Have you ever wondered if you should write “my” or “mine” before a noun? Understanding possessive adjectives can be tricky, but it’s a key part of speaking English well. Let’s explore 33 possessive adjective examples that will make your writing clearer and more accurate. With these easy-to-follow examples and rules, you’ll never mix up your possessive adjectives again.
Contents
ToggleUnderstanding Possessive Adjectives
Possessive adjectives are words that show ownership and always appear before a noun. Think of them as ownership labels that tell us who something belongs to. Unlike possessive pronouns that can stand alone, possessive adjectives need a noun to complete their meaning.
Basic Possessive Adjectives
- My (for I)
- Your (for you)
- His (for he)
- Her (for she)
- Its (for it)
- Our (for we)
- Their (for they)
Essential Rules for Using Possessive Adjectives
- Always Precede Nouns
- Correct: “My book is here”
- Incorrect: “Book my is here”
- No Apostrophes Needed
- Never use apostrophes in possessive adjectives
- “Its” is the possessive adjective (no apostrophe)
- “It’s” means “it is” or “it has”
- Match the Subject
- Use the possessive adjective that matches the subject’s person and number
- Single owner = singular possessive adjective
- Multiple owners = plural possessive adjective
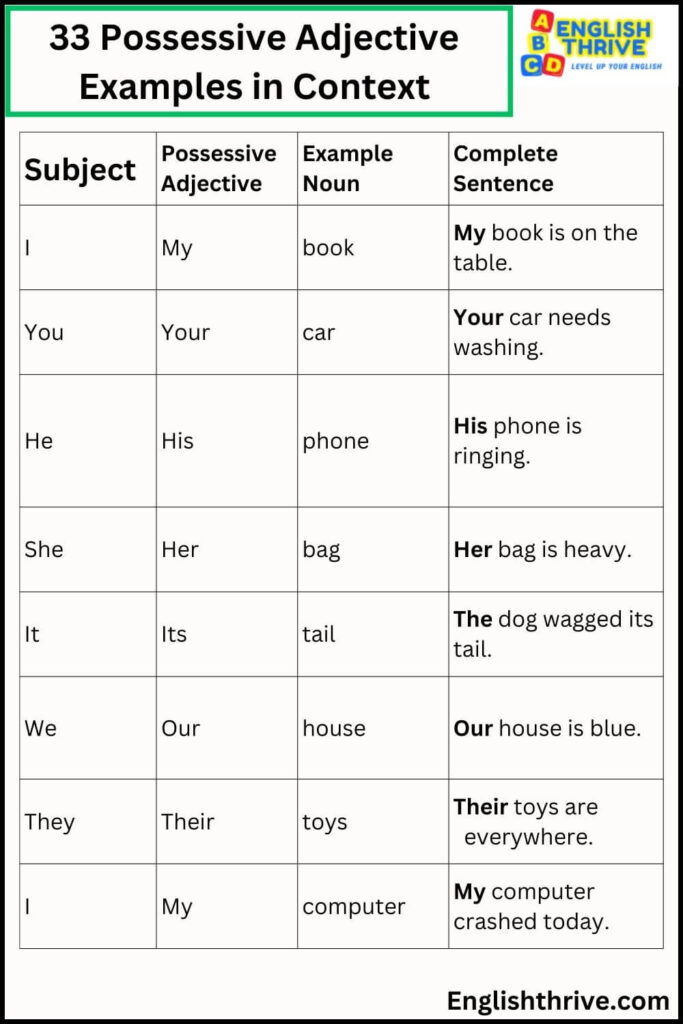
33 Possessive Adjective Examples
| Subject | Possessive Adjective | Example Noun | Complete Sentence |
|---|---|---|---|
| I | My | book | My book is on the table. |
| You | Your | car | Your car needs washing. |
| He | His | phone | His phone is ringing. |
| She | Her | bag | Her bag is heavy. |
| It | Its | tail | The dog wagged its tail. |
| We | Our | house | Our house is blue. |
| They | Their | toys | Their toys are everywhere. |
| I | My | computer | My computer crashed today. |
| You | Your | homework | Your homework is excellent. |
| He | His | guitar | His guitar needs tuning. |
| She | Her | garden | Her garden is beautiful. |
| It | Its | nest | The bird built its nest. |
| We | Our | team | Our team won the game. |
| They | Their | project | Their project won first place. |
| I | My | lunch | My lunch is packed. |
| You | Your | keys | Your keys are on the desk. |
| He | His | office | His office is upstairs. |
| She | Her | artwork | Her artwork sells well. |
| It | Its | battery | The phone lost its battery power. |
| We | Our | presentation | Our presentation starts soon. |
| They | Their | children | Their children are playing. |
| I | My | passport | My passport expires soon. |
| You | Your | schedule | Your schedule is full today. |
| He | His | bicycle | His bicycle needs repair. |
| She | Her | recipe | Her recipe tastes amazing. |
| It | Its | color | The chameleon changed its color. |
| We | Our | vacation | Our vacation starts tomorrow. |
| They | Their | business | Their business is growing. |
| I | My | glasses | My glasses are broken. |
| You | Your | opinion | Your opinion matters. |
| He | His | career | His career is successful. |
| She | Her | choice | Her choice was wise. |
| It | Its | program | The software updated its program. |
 Possessive Adjective Examples
Possessive Adjective Examples
FAQs about Possessive Adjective Examples
1. How do you identify possessive adjectives in a sentence?
Possessive adjectives are always found right before nouns and show ownership. Look for words like “my,” “your,” “his,” “her,” “its,” “our,” and “their” that appear directly before a noun. For example, in “My dog loves to play,” “my” is a possessive adjective because it shows who owns the dog and comes right before the noun “dog.”
To identify them easily:
- Find the noun in the sentence
- Look at the word right before it
- Ask if that word shows ownership
- Check if it’s one of the possessive adjectives listed above
2. What’s the difference between possessive adjectives and possessive pronouns?
The main difference lies in how they’re used in sentences:
- Possessive adjectives (my, your, his, her, its, our, their) must be followed by a noun
- Possessive pronouns (mine, yours, his, hers, its, ours, theirs) stand alone
Examples:
- Possessive adjective: “This is my car.”
- Possessive pronoun: “This car is mine.”
3. How do possessive adjectives change with plural nouns?
Possessive adjectives don’t change with plural nouns. The same form is used whether the noun is singular or plural:
- Singular: “my book”
- Plural: “my books”
- Singular: “their child”
- Plural: “their children”
4. When should you use ‘its’ vs ‘it’s’?
This common confusion can be easily resolved:
- Its (possessive adjective): Shows ownership (no apostrophe)
- It’s (contraction): Means “it is” or “it has” (with apostrophe)
Examples:
- The cat licked its paw. (showing ownership)
- It’s going to rain. (meaning “it is”)
5. How do possessive adjectives work in formal writing?
In formal writing, possessive adjectives follow these guidelines:
- Be consistent with your point of view
- Avoid overusing first-person possessives (my, our)
- Use gender-neutral language when appropriate
- Be clear about ownership in business or academic writing
Conclusion
Mastering possessive adjectives is essential for clear communication in English. Remember that they always come before nouns and show ownership. Practice using these 33 possessive adjective examples in your daily writing and speaking. Soon, choosing the right possessive adjective will become second nature. Keep practicing, and you’ll see your grammar improve quickly!


