researcher | The researcher conducts studies in various fields. |
| Scholar | The scholar is known for their deep knowledge. |
| Fellow | The fellow contributes to the research project. |
| Alumnus | The alumnus returned to give a guest lecture. |
| Graduate Student | The graduate student is working on their thesis. |
| Undergraduate Student | The undergraduate student is pursuing a bachelor’s degree. |
| Librarian | The librarian helps students find the resources they need. |
| Administrator | The administrator manages the school’s operations. |
Actions and Activities Examples
The following table provides examples of actions and activities that occur in the classroom:
| Word | Example Sentence |
|---|---|
| Read | We read a chapter from the book. |
| Write | Please write your name on the paper. |
| Listen | Listen carefully to the instructions. |
| Discuss | We will discuss the topic in groups. |
| Present | Each student will present their project. |
| Learn | We learn new things every day in school. |
| Study | I study for my exams every evening. |
| Practice | We practice our pronunciation in class. |
| Analyze | We analyze the data in the experiment. |
| Evaluate | The teacher will evaluate our performance. |
| Participate | Everyone should participate in the discussion. |
| Collaborate | We collaborate on group projects. |
| Research | We research various topics for our assignments. |
| Solve | We solve math problems in class. |
| Create | We create artwork in art class. |
| Experiment | We experiment in the science lab. |
| Explore | We explore new ideas in class. |
| Review | We review the material before the test. |
| Memorize | We memorize vocabulary words. |
| Understand | It’s important to understand the concepts. |
| Question | Don’t hesitate to question anything you don’t understand. |
| Observe | Observe the experiment carefully. |
| Summarize | Summarize the main points of the article. |
Instructions and Commands Examples
The following table provides examples of common instructions and commands given in the classroom:
| Word | Example Sentence |
|---|---|
| Open | Open your books to page 50. |
| Close | Close your books when you are finished. |
| Write | Write your answers on the answer sheet. |
| Listen | Listen carefully to the instructions. |
| Read | Read the passage and answer the questions. |
| Repeat | Repeat after me. |
| Explain | Explain your reasoning to the class. |
| Answer | Answer the questions at the end of the chapter. |
| Discuss | Discuss the topic with your partner. |
| Complete | Complete the worksheet before the end of class. |
| Submit | Submit your assignments by Friday. |
| Review | Review the notes before the quiz. |
| Circle | Circle the correct answer. |
| Underline | Underline the main idea in each paragraph. |
| Compare | Compare and contrast the two theories. |
| Contrast | Contrast the different approaches. |
| Define | Define the term in your own words. |
| Illustrate | Illustrate your point with an example. |
| Summarize | Summarize the article in a few sentences. |
| Analyze | Analyze the data provided. |
| Justify | Justify your answer with evidence. |
| Elaborate | Elaborate on your idea. |
| Identify | Identify the key points in the text. |
Assessment and Evaluation Examples
The following table provides examples of terms related to assessment and evaluation in the classroom:
| Word | Example Sentence |
|---|---|
| Exam | We have an exam next week. |
| Quiz | There will be a short quiz on Friday. |
| Grade | I received a good grade on my essay. |
| Feedback | The teacher provided helpful feedback on my work. |
| Assessment | The final assessment is worth 50% of the grade. |
| Test | The test covers all the material from the semester. |
| Mark | The teacher will mark our assignments. |
| Evaluate | The professor will evaluate our presentations. |
| Score | My score on the exam was 90%. |
| Criteria | The criteria for grading are clearly defined. |
| Performance | Our performance in the class will determine our final grade. |
| Progress | The teacher tracks our progress throughout the year. |
| Assignment | This assignment is due next Monday. |
| Project | We are working on a group project. |
| Report | We need to write a report on our findings. |
| Presentation | Each student will give a presentation. |
| Essay | We have to write an essay on the topic. |
| Homework | Don’t forget to do your homework. |
| Midterm | The midterm exam is scheduled for next week. |
| Final Exam | The final exam covers all the material from the course. |
| Rubric | The teacher provided a rubric for the essay. |
| Portfolio | We are creating a portfolio of our best work. |
| Grading Scale | The grading scale is A through F. |
Academic Terms Examples
The following table provides examples of general academic terms used in the classroom:
| Word | Example Sentence |
|---|---|
| Syllabus | The syllabus outlines the course requirements. |
| Curriculum | The curriculum covers a wide range of topics. |
| Semester | The semester lasts for 15 weeks. |
| Research | We conduct research on various topics. |
| Thesis | The graduate student is working on their thesis. |
| Dissertation | The doctoral candidate defended their dissertation. |
| Lecture | The professor gave an interesting lecture. |
| Seminar | We participate in a seminar to discuss the readings. |
| Workshop | We attended a workshop on writing skills. |
| Academic | The academic year begins in September. |
| Credits | This course is worth three credits. |
| Degree | I am pursuing a bachelor’s degree. |
| Major | My major is computer science. |
| Minor | My minor is mathematics. |
| Prerequisite | This course has a prerequisite. |
| Elective | I chose an elective course in art history. |
| Tuition | The tuition fees are due next week. |
| Scholarship | I received a scholarship to help pay for college. |
| Grant | The research project received a grant. |
| Enrollment | The enrollment for the course is limited. |
| Registration | Registration for the fall semester opens next month. |
| Transcript | I requested a copy of my transcript. |
| Alumni | The alumni association hosts networking events. |
Usage Rules for Classroom Vocabulary
Using classroom vocabulary correctly involves understanding the context in which each word or phrase is used. It’s essential to pay attention to the grammatical structure of the sentence and the specific meaning of the term.
For example, “homework” is a noun that refers to assignments students complete outside of the classroom, while “to assign” is a verb that means to give an assignment.
Another important rule is to use formal language in academic writing and presentations. Avoid slang or colloquialisms that may not be appropriate in an educational setting.
Instead, use precise and clear language to convey your ideas effectively.
When using abbreviations or acronyms, be sure to define them the first time they appear in your writing. For example, write “Teaching Assistant (TA)” before using the abbreviation “TA” in subsequent sentences.
Be mindful of the connotations of certain words. For instance, while “test” and “exam” are often used interchangeably, “exam” may imply a more comprehensive and formal assessment than “test.”
Common Mistakes with Classroom Vocabulary
One common mistake is confusing the meaning of similar-sounding words. For example, “affect” and “effect” are often mixed up. “Affect” is typically a verb meaning to influence, while “effect” is usually a noun meaning a result or consequence. Incorrect: The test will effect my grade. Correct: The test will affect my grade.
Another frequent error is using the wrong preposition with certain words. For example, “participate in” is the correct form, not “participate to.” Incorrect: I want to participate to the discussion. Correct: I want to participate in the discussion.
Misspelling words is also a common mistake. Always double-check your spelling, especially for technical or academic terms. Incorrect: The principle of the school announced the new policy. Correct: The principal of the school announced the new policy.
Using informal language in formal assignments is another mistake to avoid. Incorrect: The homework was pretty easy peasy. Correct: The homework was relatively easy.
Practice Exercises
Test your understanding of classroom vocabulary with these practice exercises. Choose the correct word or phrase to complete each sentence.
| Question | Options | Answer |
|---|---|---|
| 1. The _________ explains the lesson to the students. | a) student, b) teacher, c) principal | b) teacher |
| 2. We use a _________ to write on the whiteboard. | a) pencil, b) pen, c) marker | c) marker |
| 3. _________ is the study of living organisms. | a) History, b) Biology, c) Mathematics | b) Biology |
| 4. Please _________ your books to page 30. | a) close, b) open, c) read | b) open |
| 5. The _________ is in charge of the school. | a) student, b) teacher, c) principal | c) principal |
| 6. We take notes in our _________ during the lecture. | a) textbook, b) notebook, c) desk | b) notebook |
| 7. _________ is a subject that involves numbers and equations. | a) Science, b) History, c) Mathematics | c) Mathematics |
| 8. The teacher will _________ our assignments. | a) write, b) grade, c) read | b) grade |
| 9. We use a _________ to erase mistakes. | a) pen, b) eraser, c) ruler | b) eraser |
| 10. Don’t forget to do your _________ for tomorrow. | a) project, b) homework, c) exam | b) homework |
| 11. The _________ outlines the course requirements. | a) textbook, b) syllabus, c) notebook | b) syllabus |
| 12. We will have a short _________ on Friday. | a) exam, b) quiz, c) project | b) quiz |
| 13. Please _________ after me. | a) listen, b) write, c) repeat | c) repeat |
| 14. My _________ is computer science. | a) minor, b) major, c) elective | b) major |
| 15. We are working on a group _________. | a) homework, b) exam, c) project | c) project |
| 16. The _________ helps students find books. | a) teacher, b) librarian, c) principal | b) librarian |
| 17. We _________ the data in the science lab. | a) analyze, b) write, c) read | a) analyze |
| 18. The _________ is due next week. | a) exam, b) assignment, c) test | b) assignment |
| 19. _________ is the study of the past. | a) Science, b) History, c) Biology | b) History |
| 20. Please _________ your name on the paper. | a) read, b) write, c) open | b) write |
Advanced Topics in Classroom Vocabulary
For advanced learners, exploring the etymology and historical context of classroom vocabulary can provide a deeper understanding of their meanings and usage. For example, the word “curriculum” comes from the Latin word for “racecourse,” reflecting the idea of a structured path of learning.
Another advanced topic is the use of metaphorical language in education. Teachers often use metaphors to explain complex concepts in a more accessible way.
For instance, describing the atom as a “solar system” helps students visualize its structure.
Additionally, understanding the nuances of academic writing and discourse is crucial for advanced learners. This includes mastering the conventions of citation, argumentation, and critical analysis.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some frequently asked questions about classroom vocabulary:
What is the importance of learning classroom vocabulary?
Learning classroom vocabulary is crucial for effective communication and understanding in an educational setting. It enables students to follow instructions, participate in discussions, and complete assignments successfully. It also helps teachers manage the classroom and deliver lessons effectively.
How can I improve my classroom vocabulary?
There are several ways to improve your classroom vocabulary, including reading textbooks and academic articles, taking notes in class, using a dictionary and thesaurus, and practicing using new words in sentences. Additionally, engaging in discussions and asking questions can help reinforce your understanding of the terms.
What are some common categories of classroom vocabulary?
Common categories of classroom vocabulary include classroom objects, subjects and courses, people and roles, actions and activities, instructions and commands, assessment and evaluation, and academic terms.
What are some common mistakes people make when using classroom vocabulary ?
Common mistakes include confusing similar-sounding words, using the wrong prepositions, misspelling words, and using informal language in formal assignments. Always double-check your work and consult a dictionary or thesaurus when in doubt.
How can teachers help students learn classroom vocabulary?
Teachers can help students learn classroom vocabulary by explicitly teaching new terms, providing context and examples, using visual aids, encouraging active participation, and incorporating vocabulary review activities into their lessons. They can also create a supportive and engaging learning environment where students feel comfortable asking questions and practicing new words.
Conclusion
Mastering classroom vocabulary is essential for success in education, enabling clear communication, effective learning, and confident participation in academic activities. This comprehensive guide has provided definitions, examples, and usage rules for a wide range of classroom-related terms.
By understanding and practicing this vocabulary, students and teachers alike can create a more productive and enriching learning environment. Continue to expand your vocabulary and apply it in real-world contexts to further enhance your communication skills and academic achievements.
Remember, consistent effort and practice are key to mastering any language, including the language of the classroom.