Prepositions are essential components of the English language, acting as the glue that connects words and phrases within a sentence. Mastering prepositions enhances clarity and precision in both writing and speaking.
While many prepositions are frequently used and well-understood, some, particularly those starting with the letter “D,” can present unique challenges. This article provides a comprehensive exploration of Decoding D Prepositions offering detailed explanations, examples, and practice exercises to solidify your understanding.
Whether you’re a beginner or an advanced learner, this guide will equip you with the knowledge to confidently use these prepositions.
This article will be beneficial for English language learners of all levels, students preparing for standardized tests, and anyone who wishes to improve their grammar skills. By the end of this guide, you will have a thorough understanding of how to use prepositions starting with “D” correctly and effectively.
Contents
ToggleDefinition of Prepositions
A preposition is a word that connects a noun, noun phrase, or pronoun to other words in a sentence. It typically indicates the spatial, temporal, or logical relationship of the noun to something else.
Prepositions are crucial for establishing context and meaning within sentences. They often answer questions such as where, when, how, and why.
Prepositions can be classified based on their structure and function. Simple prepositions consist of a single word (e.g., at, in, on). Compound prepositions are formed by two or more words (e.g., according to, because of). Participle prepositions are derived from verbs (e.g., considering, during). Understanding these classifications helps in recognizing and using prepositions effectively.
The function of a preposition is to introduce a prepositional phrase, which includes the preposition and its object (the noun, noun phrase, or pronoun that follows the preposition). The prepositional phrase then modifies another word or phrase in the sentence, providing additional information about it.
This modifying role is vital for conveying precise meaning.
Structural Breakdown
The basic structure involving a preposition is: Preposition + Object of the Preposition. The object of the preposition is typically a noun, pronoun, or noun phrase. The entire phrase acts as an adjective or adverb, modifying another element in the sentence.
For example, in the sentence “The book is on the table,” “on” is the preposition, and “the table” is the object of the preposition. The entire prepositional phrase “on the table” modifies the verb “is,” indicating the location of the book.
Prepositional phrases can also be nested within other prepositional phrases, creating more complex sentence structures. For instance, “The key is in the box on the shelf” contains two prepositional phrases: “in the box” and “on the shelf.” The phrase “on the shelf” modifies “the box,” and the phrase “in the box on the shelf” modifies the verb “is.” This nesting allows for detailed and nuanced descriptions.
Types and Categories of Prepositions
Prepositions can be categorized based on the type of relationship they express. Here are some common categories:
Prepositions of Time
These prepositions indicate when something happens or exists. Examples include during, since, until, throughout.
Prepositions of Place
These prepositions indicate where something is located. Examples include at, in, on, by, beside, between.
Prepositions of Direction
These prepositions indicate movement or direction. Examples include to, toward, into, through, across.
Prepositions of Agent
These prepositions indicate who performed an action. The most common example is by.
Prepositions of Purpose
These prepositions indicate the reason for something. Examples include for, to.
Understanding these categories can help you choose the correct preposition to express your intended meaning accurately. While some prepositions may fit into multiple categories depending on the context, recognizing the primary function of each preposition is essential.
Examples of Prepositions Starting with “D”
This section provides extensive examples of prepositions that start with the letter “D,” categorized for clarity. Each example is designed to illustrate the specific usage and context of the preposition.
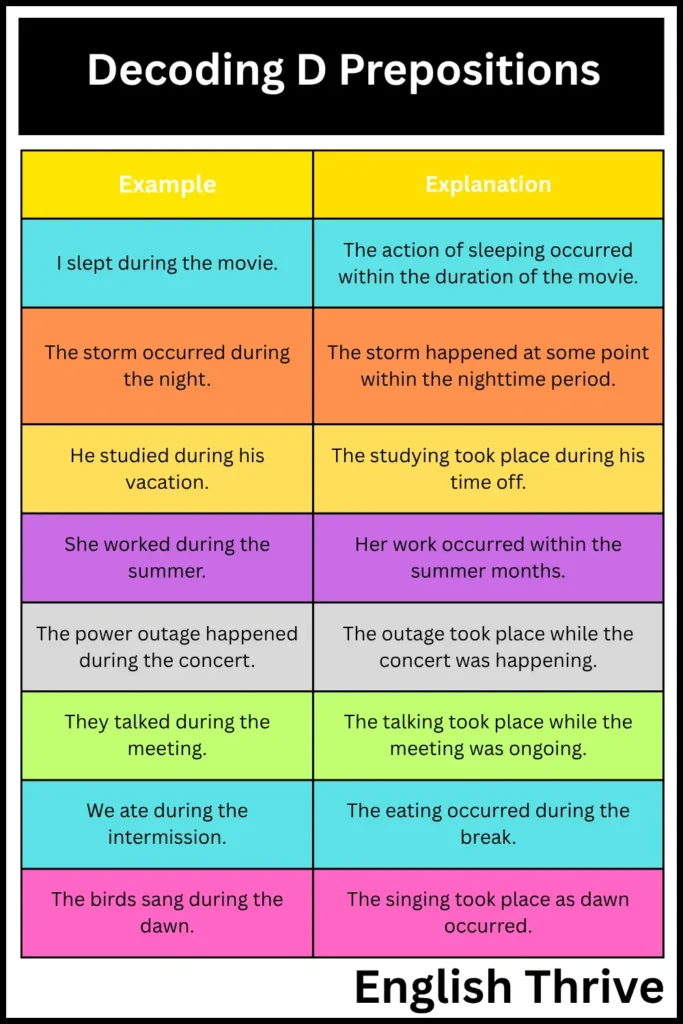
During
The preposition “during” indicates when something happens within a specific time period.
| Example | Explanation |
|---|---|
| I slept during the movie. | The action of sleeping occurred within the duration of the movie. |
| The storm occurred during the night. | The storm happened at some point within the nighttime period. |
| He studied during his vacation. | The studying took place during his time off. |
| She worked during the summer. | Her work occurred within the summer months. |
| The power outage happened during the concert. | The outage took place while the concert was happening. |
| They talked during the meeting. | The talking took place while the meeting was ongoing. |
| We ate during the intermission. | The eating occurred during the break. |
| The birds sang during the dawn. | The singing took place as dawn occurred. |
| The flowers bloomed during the spring. | The blooming happened within the springtime. |
| The leaves fell during the autumn. | The falling took place within the autumn season. |
| He felt sick during the flight. | His sickness occurred while he was on the flight. |
| She read during the train ride. | The reading took place while she was on the train. |
| The children played during the afternoon. | The playing happened within the afternoon hours. |
| The chef cooked during the morning. | The cooking took place within the morning hours. |
| The artist painted during the day. | The painting occurred during the daytime. |
| The soldiers fought during the war. | The fighting took place within the war period. |
| The negotiations occurred during the crisis. | The negotiations happened while the crisis was ongoing. |
| The renovation happened during the closure. | The renovation took place while the venue was closed. |
| The celebration occurred during the festival. | The celebration happened while the festival was ongoing. |
| The presentation happened during the conference. | The presentation took place while the conference was in session. |
| The research was conducted during the project. | The research was performed while the project was active. |
| The investigation occurred during the scandal. | The investigation happened while the scandal was ongoing. |
| The rescue happened during the flood. | The rescue took place while the flood was occurring. |
| The training was provided during the orientation. | The training was given while the orientation was happening. |
Despite
The preposition “despite” indicates that something happens or is true even though there is a reason why it might not be.
| Example | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Despite the rain, we went for a walk. | We went for a walk even though it was raining. |
| Despite his illness, he attended the meeting. | He attended the meeting even though he was sick. |
| Despite the high cost, she bought the dress. | She bought the dress even though it was expensive. |
| Despite the traffic, we arrived on time. | We arrived on time even though there was traffic. |
| Despite the difficulties, they succeeded. | They succeeded even though there were difficulties. |
| Despite her fear, she climbed the mountain. | She climbed the mountain even though she was afraid. |
| Despite the noise, I could concentrate. | I could concentrate even though there was noise. |
| Despite the warnings, he went swimming. | He went swimming even though there were warnings. |
| Despite the cold, they went camping. | They went camping even though it was cold. |
| Despite the lack of experience, he got the job. | He got the job even though he lacked experience. |
| Despite the damage, the car is still driveable. | The car is still driveable even though it’s damaged. |
| Despite the pressure, she remained calm. | She remained calm even though there was pressure. |
| Despite the criticism, he continued his work. | He continued his work even though there was criticism. |
| Despite the setback, they moved forward. | They moved forward even though there was a setback. |
| Despite the confusion, they found the answer. | They found the answer even though there was confusion. |
| Despite the competition, he won the race. | He won the race even though there was competition. |
| Despite the challenge, she completed the project. | She completed the project even though it was challenging. |
| Despite the limitations, they achieved their goal. | They achieved their goal even though there were limitations. |
| Despite the odds, they succeeded. | They succeeded even though the odds were against them. |
| Despite the obstacles, they persevered. | They persevered even though there were obstacles. |
| Despite the uncertainty, they made a decision. | They made a decision even though there was uncertainty. |
| Despite the complexity, they understood the concept. | They understood the concept even though it was complex. |
| Despite the risk, they took the chance. | They took the chance even though there was risk involved. |
| Despite the delay, they finished on time. | They finished on time even though there was a delay. |
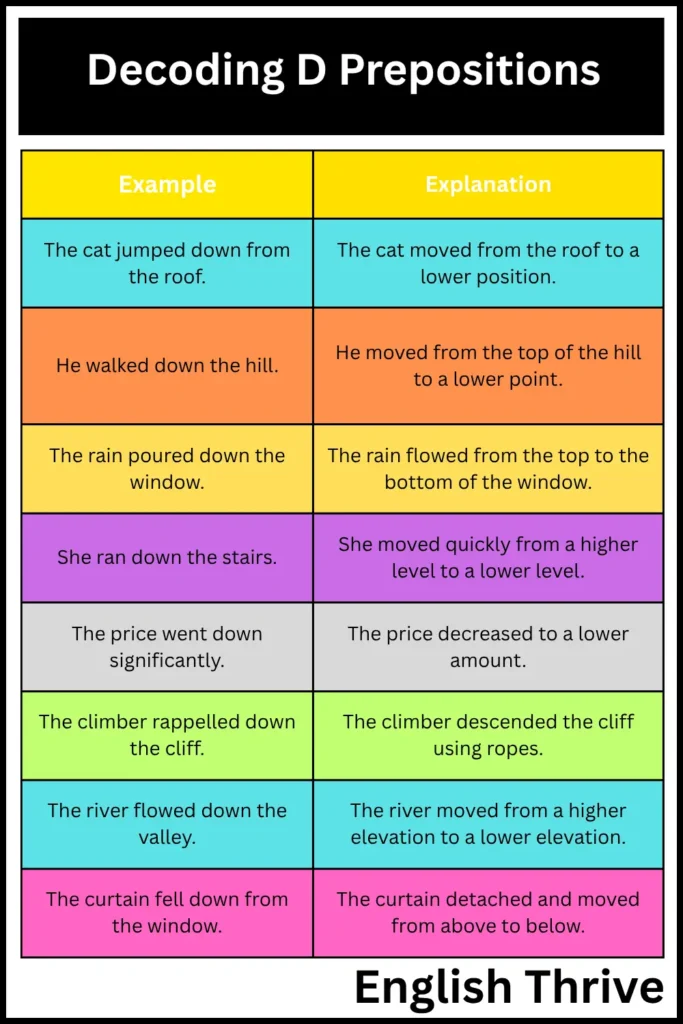
Down
The preposition “down” indicates movement from a higher to a lower point or position.
| Example | Explanation |
|---|---|
| The cat jumped down from the roof. | The cat moved from the roof to a lower position. |
| He walked down the hill. | He moved from the top of the hill to a lower point. |
| The rain poured down the window. | The rain flowed from the top to the bottom of the window. |
| She ran down the stairs. | She moved quickly from a higher level to a lower level. |
| The price went down significantly. | The price decreased to a lower amount. |
| The climber rappelled down the cliff. | The climber descended the cliff using ropes. |
| The river flowed down the valley. | The river moved from a higher elevation to a lower elevation. |
| The curtain fell down from the window. | The curtain detached and moved from above to below. |
| The airplane flew down to the airport. | The airplane descended to the airport. |
| He bent down to pick up the coin. | He lowered his body to pick up the coin. |
| The temperature went down overnight. | The temperature decreased during the night. |
| The sun went down behind the mountains. | The sun set below the horizon behind the mountains. |
| The team was down by ten points. | The team was losing by ten points. |
| She wrote down her phone number. | She recorded her phone number on paper. |
| The tree fell down in the storm. | The tree collapsed to the ground during the storm. |
| The roller coaster went down a steep drop. | The roller coaster descended rapidly. |
| The elevator went down to the first floor. | The elevator moved to a lower floor. |
| The balloon floated down gently. | The balloon descended slowly and smoothly. |
| The road sloped down towards the lake. | The road declined towards the lake. |
| The waterfall cascaded down the rocks. | The water flowed downwards over the rocks. |
| The astronaut went down the ladder. | The astronaut descended the ladder. |
| The anchor was dropped down into the sea. | The anchor was lowered into the sea. |
| He was feeling down after the news. | He was feeling depressed after the news. |
| The computer system went down unexpectedly. | The computer system stopped working unexpectedly. |
Down from
The preposition “down from” indicates movement from a higher position or place to a lower one, specifying the starting point.
| Example | Explanation |
|---|---|
| He climbed down from the tree. | He descended from a position in the tree. |
| She stepped down from the stage. | She moved from the stage to a lower level. |
| The cat jumped down from the shelf. | The cat moved from a higher shelf to the floor. |
| The child slid down from the slide. | The child descended the slide. |
| The bird flew down from the roof. | The bird descended from the roof. |
| The water flowed down from the mountain. | The water cascaded down the mountain slopes. |
| The climber rappelled down from the peak. | The climber descended the mountain peak. |
| The astronaut floated down from the spacecraft. | The astronaut moved from the spacecraft to a lower area. |
| The fireman climbed down from the ladder. | The fireman descended the ladder. |
| The actor stepped down from the podium. | The actor moved from the podium to a lower position. |
| The pilot climbed down from the cockpit. | The pilot descended from the airplane’s cockpit. |
| The worker climbed down from the scaffolding. | The worker descended from the scaffolding. |
| The speaker stepped down from the platform. | The speaker moved from the platform to a lower level. |
| The knight dismounted down from his horse. | The knight descended from his horse. |
| The manager came down from his office. | The manager descended from his office. |
| The athlete jumped down from the box. | The athlete descended from the box. |
| The engineer climbed down from the machine. | The engineer descended from the machine. |
| The artist stepped down from the ladder. | The artist descended from the ladder. |
| The guard came down from the watchtower. | The guard descended from the watchtower. |
| The technician climbed down from the pole. | The technician descended from the pole. |
| The student walked down from the stage. | The student descended from the stage. |
| The hiker descended down from the summit. | The hiker moved to a lower position from the summit. |
| The performer jumped down from the platform. | The performer descended from the platform. |
| The driver got down from the truck. | The driver descended from the truck. |
Usage Rules for Prepositions Starting with “D”
Understanding the specific rules for using prepositions starting with “D” is crucial for accurate and effective communication.
During:
- Use “during” to indicate that something happens within a specific period of time.
- “During” is followed by a noun or noun phrase representing the time period.
- Avoid using “during” to indicate a specific point in time; use “at” or “on” instead.
Despite:
- Use “despite” to show a contrast or contradiction. It indicates that something happens or is true even though there is a reason why it might not be.
- “Despite” is followed by a noun or noun phrase.
- “Despite” is similar in meaning to “in spite of,” and they can often be used interchangeably.
Down:
- Use “down” to indicate movement from a higher to a lower position or point.
- “Down” can also be used to indicate a decrease in quantity or value.
- Be mindful of the phrasal verb uses of “down,” such as “write down,” “calm down,” etc.
Down from:
- Use “down from” to indicate movement from a higher position or place to a lower one, specifying the starting point.
- It clearly identifies the initial location before the downward movement.
Common Mistakes with Prepositions Starting with “D”
Even experienced English speakers sometimes make mistakes with prepositions. Here are some common errors to avoid:
| Incorrect | Correct | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| I saw him in during the movie. | I saw him during the movie. | “During” already indicates a time period, so “in” is unnecessary. |
| Despite of the rain, we went out. | Despite the rain, we went out. | “Despite” does not require “of.” |
| He fell down from the ladder. | He fell off the ladder. | “Off” is more appropriate when something detaches. “Down from” is okay but less common in this case. |
| Down of the hill. | Down the hill. | “Down” requires “the” to specify direction. |
| During of the night. | During the night. | “During” does not require “of.” |
| Despite of his efforts, he failed. | Despite his efforts, he failed. | “Despite” should not be followed by “of.” |
Practice Exercises
Test your knowledge of prepositions starting with “D” with these practice exercises. Choose the correct preposition to complete each sentence.
Exercise 1: Fill in the Blanks (During/Despite)
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| 1. I fell asleep _______ the lecture. | During |
| 2. _______ the noise, I managed to concentrate. | Despite |
| 3. The accident happened _______ the heavy rain. | During |
| 4. _______ his hard work, he didn’t get promoted. | Despite |
| 5. The shop was closed _______ the holiday. | During |
| 6. _______ the traffic, we arrived on time. | Despite |
| 7. The concert was amazing _______ the bad weather. | Despite |
| 8. I studied _______ my lunch break. | During |
| 9. _______ the low salary, he accepted the job. | Despite |
| 10. The presentation took place _______ the conference. | During |
Exercise 2: Fill in the Blanks (Down/Down From)
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| 1. The cat jumped _______ the fence. | Down from |
| 2. The river flows _______ the mountain. | Down |
| 3. He climbed _______ the ladder. | Down from |
| 4. The rain poured _______ the window. | Down |
| 5. She walked _______ the street. | Down |
| 6. The pilot climbed _______ the cockpit. | Down from |
| 7. The sun went _______ behind the clouds. | Down |
| 8. The worker fell _______ the scaffolding. | Down from |
| 9. The price of gas went _______. | Down |
| 10. The climber rappelled _______ the cliff. | Down from |
Exercise 3: Error Correction
| Incorrect Sentence | Correct Sentence |
|---|---|
| 1. I visited the museum during of the day. | I visited the museum during the day. |
| 2. Despite of the cost, I bought it. | Despite the cost, I bought it. |
| 3. He walked down from the hill. | He walked down the hill. |
| 4. She ate during of the movie. | She ate during the movie. |
| 5. Despite of his injury, he played. | Despite his injury, he played. |
| 6. The plane flew down from to the airport. | The plane flew down to the airport. |
| 7. He studied during of the night. | He studied during the night. |
| 8. Despite of the risks, they proceeded. | Despite the risks, they proceeded. |
| 9. The cat jumped down from of the tree. | The cat jumped down from the tree. |
| 10. The balloon floated down from of the sky. | The balloon floated down from the sky. |
Advanced Topics
For advanced learners, understanding the nuances and complexities of prepositional usage is essential. This section delves into more intricate aspects of prepositions starting with “D.”
Prepositional Phrases as Adjectives and Adverbs
Prepositional phrases can function as adjectives, modifying nouns or pronouns, or as adverbs, modifying verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs. Recognizing their function within a sentence is crucial for accurate interpretation. For example: “The book on the table is mine” (adjective). “He walked down the street quickly” (adverb).
Idiomatic Expressions with Prepositions
Many idiomatic expressions incorporate prepositions, and their meanings often cannot be deduced from the individual words. For example, “down in the dumps” means feeling sad or depressed.
Learning these idioms requires memorization and contextual understanding.
Prepositional Stranding
Prepositional stranding occurs when a preposition is separated from its object, typically at the end of a sentence or clause. While traditionally considered incorrect, it is now widely accepted in modern English, especially in informal contexts. For example: “What are you looking at?”
FAQs on Decoding D Prepositions
This section addresses common questions about prepositions starting with “D,” providing detailed answers to clarify any remaining uncertainties.
What is the difference between “during” and “while”?
“During” is a preposition followed by a noun or noun phrase, indicating that something happens within a specific period of time. “While” is a conjunction followed by a clause (subject + verb), indicating that two actions occur simultaneously. Example: “During the movie, I ate popcorn.” “While I was watching the movie, I ate popcorn.”
Can “despite” and “in spite of” be used interchangeably?
Yes, “despite” and “in spite of” have the same meaning and can generally be used interchangeably. However, “in spite of” is slightly more formal. Example: “Despite the rain, we went for a walk.” “In spite of the rain, we went for a walk.”
Is it incorrect to end a sentence with a preposition like “down”?
Ending a sentence with a preposition, known as prepositional stranding, was traditionally considered incorrect. However, it is now widely accepted in modern English, especially in informal contexts. Rewriting the sentence to avoid stranding can sometimes sound awkward or unnatural. Example: “What are you looking at?” (stranded) vs. “At what are you looking?” (formal and less common).
How do I know which preposition to use in a sentence?
Choosing the correct preposition depends on the relationship you want to express between the words in the sentence. Consider the context, meaning, and the specific rules for each preposition. Practice and exposure to a wide range of English texts can also improve your intuition for preposition usage.
What are some common phrases that use “down”?
Some common phrases using “down” include: “down the street,” “down the drain,” “down to earth,” “down with (illness),” “write down,” “calm down,” “break down,” and “sit down.”
Can “during” be used with a specific time?
No, “during” is used to indicate a period of time, not a specific point in time. For specific times, use “at” or “on.” Example: “I arrived at 5 PM.” “The meeting is on Monday.” Not: “I arrived during 5 PM.”
What part of speech typically follows “despite”?
The preposition “despite” is typically followed by a noun or a noun phrase. For example, “Despite the challenges,” or “Despite his efforts.” It introduces a phrase that contrasts with the main clause of the sentence.
How can I improve my understanding of prepositions?
Improving your understanding of prepositions requires consistent practice and exposure. Read widely, pay attention to how prepositions are used in context, and practice using them in your own writing and speaking. Use online resources, grammar guides, and language learning apps to reinforce your knowledge.
Conclusion
Mastering prepositions, especially those starting with the letter “D,” is essential for achieving fluency and accuracy in English. This comprehensive guide has provided detailed explanations, examples, and practice exercises to help you understand and use prepositions like during, despite, down, and down from effectively. By understanding their specific meanings, usage rules, and common mistakes, you can enhance your communication skills and avoid errors in your writing and speaking.
Remember to continue practicing and expanding your knowledge of prepositions. Pay attention to how they are used in various contexts, and don’t hesitate to consult grammar resources when needed.
With consistent effort, you can confidently navigate the complexities of English grammar and express yourself with clarity and precision.