Do English tenses feel confusing? You’re not alone.
A small verb change can completely change meaning:
-
I eat. (now/usually)
-
I ate. (past)
-
I will eat. (future)
In this guide, English Thrive will teach you English tenses in a simple, step-by-step way—with clear rules, easy examples, common mistakes, and quick practice with answers.
✅ Important note: English is often taught as 12 main tense forms. In this guide, you’ll learn those 12 plus 4 extra forms learners use every day (like “going to” and future time clauses). That’s why this post covers 16 in total.
Let’s start.
Contents
ToggleWhat is Tense?
Tense shows when an action happens—in the present, past, or future.
English shows time mainly by changing the verb form:
-
Present: I walk. (now/regularly)
-
Past: I walked. (finished in the past)
-
Future: I will walk. (later)
Think of tense as a time signal. It helps readers and listeners instantly understand when something happens—and whether it is ongoing, finished, or continuing over time.
Examples:
-
Present: I walk. (happening now or regularly)
-
Past: I walked. (happened before)
-
Future: I will walk. (will happen later)
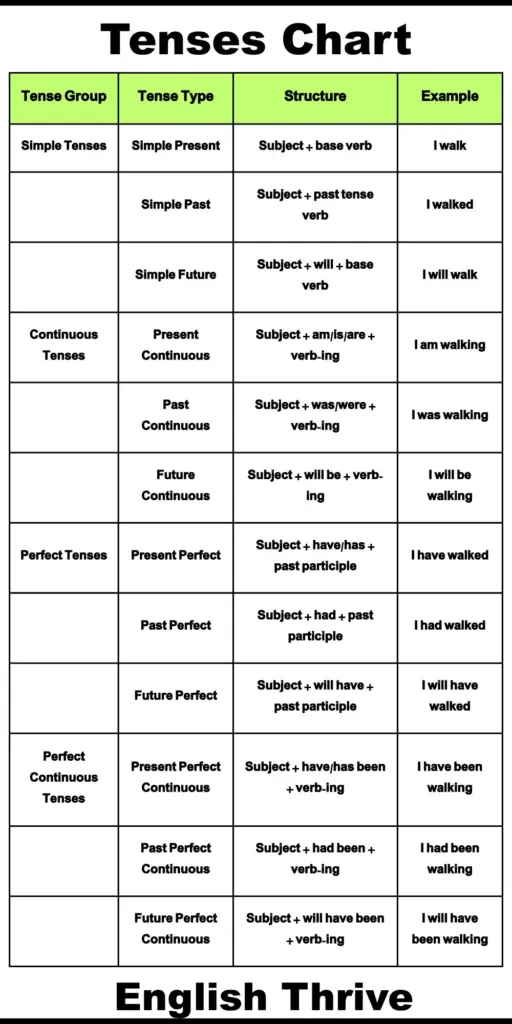
In English, these three main time periods expand into 16 tenses, each showing different aspects of time — such as whether an action is ongoing, completed, or repeated
| Tense Group | Tense Type | Structure | Example | Usage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Simple Tenses | Simple Present | Subject + base verb | I walk | Habitual actions, general truths |
| Simple Past | Subject + past tense verb | I walked | Completed actions in the past | |
| Simple Future | Subject + will + base verb | I will walk | Planned future actions | |
| Continuous Tenses | Present Continuous | Subject + am/is/are + verb-ing | I am walking | Actions happening right now |
| Past Continuous | Subject + was/were + verb-ing | I was walking | Ongoing actions in the past | |
| Future Continuous | Subject + will be + verb-ing | I will be walking | Ongoing actions in the future | |
| Perfect Tenses | Present Perfect | Subject + have/has + past participle | I have walked | Actions completed in recent past |
| Past Perfect | Subject + had + past participle | I had walked | Actions completed before another past action | |
| Future Perfect | Subject + will have + past participle | I will have walked | Actions that will be completed by a future time | |
| Perfect Continuous Tenses | Present Perfect Continuous | Subject + have/has been + verb-ing | I have been walking | Ongoing actions that started in the past and continue |
| Past Perfect Continuous | Subject + had been + verb-ing | I had been walking | Ongoing actions before another past action | |
| Future Perfect Continuous | Subject + will have been + verb-ing | I will have been walking | Ongoing actions that will continue until a future point |
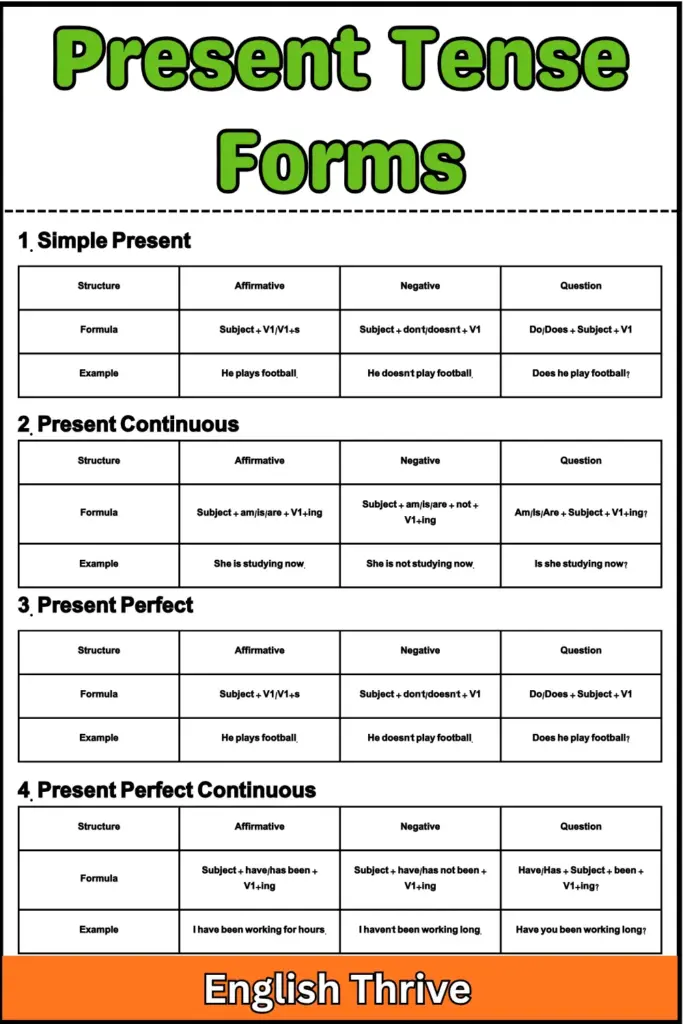
Present Tense Forms
1. Simple Present Tense
Definition
The Simple Present Tense shows habits, facts, and things that happen regularly. It’s the “everyday tense” for routines and general truths.
Examples:
I brush my teeth every morning.
The Earth revolves around the Sun.
Structure
| Type | Formula | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Affirmative | Subject + V1/V1 + s | She plays football. |
| Negative | Subject + don’t/doesn’t + V1 | He doesn’t like pizza. |
| Question | Do/Does + Subject + V1 ? | Do you play guitar ? |
Usage
-
Habits or daily routines → I wake up at 6 AM.
-
Facts and universal truths → Water boils at 100 °C.
-
Scheduled events → The train leaves at nine.
-
Feelings and opinions → I think English is fun.
Common Mistakes
| Incorrect | Correct | Why |
|---|---|---|
| He go to school. | He goes to school. | Add –s for he/she/it. |
| She don’t like apples. | She doesn’t like apples. | Use doesn’t with he/she/it. |
Quick Practice
-
She ____ (play) the piano every day.
-
They ____ (not/watch) TV on weekdays.
-
____ (you/like) coffee ?
✅ Answers: plays / don’t watch / Do you like
2. Present Continuous Tense
Definition
The Present Continuous Tense shows actions happening right now or temporary situations.
Examples:
I am writing an email.
They are studying for exams.
Structure
| Type | Formula | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Affirmative | Subject + am/is/are + V1 + ing | She is reading a book. |
| Negative | Subject + am/is/are + not + V1 + ing | He isn’t working now. |
| Question | Am/Is/Are + Subject + V1 + ing ? | Are you listening ? |
Usage
-
Actions happening right now → I am typing this.
-
Temporary actions → They are living in London this month.
-
Future arrangements → We are meeting tomorrow.
Common Mistakes
| Incorrect | Correct | Why |
|---|---|---|
| She is work now. | She is working now. | Add “-ing”. |
| I am knowing the answer. | I know the answer. | Know is a state verb (not continuous). |
Quick Practice
-
He ____ (watch) TV right now.
-
They ____ (not/play) football today.
-
____ (she/come) to school ?
✅ Answers: is watching / are not playing / Is she coming
3. Present Perfect Tense
Definition
The Present Perfect Tense connects the past to the present — it describes actions that happened recently or started in the past and still matter now.
Examples:
I have finished my homework.
She has lived here for ten years.
Structure
| Type | Formula | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Affirmative | Subject + have/has + V3 | I have eaten lunch. |
| Negative | Subject + have/has not + V3 | He has not finished yet. |
| Question | Have/Has + Subject + V3 ? | Have you seen it ? |
Usage
-
Recent actions → They have just arrived.
-
Life experience → I have visited Paris.
-
Actions continuing till now → We have lived here since 2015.
Common Mistakes
| Incorrect | Correct | Why |
|---|---|---|
| I have saw that movie. | I have seen that movie. | Use V3 form of verb. |
| He has went to school. | He has gone to school. | “Gone” is correct past participle. |
Quick Practice
-
I ____ (finish) my work.
-
She ____ (not/see) him today.
-
____ (you/ever/be) to Japan ?
✅ Answers: have finished / has not seen / Have you ever been
4. Present Perfect Continuous Tense
Definition
The Present Perfect Continuous Tense highlights an activity that started in the past and continues into the present, often showing duration.
Examples:
I have been studying English for three hours.
She has been cooking since morning.
Structure
| Type | Formula | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Affirmative | Subject + have/has been + V1 + ing | They have been waiting for you. |
| Negative | Subject + have/has not been + V1 + ing | He has not been working today. |
| Question | Have/Has + Subject + been + V1 + ing ? | Have you been studying ? |
Usage
-
Long actions continuing till now → I have been reading for two hours.
-
Explaining results → She’s tired because she has been running.
-
Repeated actions till now → He has been calling you all day.
Common Mistakes
| Incorrect | Correct | Why |
|---|---|---|
| I have been study for two hours. | I have been studying for two hours. | Add -ing to main verb. |
| He have been working hard. | He has been working hard. | Use “has” for he/she/it. |
Quick Practice
-
I ____ (work) here for five years.
-
She ____ (not/sleep) well lately.
-
____ (you/wait) long ?
✅ Answers: have been working / has not been sleeping / Have you been waiting
Past Tense Forms
1. Simple Past Tense
Definition
The Simple Past Tense shows actions that happened and finished in the past. It’s used when you clearly know when something occurred.
Examples:
I visited my grandparents last weekend.
She cooked dinner yesterday.
Structure
| Type | Formula | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Affirmative | Subject + V2 | He played football. |
| Negative | Subject + didn’t + V1 | He didn’t play football. |
| Question | Did + Subject + V1 ? | Did he play football ? |
Usage
-
Completed actions in the past → I watched that movie yesterday.
-
Past habits or routines → She walked to school every day.
-
Series of past actions → I woke up, brushed my teeth, and left home.
Common Mistakes
| Incorrect | Correct | Why |
|---|---|---|
| She didn’t went to school. | She didn’t go to school. | Use base form after “didn’t.” |
| I was watch TV. | I watched TV. | Use V2 for past actions. |
Quick Practice
-
They ____ (play) cricket yesterday.
-
I ____ (not/go) to the party.
-
____ (you/see) that movie ?
✅ Answers: played / didn’t go / Did you see
2. Past Continuous Tense
Definition
The Past Continuous Tense describes actions that were in progress at a specific time in the past.
Examples:
I was reading when you called.
They were playing football at 5 PM.
Structure
| Type | Formula | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Affirmative | Subject + was/were + V1 + ing | She was cooking dinner. |
| Negative | Subject + was/were + not + V1 + ing | They were not sleeping. |
| Question | Was/Were + Subject + V1 + ing ? | Were you studying ? |
Usage
-
Ongoing past actions → He was watching TV at 9 PM.
-
Interrupted actions → I was cooking when the phone rang.
-
Two actions happening together → While he was driving, I was reading.
Common Mistakes
| Incorrect | Correct | Why |
|---|---|---|
| I were sleeping. | I was sleeping. | Use “was” with I/he/she/it. |
| She was cook dinner. | She was cooking dinner. | Add “-ing.” |
Quick Practice
-
I ____ (sleep) when you called.
-
They ____ (not/watch) TV at that time.
-
____ (he/read) when she arrived ?
✅ Answers: was sleeping / were not watching / Was he reading
3. Past Perfect Tense
Definition
The Past Perfect Tense shows an action that happened before another past action. It’s the “past of the past.”
Examples:
I had finished dinner before she arrived.
They had left when I got there.
Structure
| Type | Formula | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Affirmative | Subject + had + V3 | She had gone to work. |
| Negative | Subject + had not + V3 | She had not gone to work. |
| Question | Had + Subject + V3 ? | Had she gone to work ? |
Usage
-
Action completed before another past action → I had eaten before he came.
-
Reported speech → She said she had met him.
-
Unreal or conditional past → If I had known, I would have helped.
Common Mistakes
| Incorrect | Correct | Why |
|---|---|---|
| I had saw him. | I had seen him. | Use V3 (past participle). |
| She had left when I was arrive. | She had left when I arrived. | Main action in simple past. |
Quick Practice
-
He ____ (finish) his work before 6 PM.
-
They ____ (not/leave) when we arrived.
-
____ (you/see) her before yesterday ?
✅ Answers: had finished / had not left / Had you seen
4. Past Perfect Continuous Tense
Definition
The Past Perfect Continuous Tense shows a long action that continued up to another point in the past.
Examples:
I had been studying for hours before dinner.
They had been working all day before they rested.
Structure
| Type | Formula | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Affirmative | Subject + had been + V1 + ing | She had been reading. |
| Negative | Subject + had not been + V1 + ing | She had not been reading. |
| Question | Had + Subject + been + V1 + ing ? | Had she been reading ? |
Usage
-
Long action before another past event → He had been working for years before retirement.
-
To explain cause in the past → She was tired because she had been studying.
-
Emphasizing duration before a past point → We had been waiting for an hour before the bus came.
Common Mistakes
| Incorrect | Correct | Why |
|---|---|---|
| I had been work all day. | I had been working all day. | Add “-ing.” |
| They had been waited for hours. | They had been waiting for hours. | Wrong verb form. |
Quick Practice
-
I ____ (study) for two hours before dinner.
-
She ____ (not/sleep) well for days.
-
____ (they/work) there long before they quit ?
✅ Answers: had been studying / had not been sleeping / Had they been working
Future Tense Forms
1. Simple Future Tense (Will)
Definition
The Simple Future Tense is used when you talk about something that will happen later — decisions, predictions, or promises.
Examples:
I will call you tomorrow.
It will rain tonight.
Structure
| Type | Formula | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Affirmative | Subject + will + V1 | She will travel next week. |
| Negative | Subject + will not (won’t) + V1 | He won’t come today. |
| Question | Will + Subject + V1 ? | Will you help me ? |
Usage
-
Predictions → It will be cold tomorrow.
-
Promises or offers → I’ll help you with homework.
-
Decisions made instantly → I’ll take the red one.
Common Mistakes
| Incorrect | Correct | Why |
|---|---|---|
| She will goes to school. | She will go to school. | Use base verb after will. |
| I will to call you. | I will call you. | No to before verb. |
Quick Practice
-
I ____ (call) you tonight.
-
They ____ (not/come) to the party.
-
____ (you/help) me with this ?
✅ Answers: will call / will not come / Will you help
2. Future Continuous Tense
Definition
The Future Continuous Tense describes actions that will be happening at a specific time in the future.
Examples:
I will be sleeping at 10 PM.
They will be traveling tomorrow morning.
Structure
| Type | Formula | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Affirmative | Subject + will be + V1 + ing | She will be cooking dinner. |
| Negative | Subject + will not be + V1 + ing | He won’t be working then. |
| Question | Will + Subject + be + V1 + ing ? | Will you be joining us ? |
Usage
-
Actions happening at a future time → This time tomorrow, I’ll be flying to Rome.
-
Polite questions → Will you be using the laptop later?
-
Predictions about continuing activities → They’ll be studying all night.
Common Mistakes
| Incorrect | Correct | Why |
|---|---|---|
| She will be cooks dinner. | She will be cooking dinner. | Add “-ing.” |
| He will working later. | He will be working later. | Missing be. |
Quick Practice
-
I ____ (study) at 8 PM tonight.
-
They ____ (not/sleep) when we arrive.
-
____ (she/work) tomorrow morning ?
✅ Answers: will be studying / will not be sleeping / Will she be working
3. Future Perfect Tense
Definition
The Future Perfect Tense shows an action that will be completed before a specific future moment.
Examples:
By next week, I will have finished this project.
They will have arrived by 6 PM.
Structure
| Type | Formula | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Affirmative | Subject + will have + V3 | He will have left by noon. |
| Negative | Subject + will not have + V3 | They won’t have finished yet. |
| Question | Will + Subject + have + V3 ? | Will she have arrived ? |
Usage
-
Completion before a future time → By 2026, she will have graduated.
-
Predictions about finished actions → You’ll have eaten before the movie starts.
-
Expressing deadlines → I’ll have completed the work by Monday.
Common Mistakes
| Incorrect | Correct | Why |
|---|---|---|
| I will have finish it. | I will have finished it. | Use V3 (past participle). |
| She will has left. | She will have left. | Wrong helping verb. |
Quick Practice
-
By tomorrow, I ____ (complete) the report.
-
They ____ (not/arrive) before 9 PM.
-
____ (you/finish) by then ?
✅ Answers: will have completed / will not have arrived / Will you have finished
4. Future Perfect Continuous Tense
Definition
The Future Perfect Continuous Tense focuses on the duration of an activity that will continue up to a certain future time.
Examples:
By next month, I will have been working here for five years.
She will have been studying since morning.
Structure
| Type | Formula | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Affirmative | Subject + will have been + V1 + ing | They will have been living here for ten years. |
| Negative | Subject + will not have been + V1 + ing | He won’t have been working long. |
| Question | Will + Subject + have been + V1 + ing ? | Will you have been studying ? |
Usage
-
To show ongoing action continuing to a future time → I’ll have been driving for hours by then.
-
To express cause → She’ll be tired because she will have been working all day.
-
To highlight duration → By June, we’ll have been learning English for six months.
Common Mistakes
| Incorrect | Correct | Why |
|---|---|---|
| I will have been study since 8. | I will have been studying since 8. | Add “-ing.” |
| She will has been working. | She will have been working. | Wrong auxiliary verb. |
Quick Practice
-
By next year, I ____ (work) here for ten years.
-
He ____ (not/sleep) well for days.
-
____ (they/live) in London for long ?
✅ Answers: will have been working / will not have been sleeping / Will they have been living
SPECIAL FUTURE FORMS & MIXED TENSE USAGE
1. “Going to” Future
Definition
The “Going to” Future form is used for plans, intentions, or predictions based on current evidence.
Think of it as the “I already decided” future.
Examples:
I am going to study tonight.
Look at those clouds! It’s going to rain.
Structure
| Type | Formula | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Affirmative | Subject + am/is/are + going to + V1 | We are going to travel next month. |
| Negative | Subject + am/is/are + not + going to + V1 | She isn’t going to come. |
| Question | Am/Is/Are + Subject + going to + V1 ? | Are you going to help me ? |
Usage
- Future plans → We are going to buy a car.
- Intentions → I’m going to start a new course.
- Predictions with present signs → Watch out! You’re going to fall.
Common Mistakes
| Incorrect | Correct | Why |
|---|---|---|
| He going to play football. | He is going to play football. | Missing is. |
| I am go to school. | I am going to school. | Missing “going to”. |
Quick Practice
- I ____ (go) visit my friend this weekend.
- They ____ (not/watch) the match.
- ____ (you/start) the project soon ?
✅ Answers: am going to / are not going to / Are you going to
2. Future in the Past
Definition
Future in the Past is used when you talk about a future event from a past point of view.
It’s like looking ahead from yesterday.
Examples:
I was going to call you, but I forgot.
She said she would help me.
Structure
| Form | Formula | Example |
|---|---|---|
| “Was/Were going to” | Subject + was/were going to + V1 | I was going to travel, but plans changed. |
| “Would” | Subject + would + V1 | He said he would call later. |
Usage
- Plans that didn’t happen → I was going to bake a cake, but I ran out of eggs.
- Reported future speech → She said she would meet us.
- Unfulfilled intentions → They were going to move abroad.
Common Mistakes
| Incorrect | Correct | Why |
|---|---|---|
| I was go to call you. | I was going to call you. | Use full phrase “was going to.” |
| He said he will come. | He said he would come. | Use would for past reporting. |
Quick Practice
- I ____ (be/go) to the party, but I got sick.
- She said she ____ (call) me later.
✅ Answers: was going / would call
3. Time Clauses in the Future
Definition
When you use time words (like when, after, before, until, as soon as) to talk about future events, you actually use the Present Tense, not the Future Tense.
Examples:
When I see her, I will tell her.
After you finish dinner, we’ll go out.
Common Time Words
when, after, before, until, as soon as, once, by the time
| Time Word | Example | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| When | When I arrive, I’ll call you. | “When” + Present Simple for future meaning. |
| Before | Before she leaves, I’ll say goodbye. | Shows order of future actions. |
| Until | Wait here until I come back. | Ongoing until another future moment. |
Usage
- Present Simple replaces future after time words.
- Expresses timing of connected future actions.
Common Mistakes
| Incorrect | Correct | Why |
|---|---|---|
| When I will see him, I will tell him. | When I see him, I will tell him. | “Will” not used after “when.” |
| After she will come, we will eat. | After she comes, we will eat. | First action uses Present Simple. |
Quick Practice
- When I ____ (finish), I’ll call you.
- Before he ____ (leave), tell him goodbye.
- Wait here until she ____ (come).
✅ Answers: finish / leaves / comes
4. Mixed Tenses (How English Really Works)
Definition
Mixed tenses happen when different time frames appear in one sentence — and that’s totally natural in English!
They show logical or conditional relationships between past, present, and future.
Common Mixed Forms
| Type | Example | Meaning |
|---|---|---|
| Present + Future | If it rains, I’ll stay home. | Present condition affecting future. |
| Past + Present | If I had studied, I know more now. | Past action affecting present. |
| Past + Future | If I had saved money, I’d buy a car now. | Missed past action affects possible future. |
| Present Perfect + Future | Once you’ve finished, we’ll leave. | Completion before future action. |
Common Mistakes
| Incorrect | Correct | Why |
|---|---|---|
| If it will rain, I’ll stay home. | If it rains, I’ll stay home. | Present for future condition. |
| If I studied, I will pass. | If I study, I will pass. | Wrong tense combination. |
Quick Practice
- If it ____ (rain), I will stay home.
- Once you ____ (finish), we will eat dinner.
- If I ____ (study) harder, I would know more.
✅ Answers: rains / finish / had studied
Narrative & Real-Life Context Mix
Definition
In real communication, tenses often mix naturally to show sequence, duration, and cause — especially in stories, conversations, and essays.
Examples:
I was reading when she called, and now I’ve just finished the book.
By the time you arrive, I’ll have been waiting for an hour.
Usage
- To connect past, present, and future smoothly.
- Used in storytelling, essays, and real conversations.
Common Tense Mistakes Learners Often Make
Even fluent English learners mix up tenses sometimes! Let’s fix that with simple corrections and logic-based examples :
| ❌ Incorrect Sentence | ✅ Correct Sentence | 💡 Why It’s Wrong |
|---|---|---|
| I am knowing the answer. | I know the answer. | “Know” is a state verb — it doesn’t take -ing. |
| She didn’t went to school. | She didn’t go to school. | Use base form after did/didn’t. |
| I have seen him yesterday. | I saw him yesterday. | Specific time (yesterday) needs Simple Past. |
| He will be comes tomorrow. | He will come tomorrow. | No “be” or extra verb after will. |
| If it will rain, we will stay home. | If it rains, we will stay home. | In if-clauses, use Present for future meaning. |
| I was go to party. | I was going to the party. | Missing continuous form “going.” |
| I am agree with you. | I agree with you. | “Agree” is not a continuous verb. |
Real-Life Usage: Choosing the Right Tense in Context
Let’s see how tenses sound natural in real situations:
Conversation Example
Teacher: Have you finished your homework yet?
Student: Yes, I finished it this morning.
Why it works:
- Have you finished → Present Perfect (asks about a recent action).
- I finished → Simple Past (gives a time reference).
Business Example
➡️ By next quarter, our company will have achieved its annual goals.
→ Future Perfect tense used for completion before a future deadline.
Academic Writing Example
➡️ Researchers have found that early exposure improves fluency.
→ Present Perfect connects past research to current understanding.
Travel Story Example
➡️ I was packing my bags when my phone rang.
→ Past Continuous shows background action interrupted by another past event.
Comprehensive Tense Practice Exercises
( Check the answer below)
Exercise Set 1: Present Tenses
Fill in the blanks with the correct present tense form:
- Sarah _____ (work) at the hospital now.
- They _____ (live) in Paris since 2010.
- I _____ (study) English for six months.
- He usually _____ (take) the bus to work.
- The Earth _____ (revolve) around the Sun.
- We _____ (wait) here for two hours.
- She _____ (cook) dinner every Sunday.
- John _____ (read) this book for a week.
- The baby _____ (sleep) right now.
- They _____ (play) tennis every weekend.
- I _____ (work) on this project since Monday.
- The sun _____ (rise) in the east.
- She _____ (teach) at this school for ten years.
- The children _____ (play) in the garden now.
- He _____ (not/smoke) anymore.
- We _____ (discuss) this issue since morning.
- The train always _____ (leave) on time.
- I _____ (think) about changing my job.
- They _____ (build) a new house currently.
- Mary _____ (practice) piano for three hours.
Exercise Set 2: Past Tenses
Complete with appropriate past tense forms:
- When I arrived, she _____ (already/leave).
- I _____ (study) when you called.
- They _____ (live) here before they moved.
- He _____ (work) all day when I saw him.
- We _____ (wait) for an hour when she came.
Exercise Set 3: Future Tenses
Complete with appropriate future tense forms:
- By next week, I _____ (finish) this project.
- This time tomorrow, we _____ (fly) to Paris.
- He _____ (work) here for ten years by June.
- I _____ (meet) her at 6 PM tomorrow.
- They _____ (arrive) by the time we get there.
- She _____ (study) medicine next year.
- We _____ (live) here for twenty years by 2025.
- The train _____ (leave) at 9 AM tomorrow.
- I _____ (complete) the task before you return.
- They _____ (wait) when you arrive.
Exercise Set 4: Mixed Tenses
Choose the correct tense:
- By the time you get there, I _____ (leave).
- If I _____ (know) earlier, I would have told you.
- She _____ (work) here since she graduated.
- While he _____ (cook), I cleaned the house.
- I _____ (never/see) such a beautiful sunset before.
- When the phone rang, I _____ (take) a shower.
- After she _____ (finish), she went home.
- He _____ (live) here for ten years now.
- I _____ (study) when the earthquake happened.
- They _____ (already/eat) when we arrived.
Exercise Set 5: Special Cases
Fill in the blanks with appropriate tenses:
- I wish I _____ (be) taller.
- If only he _____ (tell) me earlier.
- It’s time we _____ (go) home.
- You’d better _____ (start) working.
- Would you rather _____ (stay) or go?
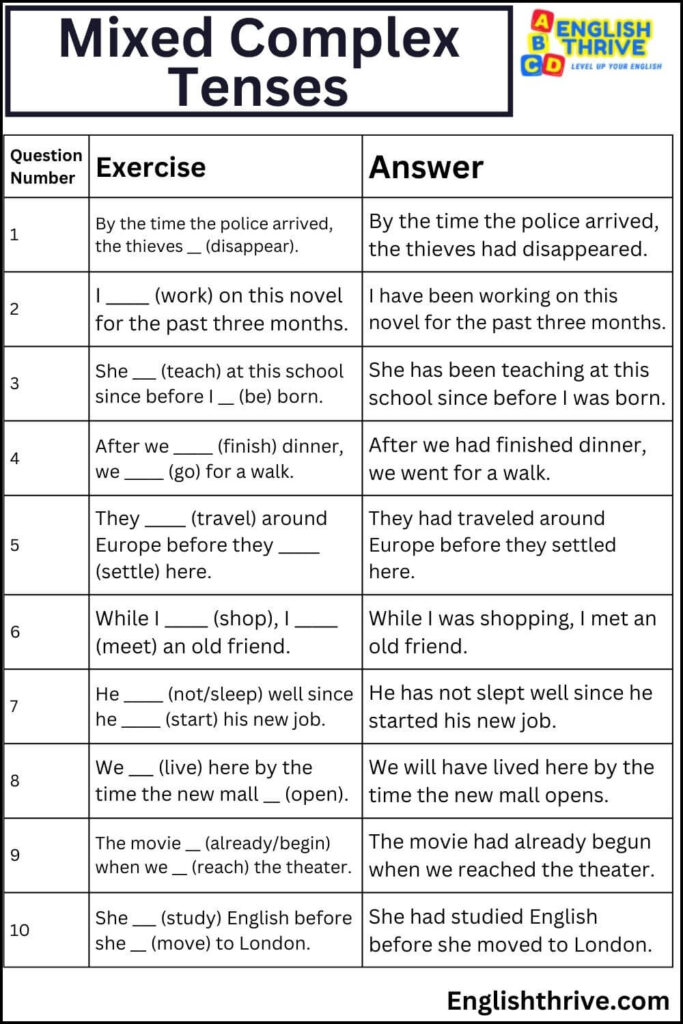
Exercise Set 6: Mixed Complex Tenses
Complete the sentences with appropriate tenses:
- By the time the police arrived, the thieves _____ (disappear).
- I _____ (work) on this novel for the past three months.
- She _____ (teach) at this school since before I _____ (be) born.
- After we _____ (finish) dinner, we _____ (go) for a walk.
- They _____ (travel) around Europe before they _____ (settle) here.
- While I _____ (shop), I _____ (meet) an old friend.
- He _____ (not/sleep) well since he _____ (start) his new job.
- We _____ (live) here by the time the new mall _____ (open).
- The movie _____ (already/begin) when we _____ (reach) the theater.
- She _____ (study) English before she _____ (move) to London.
Exercise Set 7: Passive Voice Tenses
Transform these sentences into passive voice with correct tenses:
- They build this bridge in 1990. (Past Simple)
- Someone has stolen my wallet. (Present Perfect)
- They are repairing my car. (Present Continuous)
- They will announce the results tomorrow. (Future Simple)
- They had completed the project before the deadline. (Past Perfect)
Exercise Set 8: Conditional Tenses
Complete these conditional sentences:
- If I _____ (have) time, I _____ (help) you yesterday.
- Unless it _____ (rain), we _____ (go) to the beach tomorrow.
- If she _____ (study) harder, she _____ (pass) the exam last week.
- If I _____ (be) you, I _____ (take) the job.
- Had I known earlier, I _____ (come) to help.
Exercise Set 9: Reported Speech Tenses
Change to reported speech with correct tense changes:
- “I am studying.” → He said that…
- “I have finished my work.” → She told me…
- “We will visit Paris.” → They said…
- “I can help you.” → He promised…
- “I have been waiting.” → She mentioned…
Exercise Set 10: Perfect Modal Tenses
Complete with perfect modal forms:
- She _____ (must + work) late last night; her car was there.
- They _____ (could + win) if they tried harder.
- He _____ (should + tell) me about the meeting.
- You _____ (might + lose) your way in the dark.
- We _____ (would + finish) earlier with more help.
Exercise Set 11: Advanced Mixed Tenses
Fill in with appropriate tenses:
- No sooner _____ (I/arrive) than it _____ (start) raining.
- Hardly _____ (she/leave) when the guest _____ (arrive).
- By next month, I _____ (work) here for 20 years.
- Not only _____ (he/lose) his job, but also _____ (he/break) his leg.
- Scarcely _____ (we/begin) when the power _____ (go) out.
Exercise Set 12: Time Clauses
Complete with correct time-related tenses:
- Before she _____ (arrive), we _____ (clean) the house.
- After they _____ (eat), they _____ (watch) a movie.
- As soon as he _____ (come), we _____ (leave).
- Until she _____ (return), we _____ (wait) here.
- The moment _____ (she/walk) in, everyone _____ (start) clapping.
Exercise Set 13: States vs. Actions Tenses
Complete with appropriate tenses based on state or action:
- I _____ (think) she’s right. (state of belief)
- I _____ (think) about the problem. (action of considering)
- He _____ (have) a new car. (possession)
- We _____ (have) lunch now. (action)
- She _____ (look) tired today. (state/appearance)
Exercise Set 14: Future Time Clauses
Use correct tense combinations:
- When she _____ (arrive), we _____ (go) to dinner.
- Before the sun _____ (set), we _____ (reach) the top.
- After I _____ (finish) work, I _____ (call) you.
- As soon as he _____ (get) here, we _____ (leave).
- Until it _____ (stop) raining, we _____ (stay) inside.
Exercise Set 15: Final Mixed Practice
Complete with any appropriate tense:
- By the time you read this, I _____ (already/leave).
- I _____ (never/be) to Paris before last summer.
- She _____ (work) here since she _____ (graduate).
- While he _____ (cook), the phone _____ (ring).
- Tomorrow at this time, I _____ (sit) on the beach.
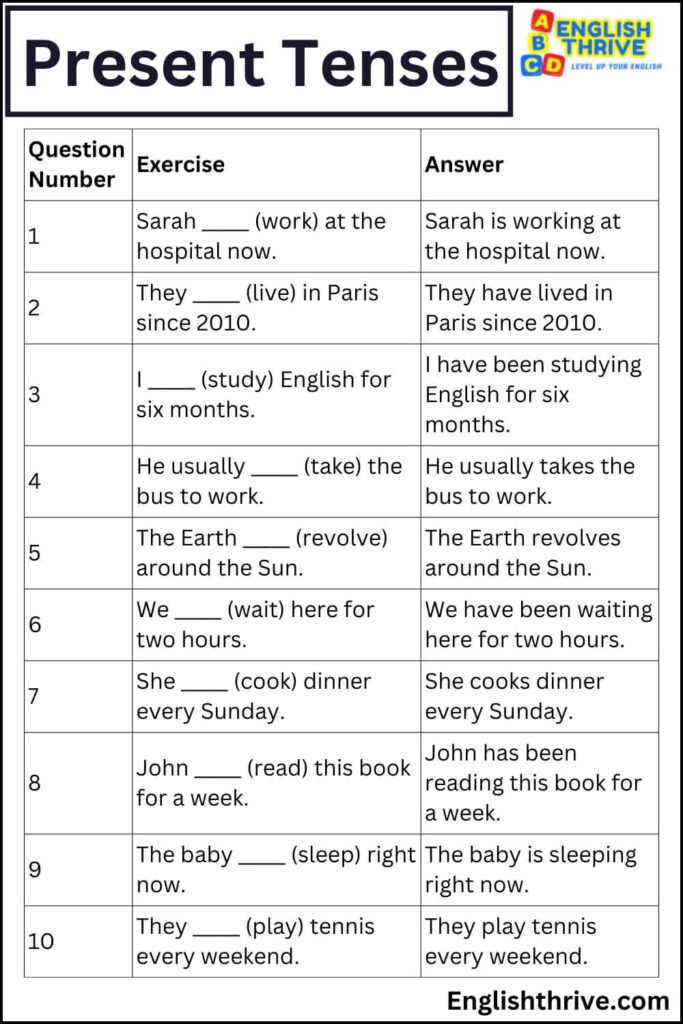
Exercise Set 1: Present Tenses
| Question Number | Exercise | Answer |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Sarah _____ (work) at the hospital now. | Sarah is working at the hospital now. |
| 2 | They _____ (live) in Paris since 2010. | They have lived in Paris since 2010. |
| 3 | I _____ (study) English for six months. | I have been studying English for six months. |
| 4 | He usually _____ (take) the bus to work. | He usually takes the bus to work. |
| 5 | The Earth _____ (revolve) around the Sun. | The Earth revolves around the Sun. |
| 6 | We _____ (wait) here for two hours. | We have been waiting here for two hours. |
| 7 | She _____ (cook) dinner every Sunday. | She cooks dinner every Sunday. |
| 8 | John _____ (read) this book for a week. | John has been reading this book for a week. |
| 9 | The baby _____ (sleep) right now. | The baby is sleeping right now. |
| 10 | They _____ (play) tennis every weekend. | They play tennis every weekend. |
| 11 | I _____ (work) on this project since Monday. | I have been working on this project since Monday. |
| 12 | The sun _____ (rise) in the east. | The sun rises in the east. |
| 13 | She _____ (teach) at this school for ten years. | She has been teaching at this school for ten years. |
| 14 | The children _____ (play) in the garden now. | The children are playing in the garden now. |
| 15 | He _____ (not/smoke) anymore. | He does not smoke anymore. |
Exercise Set 2: Past Tenses
| Question Number | Exercise | Answer |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | When I arrived, she _____ (already/leave). | When I arrived, she had already left. |
| 2 | I _____ (study) when you called. | I was studying when you called. |
| 3 | They _____ (live) here before they moved. | They had lived here before they moved. |
| 4 | He _____ (work) all day when I saw him. | He had been working all day when I saw him. |
| 5 | We _____ (wait) for an hour when she came. | We had been waiting for an hour when she came. |
Exercise Set 3: Future Tenses
| Question Number | Exercise | Answer |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | By next week, I _____ (finish) this project. | By next week, I will have finished this project. |
| 2 | This time tomorrow, we _____ (fly) to Paris. | This time tomorrow, we will be flying to Paris. |
| 3 | He _____ (work) here for ten years by June. | He will have worked here for ten years by June. |
| 4 | I _____ (meet) her at 6 PM tomorrow. | I will meet her at 6 PM tomorrow. |
| 5 | They _____ (arrive) by the time we get there. | They will have arrived by the time we get there. |
Exercise Set 4: Mixed Tenses
| Question Number | Exercise | Answer |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | By the time you get there, I _____ (leave). | By the time you get there, I will have left. |
| 2 | If I _____ (know) earlier, I would have told you. | If I had known earlier, I would have told you. |
| 3 | She _____ (work) here since she graduated. | She has been working here since she graduated. |
| 4 | While he _____ (cook), I cleaned the house. | While he was cooking, I cleaned the house. |
| 5 | I _____ (never/see) such a beautiful sunset before. | I had never seen such a beautiful sunset before. |
| 6 | When the phone rang, I _____ (take) a shower. | When the phone rang, I was taking a shower. |
| 7 | After she _____ (finish), she went home. | After she had finished, she went home. |
| 8 | He _____ (live) here for ten years now. | He has lived here for ten years now. |
| 9 | I _____ (study) when the earthquake happened. | I was studying when the earthquake happened. |
| 10 | They _____ (already/eat) when we arrived. | They had already eaten when we arrived. |
Exercise Set 5: Special Cases
| Question Number | Exercise | Answer |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | I wish I _____ (be) taller. | I wish I were taller. |
| 2 | If only he _____ (tell) me earlier. | If only he had told me earlier. |
| 3 | It’s time we _____ (go) home. | It’s time we went home. |
| 4 | You’d better _____ (start) working. | You’d better start working. |
| 5 | Would you rather _____ (stay) or go? | Would you rather stay or go? |
Exercise Set 6: Mixed Complex Tenses
| Question Number | Exercise | Answer |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | By the time the police arrived, the thieves _____ (disappear). | By the time the police arrived, the thieves had disappeared. |
| 2 | I _____ (work) on this novel for the past three months. | I have been working on this novel for the past three months. |
| 3 | She _____ (teach) at this school since before I _____ (be) born. | She has been teaching at this school since before I was born. |
| 4 | After we _____ (finish) dinner, we _____ (go) for a walk. | After we had finished dinner, we went for a walk. |
| 5 | They _____ (travel) around Europe before they _____ (settle) here. | They had traveled around Europe before they settled here. |
| 6 | While I _____ (shop), I _____ (meet) an old friend. | While I was shopping, I met an old friend. |
| 7 | He _____ (not/sleep) well since he _____ (start) his new job. | He has not slept well since he started his new job. |
| 8 | We _____ (live) here by the time the new mall _____ (open). | We will have lived here by the time the new mall opens. |
| 9 | The movie _____ (already/begin) when we _____ (reach) the theater. | The movie had already begun when we reached the theater. |
| 10 | She _____ (study) English before she _____ (move) to London. | She had studied English before she moved to London. |
Exercise Set 7: Passive Voice Tenses
| Question Number | Exercise | Answer |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | They build this bridge in 1990. (Past Simple) | This bridge was built in 1990. |
| 2 | Someone has stolen my wallet. (Present Perfect) | My wallet has been stolen. |
| 3 | They are repairing my car. (Present Continuous) | My car is being repaired. |
| 4 | They will announce the results tomorrow. (Future Simple) | The results will be announced tomorrow. |
| 5 | They had completed the project before the deadline. (Past Perfect) | The project had been completed before the deadline. |
Exercise Set 8: Conditional Tenses
| Question Number | Exercise | Answer |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | If I _____ (have) time, I _____ (help) you yesterday. | If I had had time, I would have helped you yesterday. |
| 2 | Unless it _____ (rain), we _____ (go) to the beach tomorrow. | Unless it rains, we will go to the beach tomorrow. |
| 3 | If she _____ (study) harder, she _____ (pass) the exam last week. | If she had studied harder, she would have passed the exam last week. |
| 4 | If I _____ (be) you, I _____ (take) the job. | If I were you, I would take the job. |
| 5 | Had I known earlier, I _____ (come) to help. | Had I known earlier, I would have come to help. |
Exercise Set 9: Reported Speech Tenses
| Question Number | Exercise | Answer |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | “I am studying.” → He said that… | He said that he was studying. |
| 2 | “I have finished my work.” → She told me… | She told me that she had finished her work. |
| 3 | “We will visit Paris.” → They said… | They said that they would visit Paris. |
| 4 | “I can help you.” → He promised… | He promised that he could help me. |
| 5 | “I have been waiting.” → She mentioned… | She mentioned that she had been waiting. |
Exercise Set 10: Perfect Modal Tenses
| Question Number | Exercise | Answer |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | She _____ (must + work) late last night; her car was there. | She must have worked late last night; her car was there. |
| 2 | They _____ (could + win) if they tried harder. | They could have won if they had tried harder. |
| 3 | He _____ (should + tell) me about the meeting. | He should have told me about the meeting. |
| 4 | You _____ (might + lose) your way in the dark. | You might have lost your way in the dark. |
| 5 | We _____ (would + finish) earlier with more help. | We would have finished earlier with more help. |
Exercise Set 11: Advanced Mixed Tenses
| Question Number | Exercise | Answer |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | No sooner _____ (I/arrive) than it _____ (start) raining. | No sooner had I arrived than it started raining. |
| 2 | Hardly _____ (she/leave) when the guest _____ (arrive). | Hardly had she left when the guest arrived. |
| 3 | By next month, I _____ (work) here for 20 years. | By next month, I will have worked here for 20 years. |
| 4 | Not only _____ (he/lose) his job, but also _____ (he/break) his leg. | Not only did he lose his job, but also he broke his leg. |
| 5 | Scarcely _____ (we/begin) when the power _____ (go) out. | Scarcely had we begun when the power went out. |
Exercise Set 12: Time Clauses
| Question Number | Exercise | Answer |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Before she _____ (arrive), we _____ (clean) the house. | Before she arrived, we had cleaned the house. |
| 2 | After they _____ (eat), they _____ (watch) a movie. | After they had eaten, they watched a movie. |
| 3 | As soon as he _____ (come), we _____ (leave). | As soon as he comes, we will leave. |
| 4 | Until she _____ (return), we _____ (wait) here. | Until she returns, we will wait here. |
| 5 | The moment _____ (she/walk) in, everyone _____ (start) clapping. | The moment she walked in, everyone started clapping. |
Exercise Set 13: States vs. Actions Tenses
| Question Number | Exercise | Answer |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | I _____ (think) she’s right. (state of belief) | I think she’s right. |
| 2 | I _____ (think) about the problem. (action of considering) | I am thinking about the problem. |
| 3 | He _____ (have) a new car. (possession) | He has a new car. |
| 4 | We _____ (have) lunch now. (action) | We are having lunch now. |
| 5 | She _____ (look) tired today. (state/appearance) | She looks tired today. |
Exercise Set 14: Future Time Clauses
| Question Number | Exercise | Answer |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | When she _____ (arrive), we _____ (go) to dinner. | When she arrives, we will go to dinner. |
| 2 | Before the sun _____ (set), we _____ (reach) the top. | Before the sun sets, we will reach the top. |
| 3 | After I _____ (finish) work, I _____ (call) you. | After I finish work, I will call you. |
| 4 | As soon as he _____ (get) here, we _____ (leave). | As soon as he gets here, we will leave. |
| 5 | Until it _____ (stop) raining, we _____ (stay) inside. | Until it stops raining, we will stay inside. |
Exercise Set 15: Final Mixed Tense Practice
| Question Number | Exercise | Answer |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | By the time you read this, I _____ (already/leave). | By the time you read this, I will have already left. |
| 2 | I _____ (never/be) to Paris before last summer. | I had never been to Paris before last summer. |
| 3 | She _____ (work) here since she _____ (graduate). | She has worked here since she graduated. |
| 4 | While he _____ (cook), the phone _____ (ring). | While he was cooking, the phone rang. |
| 5 | Tomorrow at this time, I _____ (sit) on the beach. | Tomorrow at this time, I will be sitting on the beach. |
Summary
Mastering English tenses isn’t just about memorizing formulas — it’s about telling time through words.
When you understand when something happens (past, present, or future) and how long it lasts, your English becomes fluent, precise, and professional.
Ready to Practice More?
Check out our full exercises and guides here: https://englishthrive.com/100-examples-of-present-past-and-future-tense/