Subject-verb agreement is one of the fundamental rules of grammar, and it plays a crucial role in ensuring clarity and correctness in both writing and speaking. Whether you’re writing essays, emails, or simply engaging in conversation, mastering subject-verb agreement is essential for conveying your ideas properly. This blog post will provide you with detailed explanations, examples, and exercises to help you better understand and practice subject-verb agreement.
When we talk about subject-verb agreement, we’re referring to the grammatical rule that the subject and the verb in a sentence must match in terms of number (singular or plural) and person (first, second, or third). Understanding how to match subjects with verbs correctly ensures that your sentences are grammatically sound.
In this blog post, we’ll focus on paragraph exercises to help you master subject-verb agreement. These exercises will cover different sentence types, and you’ll get more than 5 examples and over 10 exercises of each type. At the end of the post, you’ll find a comprehensive answer table to help you check your work and improve your skills.
What is Subject-Verb Agreement?
At its core, subject-verb agreement means that the verb must agree with its subject in number. In simpler terms, singular subjects take singular verbs, and plural subjects take plural verbs. For example, “The cat runs fast” (singular subject, singular verb) vs. “The cats run fast” (plural subject, plural verb).
There are certain rules that guide how subject-verb agreement works, and we’ll cover those in detail as we go along.
Types of Sentences to Focus On
Before we dive into the exercises, let’s take a quick look at the different types of sentences that we will be working with:
- Affirmative Sentences – These sentences make a statement, and the subject and verb must agree.
- Example: “She likes chocolate.”
- Interrogative Sentences – These sentences ask a question. The subject and verb must agree even in questions.
- Example: “Does she like chocolate?”
- Negative Sentences – These sentences deny something. Again, subject-verb agreement is crucial here.
- Example: “She does not like chocolate.”
- Compound Sentences – These sentences join two independent clauses. Subject-verb agreement becomes tricky when dealing with compound subjects.
- Example: “Tom and Jerry are friends.”
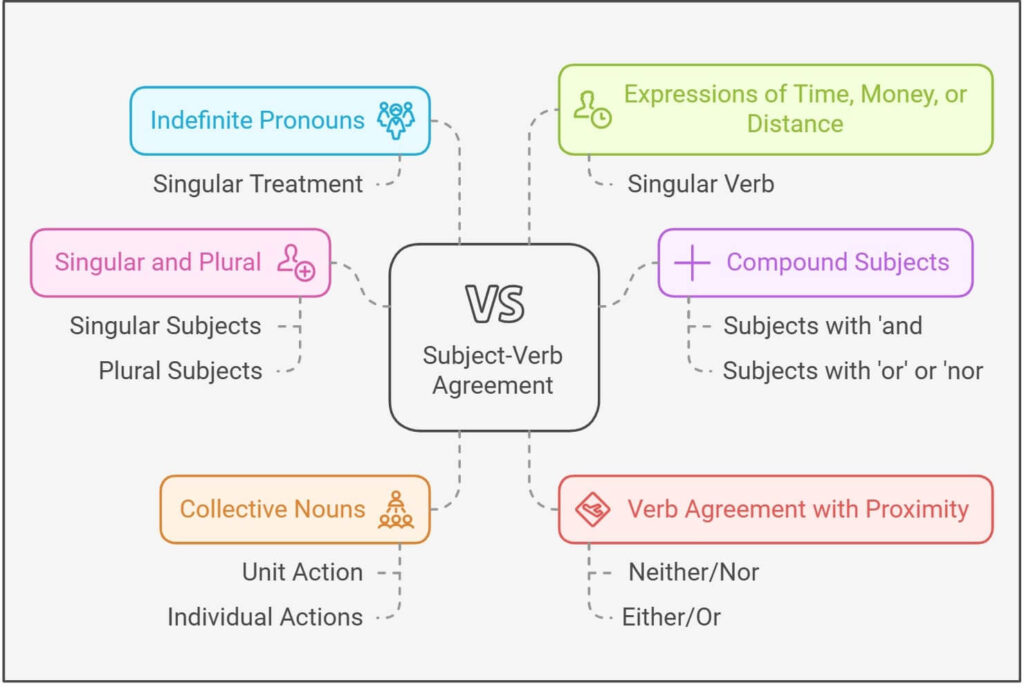
Rules for Subject-Verb Agreement
Now, let’s take a look at the essential rules that govern subject-verb agreement:
- Singular subjects take singular verbs, and plural subjects take plural verbs.
- Singular: “The dog runs fast.”
- Plural: “The dogs run fast.”
- When two subjects are connected by ‘and’, the verb is typically plural.
- Example: “Tom and Jerry are friends.”
- When two subjects are connected by ‘or’ or ‘nor’, the verb agrees with the subject closest to it.
- Example: “Neither Tom nor Jerry is going to the party.”
- Example: “Neither Tom nor his friends are going to the party.”
- Indefinite pronouns (e.g., everyone, someone, each, neither, etc.) are generally treated as singular.
- Example: “Everyone is invited to the party.”
- When the subject is a collective noun, the verb can be singular or plural depending on whether the subject is acting as a unit or as individuals.
- Example: “The team is playing well.” (Unit)
- Example: “The team are arguing among themselves.” (Individuals)
- The verb must agree with the subject in terms of number and not the object.
- Example: “The teacher, along with the students, is excited about the trip.”
- With expressions of time, money, or distance, use a singular verb if the subject is considered singular.
- Example: “Ten dollars is a reasonable price.”
Exercises
Now that we’ve reviewed the rules, let’s move on to the exercises. In these exercises, you will practice subject-verb agreement in different types of sentences. Remember to check if the subject is singular or plural, and apply the rules accordingly.
Exercise 1: Choose the correct verb
- Neither the cat nor the dog (was / were) at the door.
- The team (has / have) finished their practice.
- Both of the boys (likes / like) playing soccer.
- My brother and I (is / are) going to the concert.
- The teacher, along with the students, (is / are) preparing for the event.
- Neither of the answers (is / are) correct.
- The books on the table (needs / need) to be returned to the library.
- The group of friends (has / have) planned a surprise for her.
- The children in the class (is / are) excited about the trip.
- The news (is / are) surprising.
Exercise 2: Choose the correct verb
- She (has / have) been working on this project for months.
- The manager or his assistants (was / were) responsible for the mistake.
- Both of the answers (is / are) acceptable.
- Everyone (is / are) invited to the wedding.
- The students (has / have) finished their exams.
- Neither the teacher nor the students (was / were) ready for the test.
- A few of the cars in the parking lot (is / are) new.
- The committee (is / are) discussing the budget for next year.
- Neither John nor his friends (was / were) available to attend the meeting.
- The number of students in the class (has / have) increased this semester.
Exercise 3: Choose the correct verb
- His shoes (is / are) on the floor.
- The dog and the cat (is / are) playing outside.
- A few of the books (is / are) missing from the shelf.
- The team of researchers (has / have) completed their study.
- The children (was / were) running in the park.
- Each of the students (is / are) required to submit their assignment.
- Neither the teacher nor the principal (is / are) present.
- The workers in the factory (is / are) on strike.
- The price of the tickets (is / are) too high.
- Neither the rain nor the cold weather (was / were) enough to stop the event.
Exercise 4: Choose the correct verb
- The jury (was / were) deliberating on the case.
- Tom, as well as his brothers, (is / are) going to the game.
- The company (has / have) received multiple awards for its work.
- The news about the accident (was / were) shocking.
- Both Mary and John (was / were) at the meeting.
- Neither the manager nor the employees (was / were) at the office yesterday.
- The book that you gave me (is / are) on the table.
- The children’s toys (was / were) scattered all over the room.
- The car that we rented (is / are) already in the parking lot.
- Either you or she (is / are) going to have to make the decision.
Exercise 5: Choose the correct verb
- The coffee and the bagels (is / are) on the table.
- The music and the dance (was / were) beautiful.
- The company’s profits (has / have) increased this year.
- Neither the chair nor the table (was / were) damaged in the storm.
- The cat, along with the dog, (has / have) eaten their food.
- A number of people (was / were) waiting outside the building.
- The family members (is / are) going on vacation next month.
- Each of the items in the basket (is / are) handmade.
- The class (is / are) working on their project.
- The manager and the assistant manager (is / are) meeting with the clients.
Answers
See answers in the table below:
| Exercise | Sentence | Correct Verb |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Neither the cat nor the dog (was / were) at the door. | was |
| 1 | The team (has / have) finished their practice. | has |
| 1 | Both of the boys (likes / like) playing soccer. | like |
| 1 | My brother and I (is / are) going to the concert. | are |
| 1 | The teacher, along with the students, (is / are) preparing for the event. | is |
| 1 | Neither of the answers (is / are) correct. | is |
| 1 | The books on the table (needs / need) to be returned to the library. | need |
| 1 | The group of friends (has / have) planned a surprise for her. | has |
| 1 | The children in the class (is / are) excited about the trip. | are |
| 1 | The news (is / are) surprising. | is |
| 2 | She (has / have) been working on this project for months. | has |
| 2 | The manager or his assistants (was / were) responsible for the mistake. | were |
| 2 | Both of the answers (is / are) acceptable. | are |
| 2 | Everyone (is / are) invited to the wedding. | is |
| 2 | The students (has / have) finished their exams. | have |
| 2 | Neither the teacher nor the students (was / were) ready for the test. | were |
| 2 | A few of the cars in the parking lot (is / are) new. | are |
| 2 | The committee (is / are) discussing the budget for next year. | is |
| 2 | Neither John nor his friends (was / were) available to attend the meeting. | were |
| 2 | The number of students in the class (has / have) increased this semester. | has |
| 3 | His shoes (is / are) on the floor. | are |
| 3 | The dog and the cat (is / are) playing outside. | are |
| 3 | A few of the books (is / are) missing from the shelf. | are |
| 3 | The team of researchers (has / have) completed their study. | has |
| 3 | The children (was / were) running in the park. | were |
| 3 | Each of the students (is / are) required to submit their assignment. | is |
| 3 | Neither the teacher nor the principal (is / are) present. | is |
| 3 | The workers in the factory (is / are) on strike. | are |
| 3 | The price of the tickets (is / are) too high. | is |
| 3 | Neither the rain nor the cold weather (was / were) enough to stop the event. | was |
| 4 | The jury (was / were) deliberating on the case. | was |
| 4 | Tom, as well as his brothers, (is / are) going to the game. | is |
| 4 | The company (has / have) received multiple awards for its work. | has |
| 4 | The news about the accident (was / were) shocking. | was |
| 4 | Both Mary and John (was / were) at the meeting. | were |
| 4 | Neither the manager nor the employees (was / were) at the office yesterday. | were |
| 4 | The book that you gave me (is / are) on the table. | is |
| 4 | The children’s toys (was / were) scattered all over the room. | were |
| 4 | The car that we rented (is / are) already in the parking lot. | is |
| 4 | Either you or she (is / are) going to have to make the decision. | is |
| 5 | The coffee and the bagels (is / are) on the table. | are |
| 5 | The music and the dance (was / were) beautiful. | were |
| 5 | The company’s profits (has / have) increased this year. | have |
| 5 | Neither the chair nor the table (was / were) damaged in the storm. | were |
| 5 | The cat, along with the dog, (has / have) eaten their food. | has |
| 5 | A number of people (was / were) waiting outside the building. | were |
| 5 | The family members (is / are) going on vacation next month. | are |
| 5 | Each of the items in the basket (is / are) handmade. | is |
| 5 | The class (is / are) working on their project. | is |
| 5 | The manager and the assistant manager (is / are) meeting with the clients. | are |
By practicing these exercises and reviewing the answers, you’ll significantly improve your understanding of subject-verb agreement. Be sure to continue practicing to strengthen your grammar skills!

