Ever wondered why we say “John’s car” instead of “the car of John”? Possessive nouns show ownership or belonging, and they’re essential for clear communication. As an English teacher who’s helped countless students master these tricky words, I’ll share 147 possessive noun examples that will make your writing more precise and natural.
Contents
ToggleWhat Are Possessive Nouns?
Possessive nouns show ownership, belonging, or a close relationship between people, animals, or things. They’re typically formed by adding an apostrophe and ‘s’ (‘s) to the end of a noun, though there are some special rules for plural nouns and proper names.
Types of Possessive Nouns Examples and Sentences
1. Singular Possessive Nouns
| Base Noun | Possessive Form |
|---|---|
| dog | dog’s |
| cat | cat’s |
| teacher | teacher’s |
| book | book’s |
| child | child’s |
Example Sentences:
- The dog’s bowl is empty.
- The cat’s tail is fluffy.
- The teacher’s desk needs cleaning.
- The book’s cover is torn.
- The child’s toy is missing.
2. Plural Possessive Nouns
| Base Noun | Possessive Form |
|---|---|
| dogs | dogs’ |
| cats | cats’ |
| teachers | teachers’ |
| books | books’ |
| children | children’s |
Example Sentences:
- The dogs’ kennels need cleaning.
- The cats’ food bowls are full.
- The teachers’ lounge is quiet.
- The books’ pages are yellowed.
- The children’s playground is busy.
3. Proper Name Possessives
| Base Noun | Possessive Form |
|---|---|
| John | John’s |
| Sarah | Sarah’s |
| James | James’s |
| Chris | Chris’s |
| Thomas | Thomas’ |
Example Sentences:
- John’s car broke down yesterday.
- Sarah’s house is painted blue.
- James’s guitar needs new strings.
- Chris’s phone is ringing.
- Thomas’ bike was stolen.
4. Time and Distance Possessives
| Base Noun | Possessive Form |
|---|---|
| day | day’s |
| week | week’s |
| month | month’s |
| mile | mile’s |
| hour | hour’s |
Example Sentences:
- A day’s work is complete.
- This week’s schedule is full.
- Last month’s rent is due.
- A mile’s walk refreshed me.
- An hour’s delay caused problems.
5. Compound Possessives
| Base Noun | Possessive Form |
|---|---|
| mother-in-law | mother-in-law’s |
| sister-in-law | sister-in-law’s |
| editor-in-chief | editor-in-chief’s |
| father-in-law | father-in-law’s |
| passer-by | passer-by’s |
Example Sentences:
- My mother-in-law’s cooking is excellent.
- The sister-in-law’s car is new.
- The editor-in-chief’s decision is final.
- My father-in-law’s advice was helpful.
- The passer-by’s help was appreciated.
Complete List of Possessive Nouns
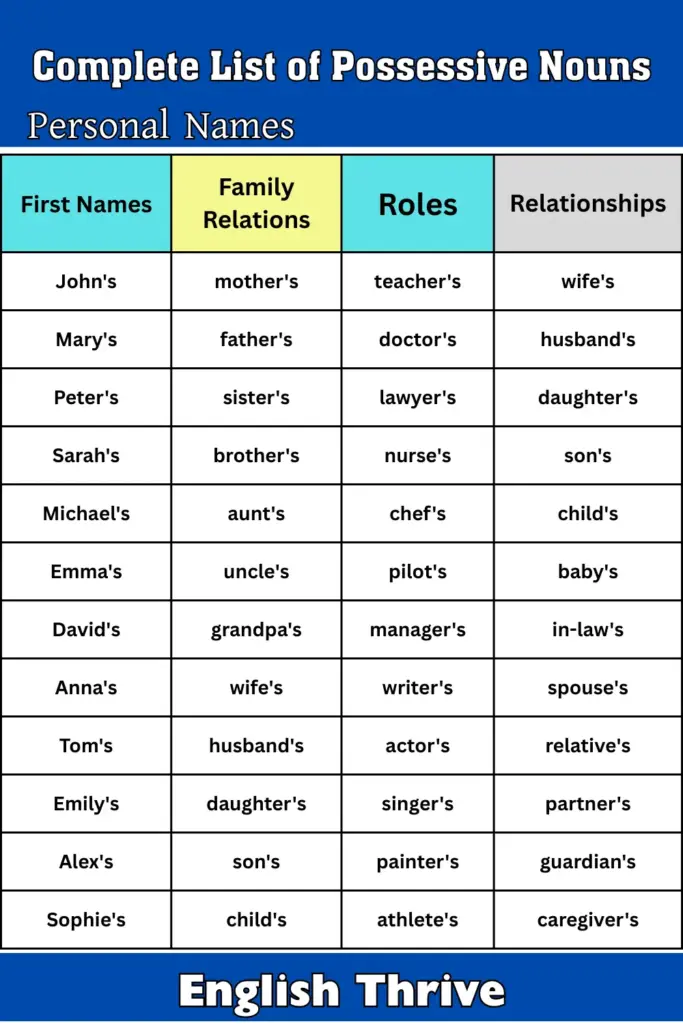
Personal Names
| First Names | Family Relations | Roles | Relationships |
|---|---|---|---|
| John’s | mother’s | teacher’s | wife’s |
| Mary’s | father’s | doctor’s | husband’s |
| Peter’s | sister’s | lawyer’s | daughter’s |
| Sarah’s | brother’s | nurse’s | son’s |
| Michael’s | aunt’s | chef’s | child’s |
| Emma’s | uncle’s | pilot’s | baby’s |
| James’s | cousin’s | dentist’s | grandchild’s |
| Lisa’s | grandma’s | engineer’s | sibling’s |
| David’s | grandpa’s | manager’s | in-law’s |
| Anna’s | wife’s | writer’s | spouse’s |
| Tom’s | husband’s | actor’s | relative’s |
| Emily’s | daughter’s | singer’s | partner’s |
| Alex’s | son’s | painter’s | guardian’s |
| Sophie’s | child’s | athlete’s | caregiver’s |
| Chris’s | baby’s | artist’s | mentor’s |
Animals
| Wild Animals | Domestic Animals | Zoo Animals | Marine Life |
|---|---|---|---|
| dog’s | cat’s | lion’s | elephant’s |
| bird’s | horse’s | tiger’s | wolf’s |
| computer’s | bear’s | monkey’s | giraffe’s |
| lion’s | penguin’s | elephant’s | dolphin’s |
| tiger’s | rabbit’s | snake’s | seal’s |
Objects
| Furniture | Electronics | Writing Tools | Household Items |
|---|---|---|---|
| book’s | phone’s | computer’s | desk’s |
| chair’s | lamp’s | pen’s | bed’s |
| desk’s | clock’s | cup’s | door’s |
| window’s | plate’s | key’s | table’s |
| door’s | plate’s | key’s | lamp’s |
Places
| Buildings | Public Spaces | Natural Locations | Transportation Hubs |
|---|---|---|---|
| school’s | store’s | garden’s | airport’s |
| house’s | office’s | park’s | stadium’s |
| hotel’s | mall’s | beach’s | theater’s |
| church’s | hospital’s | mountain’s | gym’s |
| library’s | university’s | river’s | clinic’s |
Professions
| Service Professionals | Creative Professionals | Academic Professionals | Business Professionals |
|---|---|---|---|
| teacher’s | writer’s | doctor’s | manager’s |
| lawyer’s | artist’s | engineer’s | chef’s |
| nurse’s | singer’s | pilot’s | actor’s |
| dentist’s | painter’s | athlete’s | dancer’s |
| pharmacist’s | musician’s | researcher’s | consultant’s |
Time Periods
| Daily Periods | Seasons | Larger Time Spans | Specific Moments |
|---|---|---|---|
| day’s | spring’s | year’s | morning’s |
| week’s | summer’s | month’s | evening’s |
| hour’s | autumn’s | decade’s | night’s |
| minute’s | winter’s | century’s | season’s |
| second’s | holiday’s | millennium’s | moment’s |
Organizations
| Business Entities | Educational Institutions | Government Bodies | Cultural Institutions |
|---|---|---|---|
| company’s | school’s | government’s | museum’s |
| bank’s | university’s | church’s | library’s |
| hospital’s | college’s | state’s | gallery’s |
| factory’s | institute’s | nation’s | theater’s |
| restaurant’s | academy’s | corporation’s | zoo’s |
Nature
| Celestial Bodies | Earth Features | Plant Life | Atmospheric Elements |
|---|---|---|---|
| sun’s | tree’s | plant’s | cloud’s |
| moon’s | river’s | flower’s | sky’s |
| star’s | ocean’s | grass’s | rain’s |
| mountain’s | lake’s | forest’s | wind’s |
| planet’s | beach’s | leaf’s | storm’s |
Vehicles
| Land Vehicles | Water Vehicles | Air Vehicles | Specialized Vehicles |
|---|---|---|---|
| car’s | boat’s | plane’s | bicycle’s |
| truck’s | ship’s | helicopter’s | rocket’s |
| bike’s | yacht’s | spacecraft’s | scooter’s |
| bus’s | canoe’s | drone’s | submarine’s |
| taxi’s | ferry’s | airship’s | hovercraft’s |
Additional Categories and Special Cases:
-
Joint Possession
- Tom and Jerry’s house
- Mom and Dad’s car
- Jack and Jill’s bucket
-
Separate Possession
- Tom’s and Jerry’s rooms
- Mom’s and Dad’s cars
- Jack’s and Jill’s buckets
-
Inanimate Objects
- Earth’s atmosphere
- fire’s heat
- water’s surface
FAQs about Possessive Nouns Examples- Definition Rules and Exercises
1. How do you form possessive nouns correctly?
Forming possessive nouns follows these basic rules:
- For singular nouns: Add ‘s (dog’s bone)
- For plural nouns ending in s: Add just an apostrophe (dogs’ bones)
- For plural nouns not ending in s: Add ‘s (children’s toys)
- For proper names ending in s: Either ‘s or just ‘ (James’s or James’ book)
- For compound nouns: Add ‘s to the last word (mother-in-law’s house)
2. What are the common mistakes with possessive nouns?
Common mistakes include:
- Confusing its/it’s
- Misplacing apostrophes (teachers room vs. teacher’s room)
- Using apostrophes with plural nouns (dog’s vs. dogs)
- Incorrect formation with proper names ending in s
- Confusion with joint vs. separate possession
3. How do possessive nouns differ from possessive pronouns?
Possessive nouns and pronouns serve similar functions but differ in form:
- Nouns use apostrophes (Mary’s book)
- Pronouns don’t use apostrophes (her book)
- Nouns specify the owner (teacher’s desk)
- Pronouns reference previously mentioned owners (his desk)
4. What are the rules for joint and separate possession?
Joint possession (shared ownership):
- Use apostrophe only with the last noun (Mom and Dad’s house)
- Implies shared ownership of one thing
Separate possession (individual ownership):
- Use apostrophe with each noun (Mom’s and Dad’s cars)
- Implies separate items owned by different people
5. How do possessive nouns work with time expressions?
Time expressions follow special rules:
- Use possessive form for periods of time (a day’s work)
- Use possessive for worth or measure (a dollar’s worth)
- Use regular form for descriptive time (a six-hour day)
Conclusion
Mastering possessive nouns enhances your ability to express ownership and relationships clearly in English. These 147 possessive noun examples demonstrate the various ways to show possession in different contexts. Remember that while the rules might seem complex at first, regular practice will make their use natural and intuitive.