Can you touch happiness? Can you see love? Welcome to the fascinating world of abstract nouns! These special words help us express ideas, feelings, and concepts that we can’t physically touch or see.
As an English teacher who’s helped countless students grasp these intangible concepts, I’ll share 136 abstract noun examples that will enrich your understanding and vocabulary.
Contents
ToggleWhat Are Abstract Nouns?
Abstract nouns name things that cannot be experienced through our physical senses. Unlike concrete nouns (like “book” or “tree”), abstract nouns represent ideas, emotions, qualities, states, or concepts that we can only understand through our mind and heart.
Types of Abstract Nouns with Examples and Sentences
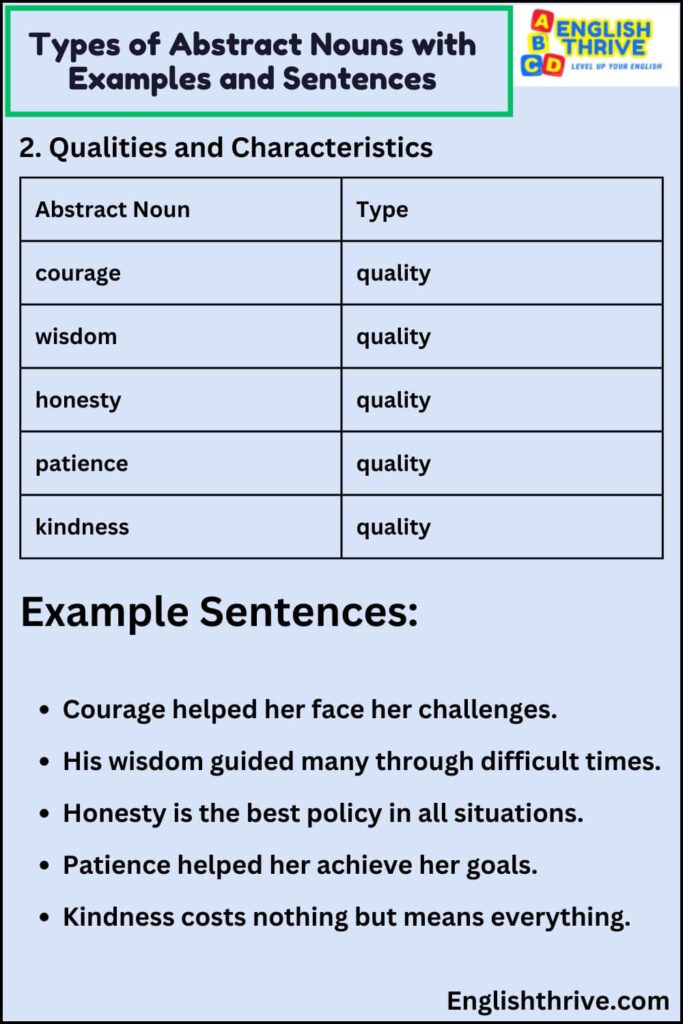
1. Emotions and Feelings
| Abstract Noun | Type |
|---|---|
| happiness | emotion |
| sadness | emotion |
| anger | emotion |
| love | emotion |
| fear | emotion |
Example Sentences:
- Happiness filled the room when she announced her engagement.
- Her sadness was visible in her eyes.
- His anger quickly turned to understanding.
- Love transforms everything it touches.
- Fear prevented him from trying new things.
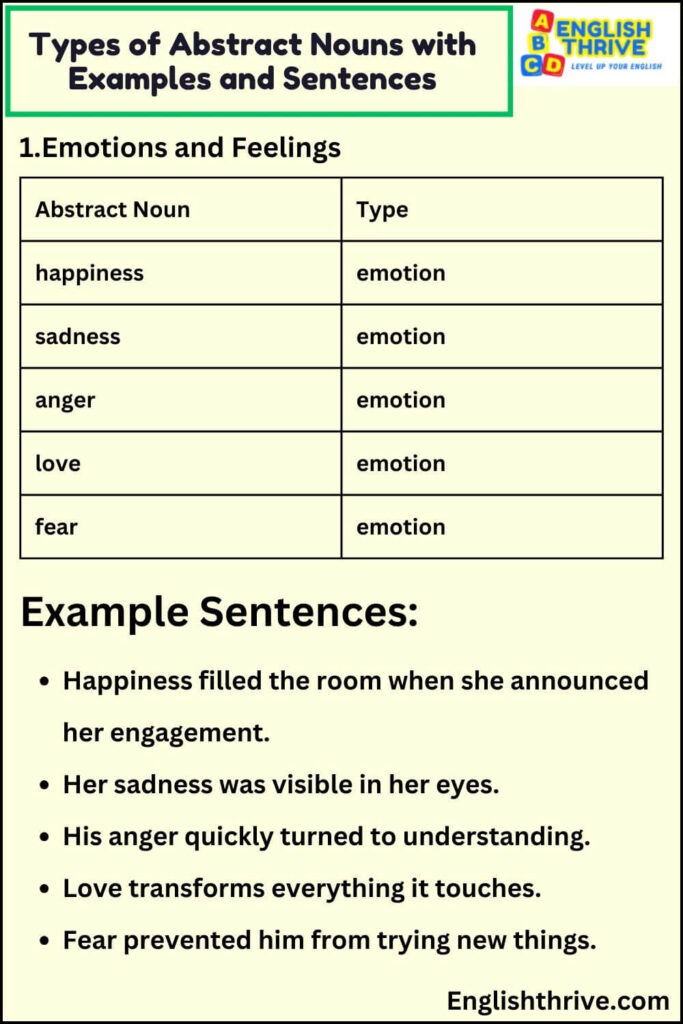
2. Qualities and Characteristics
| Abstract Noun | Type |
|---|---|
| courage | quality |
| wisdom | quality |
| honesty | quality |
| patience | quality |
| kindness | quality |
Example Sentences:
- Courage helped her face her challenges.
- His wisdom guided many through difficult times.
- Honesty is the best policy in all situations.
- Patience helped her achieve her goals.
- Kindness costs nothing but means everything.
3. States and Conditions
| Abstract Noun | Type |
|---|---|
| freedom | state |
| peace | state |
| health | state |
| poverty | state |
| silence | state |
Example Sentences:
- Freedom brings responsibility.
- Peace descended upon the valley.
- Health should never be taken for granted.
- Poverty affects millions worldwide.
- Silence filled the empty hallway.
4. Concepts and Ideas
| Abstract Noun | Type |
|---|---|
| justice | concept |
| truth | concept |
| democracy | concept |
| education | concept |
| success | concept |
Example Sentences:
- Justice prevailed in the end.
- Truth always comes to light.
- Democracy requires active participation.
- Education opens many doors.
- Success comes to those who persevere.
5. Time and Movement
| Abstract Noun | Type |
|---|---|
| childhood | time |
| future | time |
| progress | movement |
| growth | movement |
| change | movement |
Example Sentences:
- Childhood memories last forever.
- The future holds endless possibilities.
- Progress happens one step at a time.
- Growth requires patience and nurturing.
- Change is the only constant in life.
Emotions
| Emotion 1 | Emotion 2 | Emotion 3 | Emotion 4 |
|---|---|---|---|
| love | hate | sorrow | joy |
| anger | pride | envy | jealousy |
| hope | fear | compassion | passion |
| kindness | generosity | curiosity | humor |
Qualities and Virtues
| Virtue 1 | Virtue 2 | Virtue 3 | Virtue 4 |
|---|---|---|---|
| courage | honesty | loyalty | integrity |
| dignity | wisdom | respect | humility |
| patience | trust | faith | bravery |
| grace | strength | creativity | devotion |
Mental States and Concepts
| Mental State 1 | Mental State 2 | Concept 1 | Concept 2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| thought | imagination | belief | consciousness |
| knowledge | reason | intuition | intelligence |
| memory | dream | destiny | awareness |
| perception | balance | effort | evolution |
Social and Political Concepts
| Social Concept 1 | Social Concept 2 | Political Concept 1 | Political Concept 2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| friendship | leadership | democracy | politics |
| justice | freedom | power | unity |
| culture | education | religion | science |
| language | literature | tradition | harmony |
States and Conditions
| State 1 | State 2 | Condition 1 | Condition 2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| health | illness | poverty | wealth |
| safety | danger | comfort | rest |
| progress | chaos | movement | action |
| success | failure | change | growth |
Time-Related Abstract Nouns
| Past | Present | Future | Eternal |
|---|---|---|---|
| history | moment | future | eternity |
| childhood | youth | age | time |
| past | present | evolution | infinity |
Personal and Emotional States
| Personal State 1 | Personal State 2 | Emotional State 1 | Emotional State 2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| fame | status | influence | popularity |
| energy | passion | fatigue | exhaustion |
| ambition | curiosity | empathy | conflict |
| play | work | study | sleep |
Additional Abstract Concepts
| Concept 1 | Concept 2 | Concept 3 | Concept 4 |
|---|---|---|---|
| art | music | dance | silence |
| beauty | order | pain | pleasure |
| life | death | mercy | authority |
| philosophy | music | rivalry | peace |
Additional Categories:
Abstract Nouns from Verbs
- achievement
- development
- improvement
- understanding
- learning
Abstract Nouns of Perception
- beauty
- ugliness
- darkness
- brightness
- silence
Abstract Nouns of Measurement
- distance
- speed
- height
- depth
- weight
FAQs about Abstract Nouns Examples Definition with Exercises
1. How do abstract nouns differ from concrete nouns?
The key differences include:
- Abstract nouns cannot be experienced through physical senses
- They represent intangible concepts and ideas
- They often express emotions and qualities
- They can’t be physically measured
- They often have subjective meanings
For example, you can touch a “book” (concrete noun) but not “knowledge” (abstract noun).
2. Why are abstract nouns important in communication?
Abstract nouns are vital because they:
- Express complex emotions and feelings
- Describe important concepts and ideas
- Help communicate philosophical thoughts
- Enable discussion of qualities and values
- Facilitate deeper meaningful conversations
3. How can you identify abstract nouns in sentences?
You can identify abstract nouns by asking:
- Can you physically touch it?
- Can you see it directly?
- Can you measure it with standard units?
- Does it represent a feeling, idea, or quality?
- Is it something that exists only in the mind?
4. What are the common patterns in forming abstract nouns?
Abstract nouns often follow these formation patterns:
- Adding suffixes (-ness, -ity, -tion)
- Converting adjectives (brave → bravery)
- Converting verbs (achieve → achievement)
- Using base words (love, hate, peace)
- Combining concepts (homesickness)
5. How do abstract nouns function in different types of writing?
Abstract nouns serve different purposes:
- In poetry: Create emotion and mood
- In academic writing: Express complex ideas
- In narrative writing: Develop themes
- In technical writing: Define concepts
- In persuasive writing: Appeal to values
Conclusion
Abstract nouns are essential tools for expressing the intangible aspects of human experience. These 136 abstract noun examples demonstrate how we can communicate complex ideas, emotions, and concepts that shape our understanding of the world. Whether you’re writing creatively, academically, or professionally, mastering abstract nouns will help you express deeper meanings and connect with your audience on an emotional level.