Understanding the vocabulary surrounding law and order is crucial for anyone looking to improve their English proficiency, particularly in legal, political, or social contexts. This article provides a comprehensive guide to 50 key words associated with law and order, exploring their definitions, grammatical functions, usage, and common mistakes.
Whether you’re an ESL student, a legal professional, or simply interested in expanding your vocabulary, this guide will equip you with the knowledge to use these terms accurately and confidently.
Contents
ToggleDefinition of Law and Order Vocabulary
The vocabulary associated with law and order encompasses a wide range of terms related to the establishment, maintenance, and enforcement of rules and regulations within a society. These words are essential for discussing legal processes, crime, justice, and the overall functioning of a structured community.
Understanding these terms allows for more precise and nuanced communication about complex social and political issues.
This vocabulary includes nouns that represent concepts such as laws, courts, and punishments; verbs that describe actions like arresting, prosecuting, and judging; adjectives that characterize aspects of the legal system, such as lawful or illegal; and adverbs that modify these actions, like justly or unfairly. Each part of speech plays a critical role in conveying the intricacies of law and order.
Structural Breakdown
The structure of law and order vocabulary often reflects its origins in legal and formal language. Many terms are derived from Latin or French, contributing to their often complex and precise meanings.
Understanding the etymology and morphology of these words can aid in comprehension and usage.
For instance, words like “jurisdiction” (from Latin jus, meaning law, and dicere, meaning to say) and “adjudicate” (from Latin ad-, meaning to, and judicare, meaning to judge) reveal their legal roots through their structural components. Recognizing prefixes, suffixes, and root words can help decipher the meanings of unfamiliar terms within this domain. Furthermore, many legal terms have specific connotations and are used in particular contexts, making it essential to understand their structural nuances for proper application.
Types and Categories
Law and order vocabulary can be categorized based on their grammatical function. Here’s a breakdown of the main categories:
Nouns
Nouns in this context refer to people, places, things, or ideas related to the legal system. Examples include judge, court, crime, law, evidence, verdict, sentence, and justice. These nouns form the foundation of legal discussions and narratives.
Verbs
Verbs describe actions within the legal framework. Common verbs include arrest, prosecute, defend, convict, acquit, sentence, investigate, and legislate. These verbs illustrate the dynamic processes involved in law enforcement and legal proceedings.
Adjectives
Adjectives modify nouns, providing descriptive details about legal concepts. Examples include lawful, illegal, just, unjust, guilty, innocent, criminal, and evidentiary. These adjectives add precision and clarity to legal descriptions.
Adverbs
Adverbs modify verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs, indicating how actions are performed or to what extent qualities are present. Examples include lawfully, illegally, justly, unjustly, fairly, unfairly, and deliberately. Adverbs enhance the nuance and detail of legal discourse.
Examples
The following tables provide examples of law and order vocabulary categorized by their part of speech.
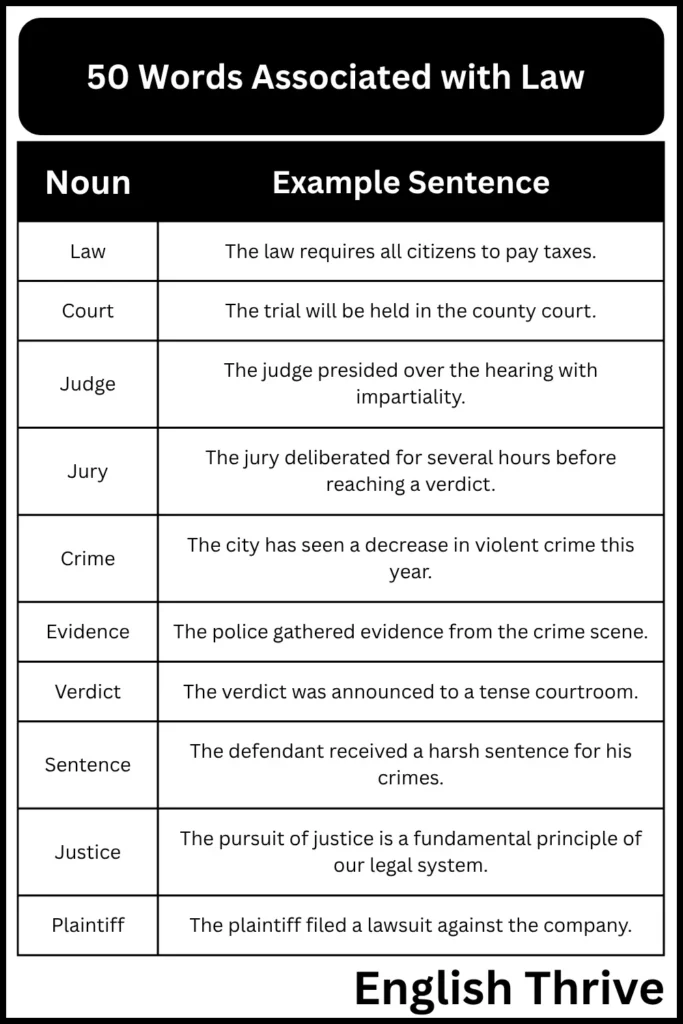
Nouns Examples
This table contains examples of nouns related to law and order. These nouns represent key elements and concepts within the legal and justice systems.
| Noun | Example Sentence |
|---|---|
| Law | The law requires all citizens to pay taxes. |
| Court | The trial will be held in the county court. |
| Judge | The judge presided over the hearing with impartiality. |
| Jury | The jury deliberated for several hours before reaching a verdict. |
| Crime | The city has seen a decrease in violent crime this year. |
| Evidence | The police gathered evidence from the crime scene. |
| Verdict | The verdict was announced to a tense courtroom. |
| Sentence | The defendant received a harsh sentence for his crimes. |
| Justice | The pursuit of justice is a fundamental principle of our legal system. |
| Plaintiff | The plaintiff filed a lawsuit against the company. |
| Defendant | The defendant maintained his innocence throughout the trial. |
| Attorney | The attorney presented a strong case for his client. |
| Police | The police responded quickly to the emergency call. |
| Prison | He was sentenced to five years in prison. |
| Appeal | The lawyer filed an appeal after the unfavorable verdict. |
| Legislation | New legislation was passed to address the issue. |
| Regulation | The company must comply with all environmental regulations. |
| Fine | He had to pay a fine for the traffic violation. |
| Imprisonment | Imprisonment is a common punishment for serious crimes. |
| Lawyer | The lawyer advised her client on the best course of action. |
| Officer | The police officer arrived at the scene promptly. |
| Testimony | The witness’s testimony was crucial to the case. |
| Hearing | The judge scheduled a hearing to review the evidence. |
| Warrant | The police obtained a warrant to search the premises. |
| Statute | The statute outlines the specific requirements for the process. |
| Code | The building code ensures safety standards are met. |
Verbs Examples
This table provides example sentences using verbs associated with law and order. These verbs describe actions performed within the legal and justice systems.
| Verb | Example Sentence |
|---|---|
| Arrest | The police arrested the suspect at the scene. |
| Prosecute | The district attorney will prosecute the case vigorously. |
| Defend | The lawyer will defend her client’s rights in court. |
| Convict | The jury convicted the defendant of all charges. |
| Acquit | The judge acquitted the defendant due to lack of evidence. |
| Sentence | The judge will sentence the convicted criminal next week. |
| Investigate | Detectives are investigating the cause of the fire. |
| Legislate | The government legislated new laws to address the problem. |
| Enforce | The police enforce the laws of the city. |
| Adjudicate | The court will adjudicate the dispute between the two companies. |
| Appeal | The defendant decided to appeal the verdict. |
| Testify | The witness will testify in court tomorrow. |
| Judge | The judge judged the case fairly. |
| Sue | The company decided to sue the supplier for damages. |
| File | The lawyer will file a motion to dismiss the case. |
| Plead | The defendant decided to plead guilty to the charges. |
| Review | The court will review the evidence before making a decision. |
| Detain | The police detained the suspect for questioning. |
| Question | The detectives will question the witnesses about the incident. |
| Examine | The lawyer will examine the evidence closely. |
| Hear | The judge will hear the case next week. |
| Rule | The judge ruled in favor of the plaintiff. |
| Issue | The court will issue a warrant for his arrest. |
| Serve | The police served the warrant on the suspect. |
| Comply | The company must comply with the new regulations. |
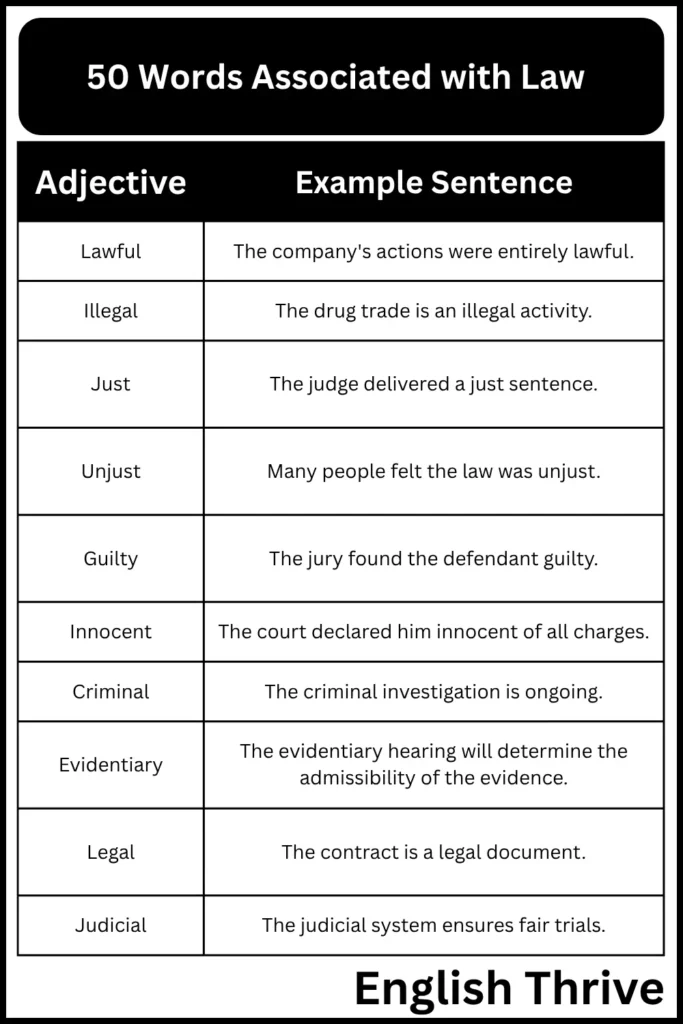
Adjectives Examples
This table lists adjectives commonly used to describe aspects of law and order. These adjectives add detail and precision to legal discussions.
| Adjective | Example Sentence |
|---|---|
| Lawful | The company’s actions were entirely lawful. |
| Illegal | The drug trade is an illegal activity. |
| Just | The judge delivered a just sentence. |
| Unjust | Many people felt the law was unjust. |
| Guilty | The jury found the defendant guilty. |
| Innocent | The court declared him innocent of all charges. |
| Criminal | The criminal investigation is ongoing. |
| Evidentiary | The evidentiary hearing will determine the admissibility of the evidence. |
| Legal | The contract is a legal document. |
| Judicial | The judicial system ensures fair trials. |
| Regulatory | The regulatory agency oversees the industry. |
| Federal | The case was tried in federal court. |
| State | The state laws vary from state to state. |
| Civil | The civil lawsuit seeks damages for the injury. |
| Penal | The penal code outlines the punishments for crimes. |
| Procedural | The procedural rules must be followed carefully. |
| Substantive | The substantive law defines the rights and duties of individuals. |
| Due | He is entitled to due process under the law. |
| Valid | The contract is valid and enforceable. |
| Void | The agreement was declared void by the court. |
| Accusatorial | The legal system is accusatorial in nature. |
| Admissible | The evidence was deemed admissible in court. |
| Compelling | The prosecutor presented a compelling argument. |
| Incontrovertible | The incontrovertible evidence proved his guilt. |
| Preliminary | The preliminary hearing will determine if there is enough evidence to proceed. |
Adverbs Examples
This table presents adverbs that modify actions and descriptions within the context of law and order. These adverbs add nuance and detail to legal narratives.
| Adverb | Example Sentence |
|---|---|
| Lawfully | The police acted lawfully during the arrest. |
| Illegally | The company was operating illegally. |
| Justly | The case was resolved justly. |
| Unjustly | He was unjustly accused of the crime. |
| Fairly | The trial was conducted fairly. |
| Unfairly | She felt she was treated unfairly by the court. |
| Deliberately | He deliberately violated the law. |
| Negligently | The accident occurred because he acted negligently. |
| Strictly | The rules are strictly enforced. |
| Properly | The evidence was properly collected. |
| Wrongfully | He was wrongfully convicted of the crime. |
| Carefully | The judge carefully considered all the evidence. |
| Thoroughly | The police investigated the crime thoroughly. |
| Promptly | The authorities responded promptly to the emergency. |
| Arbitrarily | The decision was made arbitrarily, without proper reasoning. |
| Diligently | The attorney worked diligently on the case. |
| Judiciously | The funds were judiciously allocated. |
| Legally | The company is legally bound by the contract. |
| Officially | The results were officially announced. |
| Rightfully | The property was rightfully returned to its owner. |
Usage Rules
The correct usage of law and order vocabulary requires attention to context, nuance, and grammatical structure. Here are some key rules to consider:
- Context is crucial: The meaning of legal terms can vary depending on the specific legal context. For example, “assault” has a specific legal definition that differs from its everyday usage.
- Precision matters: Legal language demands precision. Using the correct term can significantly impact the meaning of a statement. For instance, “robbery” and “burglary” are distinct crimes with different elements.
- Grammatical agreement: Ensure that verbs and nouns agree in number and tense. For example, “The judge rules” (singular) vs. “The judges rule” (plural).
- Formal tone: Legal writing typically requires a formal and objective tone. Avoid colloquialisms and informal language.
- Proper nouns: Names of courts, laws, and organizations should be capitalized (e.g., Supreme Court, Constitution).
Common Mistakes
Several common mistakes arise when using law and order vocabulary. Being aware of these errors can help you avoid them.
| Incorrect | Correct | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| “He was accused for the crime.” | “He was accused of the crime.” | The correct preposition to use with “accused” is “of.” |
| “The judge sentenced him to jail.” | “The judge sentenced him to prison.” | “Jail” is typically for shorter sentences, while “prison” is for longer terms. |
| “The police investigated about the incident.” | “The police investigated the incident.” | The verb “investigate” does not require the preposition “about.” |
| “The law was enforced hardly.” | “The law was strictly enforced.” | “Hardly” means “barely,” while “strictly” means “rigorously.” |
| “He breaked the law.” | “He broke the law.” | The past tense of “break” is “broke.” |
| “The evidence was inadmissible.” | “The evidence was inadmissible.” | This example highlights correct usage. |
| “They are suspecting him.” | “They suspect him.” | “Suspect” is a stative verb and doesn’t usually take the continuous form. |
Practice Exercises: Words Associated with Law and Order
Test your understanding of law and order vocabulary with the following exercises.
Exercise 1: Fill in the Blanks
Complete the following sentences with the appropriate word from the provided list.
Word List: evidence, verdict, defend, arrest, judge, crime, lawyer, sentence, appeal, court
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| 1. The police decided to ______ the suspect after the robbery. | arrest |
| 2. The ______ listened attentively to the arguments presented by both sides. | judge |
| 3. The ______ presented a strong case on behalf of his client. | lawyer |
| 4. The ______ found the defendant guilty. | verdict |
| 5. The ______ will ______ his client to the best of his ability. | lawyer, defend |
| 6. The ______ presented at the trial was compelling and convincing. | evidence |
| 7. He plans to ______ the ______’s decision. | appeal, court |
| 8. The ______ rate has decreased significantly in recent years. | crime |
| 9. The ______ was severe, reflecting the seriousness of the offense. | sentence |
| 10. The case was heard in the supreme ______. | court |
Exercise 2: Sentence Construction
Create sentences using the following words related to law and order.
| Word | Example Sentence |
|---|---|
| Prosecute | The state will prosecute the individuals involved in the fraud. |
| Convict | The jury chose to convict the defendant of the crime. |
| Acquit | The court was forced to acquit the suspect due to lack of evidence. |
| Legislation | The new legislation aims to reduce pollution. |
| Regulation | The company must adhere to strict environmental regulations. |
| Testify | The witness agreed to testify in court. |
| Warrant | The police obtained a warrant to search the premises. |
| Appeal | The defendant’s lawyer filed an appeal after the guilty verdict. |
| Fine | He had to pay a hefty fine for speeding. |
| Imprisonment | Imprisonment is a serious consequence for criminal behavior. |
Exercise 3: Error Correction
Identify and correct the errors in the following sentences.
| Incorrect Sentence | Correct Sentence |
|---|---|
| He was arrested for stealing the car. | He was arrested for stealing the car. |
| The judge sentenced him to jail for five years. | The judge sentenced him to prison for five years. |
| The police investigated about the crime. | The police investigated the crime. |
| She is accuse for the theft. | She is accused of the theft. |
| The jury give their verdict. | The jury gave its verdict. |
| He don’t know the law. | He doesn’t know the law. |
| They is enforcing the rule. | They are enforcing the rule. |
| The evidence was inadmissible. | The evidence was inadmissible. |
| The judge said he is innocent. | The judge said he was innocent. |
| He has broke the law. | He has broken the law. |
Advanced Topics
For advanced learners, exploring the nuances of legal jargon and the historical context of legal terms can provide a deeper understanding. Topics such as legal precedent, constitutional law, and international law offer further avenues for expanding one’s vocabulary and knowledge in this domain.
Additionally, studying landmark legal cases and analyzing legal documents can enhance comprehension and analytical skills. Understanding the philosophical underpinnings of different legal systems (e.g., common law vs. civil law) also contributes to a more comprehensive grasp of law and order vocabulary.
FAQs on Words Associated with Law and Order
What is the difference between “jail” and “prison”?
Jail is typically a short-term holding facility for individuals awaiting trial or serving sentences of less than a year. Prison, on the other hand, is a long-term correctional facility for individuals convicted of more serious crimes and serving sentences of more than a year.
What does “due process” mean?
Due process refers to the legal requirement that the government must respect all legal rights that are owed to a person. It ensures fairness and impartiality in legal proceedings, protecting individuals from arbitrary or unfair treatment by the state.
What is the role of a “prosecutor”?
A prosecutor is a legal representative of the government who presents the case against the defendant in a criminal trial. Their role is to prove beyond a reasonable doubt that the defendant committed the crime.
What is the difference between “robbery” and “burglary”?
Robbery involves taking property from someone’s person or immediate presence by force or threat of force. Burglary, on the other hand, involves unlawfully entering a building with the intent to commit a crime, typically theft.
What does “plead the fifth” mean?
To “plead the Fifth” is to invoke the Fifth Amendment of the U.S. Constitution, which protects individuals from being compelled to incriminate themselves. It means refusing to answer questions that could potentially lead to self-incrimination.
Conclusion On Words Associated with Law and Order
Mastering the vocabulary associated with law and order is essential for anyone seeking a deeper understanding of legal processes, social justice, and the functioning of a structured society. This guide has provided a comprehensive overview of 50 key words, exploring their definitions, grammatical functions, usage rules, and common mistakes.
By practicing these terms and applying them in context, you can enhance your communication skills and navigate legal discussions with greater confidence.
Remember to pay attention to context, prioritize precision, and maintain a formal tone when using law and order vocabulary. Continue to expand your knowledge by exploring advanced topics, analyzing legal documents, and staying informed about current legal issues.
With consistent effort and dedication, you can achieve fluency in this specialized domain and contribute to more informed and nuanced conversations about law and order.